JC virus (JCV), known as a cause of progressive multifocal encephalopathy in immunocompromised patients, is a member of the polyomavirus family. The tropism of JCV to the colon, astrocyte, lymphocyte, and kidney epithelium is known, and viral sequences and T antigen expression of JCV have been demonstrated in medulloblastomas, lymphomas, and colon tumors.1 On the other hand, to our knowledge, JCV expression in renal cell carcinoma tissue has not been shown before. Here, we describe a kidney transplant recipient with renal cell carcinoma with the expression of JCV.
A 60-year-old man had cadaver-donor transplantation in 2001 after eleven years of hemodialysis. The post-transplant follow-up was uneventful for twelve years, and maintenance immunosuppression therapy consisted of cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil and, prednisolone. In 2013, the patient was diagnosed with diffuse B-cell lymphoma and received six cycles of the R-CHOP (Rituximab, Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, Prednisolone) regimen. Also, cyclosporine was switched to everolimus, and mycophenolate was discontinued due to persistent cytopenia. Complete remission was achieved after treatment, and no recurrence occurred during follow-up.
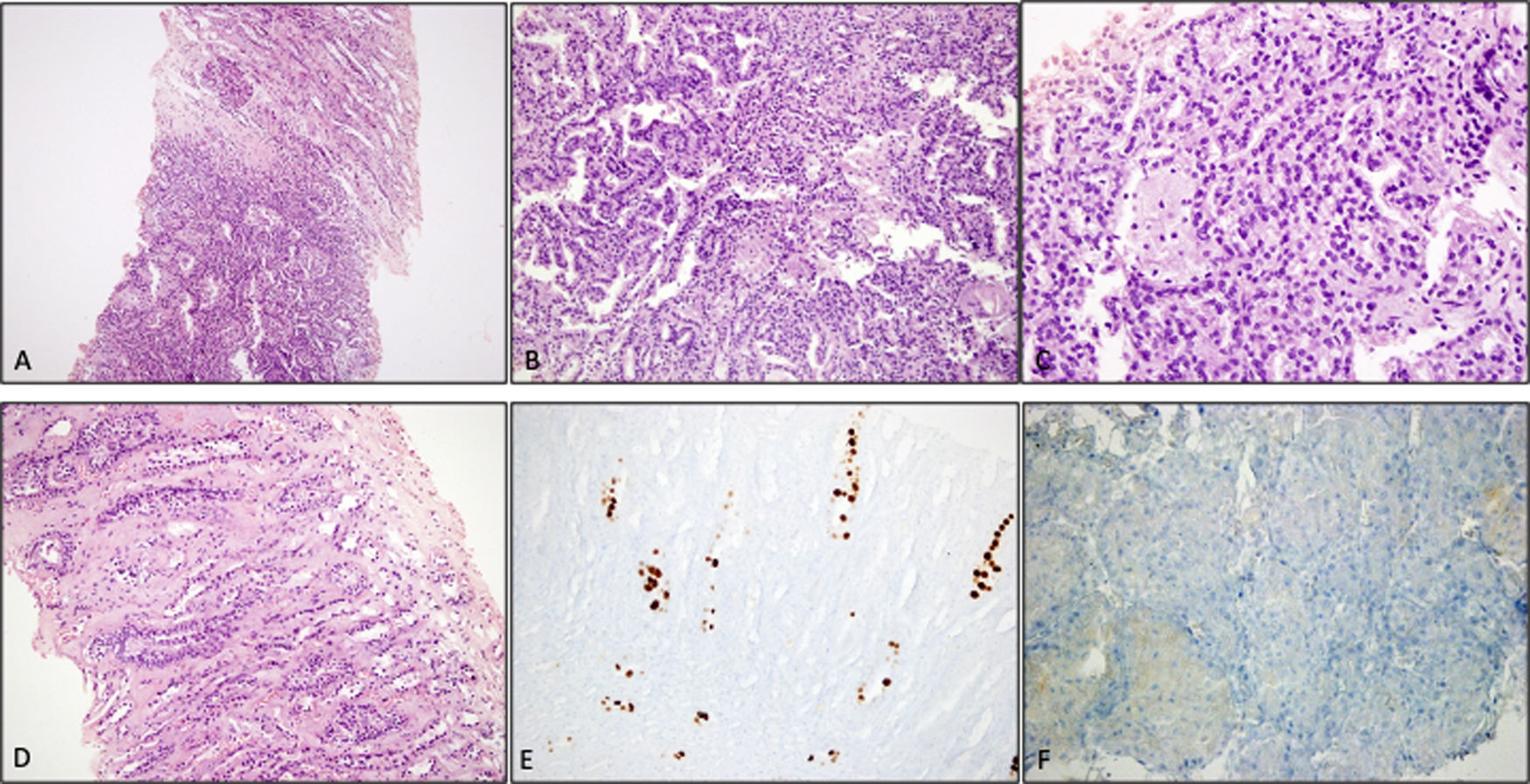
In 2017, routine ultrasound examination showed a 42mm×38mm solid lesion in the middle part of the allograft kidney. Laboratory tests were demonstrated as serum creatinine: 1.2mg/dL, 0.1g/day proteinuria. An ultrasound-guided biopsy of the lesion was performed, and pathologic examination revealed renal cell carcinoma (papillary type). Also, the simian virus 40 (SV40) large T antigen was detected by immunohistochemistry in the adjacent renal medulla (Fig. 1). Positron emission tomography and computed tomography scans showed no evidence of metastases. Also, BK virus deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was not detected in the serum and urine samples. The JCV viral load was 12×106 copies, and serum was negative. The patient refused the surgical removal of the tumor, and he was under follow-up in the outpatient clinic.
Renal tru-cut biopsy shows a papillary type renal cell carcinoma adjacent to the medulla (A). Tumor cells form papillary structures and foamy macrophages are present (B, C). Renal medullary tubular epithelial cells do not show viral inclusions (D). Anti SV-40 antibody is positive in the nuclei of renal medullary tubules (E). Note the SV40 negativity within the tumor cells (F).
Renal cell carcinoma is the most common urogenital malignancy after kidney transplantation. The risk is six to ten-fold increased in kidney transplant recipients than in the general population.2 Advanced age of the donor and recipient, male gender, smoking, and longer dialysis time are well-known risk factors. Recently, BK virus (BKV) associated urogenital malignancy has been described from various centers. The oncogenic activity of the BKV was explained by the binding of the large T antigen to the tumor suppressor gene of p53, the same part of JCV and BKV.3,4 Also, JCV-associated urothelial carcinoma, which develops with a similar mechanism, has been described previously.5 In our case, the diagnosis of JCV was made by the presence of T antibody of SV40 in the adjacent renal parenchyma and the detection of JC viruria. Nevertheless, these data are not sufficient to show the oncogenic activity of JCV in renal cell carcinoma. Well-designed trials are needed to define the oncogenic potential of JCV in urogenital malignancy.
Informed consentInformed consent was taken from relatives of patient.
Conflict of interestThe authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the American Journal of Transplantation.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.