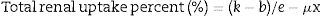We previously serially measured the serum and urine neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) during the first week after renal transplantation and found that mild ischemic injury may increase this lipocalin.1 In this study, we investigated the level of this marker after one month post-transplant with the aim of finding a relationship between NGAL quantities and graft function.
Twenty-one pediatric renal transplant recipients without any infection at the time of assessment were included in this study. Glomerular filtration rate was estimated by Schwartz equation and DTPA scan concurrently. Scintigraphic measurement of GFR was performed using an ADAC single-headed gamma camera with the following formula:
Pre-post – k: kidney count; b: background count; x: renal depth; e: constant; μ: attenuation coefficient of 99mTc in soft tissue (0.153cm−1); GFR=total renal uptake percent (%)×100×9.81270−6.82519.The mean age of patients was 9.9±3 years old. Nine patients (43%) were male. The mean time from transplantation was 6.8±2.47 years. The mean serum creatinine was 1.16±0.18mg/dl. The mean Schwartz calculated GFR was 69.8±12.2cc/min/1.73m2. The mean DTPA measured GFR was 50.6±16cc/min/1.73m2. All patients had GFR less than 90cc/min/1.73m2 by scan and Schwartz formula. The mean serum NGAL was 140±94ng/ml (15–324ng/ml). The mean urine NGAL was 17.8ng/ml (3.2–68ng/ml).
We assessed the correlation between serum NGAL and serum creatinine, Schwartz GFR, and DTPA-related GFR. The coefficient of correlation with serum creatinine was 0.67 (P=0.09), −0.2 (P=0.3) with Schwartz GFR, and −0.26 (P=0.46) with DTPA GFR. Regarding urine NGAL, the correlation coefficient with serum creatinine was 0.2 (P=0.37), −0.007 (P=0.9) with Schwartz GFR, and −0.24 (P=0.48) with DTPA GFR.
We did not find any significant association between the transplant time and serum NGAL (r=0.05, P=0.8) and urine NGAL (r=0.06, P=0.77). Three patients had slow graft function in this study without need for dialysis in the first week post-transplant. The mean serum and urine NGAL was not different between patients with SGF and those without SGF (for serum NGAL 106 vs 145.5ng/ml and for urine NGAL 12.2 vs 21.6ng/ml).
Studies have shown that expression of NGAL protein is significantly increased during ischemic insults in renal transplant recipients with delayed graft function.2 Magnusson et al. have shown that plasma NGAL levels were significantly higher than normal in renal transplant recipients.3 Malyszko et al. also found a strong correlation between serum NGAL and serum creatinine in 100 kidney transplant recipients.4
This study is the first study in pediatric renal transplant recipients in which the association between serum and urine NGAL with graft function was assessed long term. We did not find any significant association between the amounts of NGAL in serum and urine with serum creatinine and GFR estimated by Schwartz formula or measured by DTPA scan. We think we cannot use serum and urine NGAL as markers of graft function in pediatric renal transplant recipients, but this result needs confirmation by more studies with more cases.