INTRODUCCIÓN
En la historia de la hemodiálisis hay ejemplos de avances técnicos que sustituyeron a procedimientos previos. El control volumétrico de la ultrafiltración, la utilización de bicarbonato en el líquido de diálisis y las membranas sintéticas conllevaron el abandono de los sistemas de ultrafiltración por gradiente de presión, del baño de acetato y de las membranas de celulosa. Los criterios que justificaron los cambios no fueron siempre los mismos: la implantación de las novedades técnicas en los dos primeros casos no se realizó por la evidencia científica proporcionada por estudios de investigación, sino porque la experiencia clínica confirmó la mayor precisión del control volumétrico de ultrafiltración y la mejor tolerancia a la sesión de diálisis con el baño de bicarbonato. Por el contrario, el abandono progresivo de las membranas de celulosa fue una consecuencia de las investigaciones que demostraron que las membranas sintéticas inducían una menor reacción inflamatoria y tenían un efecto favorable sobre la incidencia y gravedad de la amiloidosis por depósito de beta-2-microglobulina. En la actualidad estamos asistiendo al auge de técnicas de diálisis en las que predomina el principio de convección sobre el de difusión y el debate que se plantea es si ha llegado el momento de la sustitución de la hemodiálisis tradicional por los procedimientos convectivos.
La utilización de la convección en vez de la difusión como principal mecanismo de depuración renal no es una propuesta actual. La técnica convectiva pura (la hemofiltración) es un procedimiento tan antiguo como la hemodiálisis. Posteriormente surgieron técnicas convectivas mixtas en sus diversas variedades (hemodiafiltración, biofiltración, PFD, AFB). Ninguna de ellas llegó a representar una verdadera alternativa al tratamiento convencional por su complejidad, mayor coste y ausencia de resultados que mostraran una evidente ventaja clínica. La producción de un baño de diálisis estéril (baño ultrapuro) capaz de ser utilizado como líquido de reposición intravenosa en las técnicas convectivas (convección «on-line») fue el gran avance técnico que solucionó parte de los inconvenientes previos y renovó el interés por estos procedimientos. La convección «on-line» permite obtener grandes volúmenes de ultrafiltración de forma sencilla y con una disminución considerable del precio.
De las diversas técnicas convectivas que incorporaron la infusión del baño de diálisis, es la hemodiafiltración «on-line» la que ha adquirido una mayor relevancia tanto por su progresiva expansión como por el número de publicaciones científicas que genera. Revisiones generales y comentarios editoriales recientes afirman que la hemodiafiltración «on-line» es una técnica segura, que proporciona mayor eficacia depurativa y mejores resultados clínicos a un coste no muy superior a la hemodiálisis1-9. Una encuesta reciente dirigida a profesionales de la diálisis indica que para los nefrólogos europeos la hemodiafiltración «on-line» es el mejor procedimiento de diálisis existente en la actualidad10.
Con datos procedentes de trabajos publicados, ¿hay criterio suficiente para plantear la sustitución de la hemodiálisis por las técnicas convectivas y especialmente por la hemodiafiltración «on-line» como modalidad más representativa?
PROBLEMAS METODOLÓGICOS EN ESTUDIOS COMPARATIVOS
Muchos de los estudios referidos a las técnicas convectivas tienen aspectos metodológicos que hay que tener en cuenta en el momento de valorar los resultados.
Las técnicas convectivas «on-line» utilizan una membrana biocompatible de alto flujo y un baño de diálisis ultrapuro. La biocompatibilidad y la permeabilidad de la membrana tienen una influencia determinante en la concentración plasmática de beta-2-microglobulina11-16, en el desencadenamiento de los fenómenos inflamatorios inducidos por la diálisis15,17-20 y en la aparición de complicaciones clínicas por amiloidosis del enfermo dializado21-27, siendo controvertidos sus posibles efectos beneficiosos sobre anemia, nutrición y mortalidad12,14,15,25,28-34. El baño de diálisis ultrapuro se ha relacionado con acciones favorables sobre la anemia35-41 nutrición35,40,42,43, inflamación36,38-42,44,45, estrés oxidativo45,46, reducción de los niveles de beta-2-microglobulina38,43,45, prevalencia de la amiloidosis relacionada con la diálisis26,47,48, y morbilidad cardiovascular44. Muchos de estos efectos beneficiosos se describen en enfermos tratados con técnicas convectivas y es difícil determinar si deben atribuirse a la calidad de la membrana, a la pureza del baño de diálisis o a la propia convección. Para poder valorar la influencia de la convección, la técnica de hemodiálisis con la que se compare debe realizarse en idénticas condiciones de calidad del baño y membrana. Y, por supuesto, con igualdad de superficie del dializador, flujo arterial y flujo del baño de diálisis.
Otro aspecto a tener en cuenta es la ausencia de grupo control en muchos estudios observacionales, especialmente los que analizan los datos antes y después del cambio de técnica. La mejoría de resultados por el «efecto ensayo» es un sesgo a tener en cuenta en este tipo de trabajos. Hay dos ejemplos sobre la importancia del grupo control: el trabajo de Locatelli sobre permeabilidad de membrana y anemia14 y el de Ward sobre hemodiafiltración y concentración sérica de beta-2-microglobulina49. Las conclusiones de ambos estudios hubieran sido totalmente diferentes de no haberse utilizado un grupo control.
Por último, hay que resaltar la cautela con la que deben ser analizados los resultados de los estudios no aleatorizados. La técnica convectiva, especialmente en la variante posdilucional, precisa un flujo de sangre adecuado que condiciona el criterio de selección de enfermos. El hecho de constituir un tratamiento alternativo al habitual conlleva la tendencia a no aplicar dicho procedimiento a enfermos en los que se presuponga un mal pronóstico a corto plazo, sobre todo en los períodos iniciales en los que se pretende adquirir experiencia con esta técnica. El sesgo de selección condicionado por el acceso vascular y la presunción pronóstica es inherente a todo estudio no aleatorizado.
A pesar de todas las limitaciones anteriores, ¿se puede asegurar con las publicaciones existentes que los resultados clínicos obtenidos con las técnicas convectivas «on-line» son claramente superiores a los conseguidos con la hemodiálisis?
RESULTADOS DE LOS ESTUDIOS SOBRE CONVECCIÓN: REVISIONES SISTEMÁTICAS
Se han publicado dos revisiones sistemáticas que analizan este tópico. La revisión de Rabindranath, et al incluye sólo ensayos clínicos aleatorizados y controlados; se analizaron inicialmente 18 estudios con 588 enfermos50 y posteriormente se amplió a 20 estudios con 657 enfermos51. La revisión de Varela y Ruano incluye, además, estudios observacionales de cohorte, pero excluye todos los estudios con menos de 20 enfermos; el apartado referente a técnicas convectivas es un análisis de los datos de 17 trabajos, siete de los cuales están también incluidos en la revisión de Rabindranath, et al, con un total de 1.489 enfermos52. Los autores de ambas revisiones sistemáticas concluyen que no es posible demostrar que las técnicas convectivas aporten ventajas en aspectos clínicos relevantes como mortalidad, morbilidad, tolerancia a la diálisis o calidad de vida. Resaltan también las deficiencias metodológicas de muchos estudios y la necesidad de realizar ensayos clínicos de mayor calidad para alcanzar conclusiones definitivas.
Resumiremos a continuación los datos más importantes, incluyendo publicaciones posteriores y aspectos que no han sido considerados en las dos revisiones sistemáticas previas.
Mortalidad
Dos nuevos ensayos clínicos aleatorizados y controlados analizan la mortalidad. En el primero de ellos no se observó diferencia entre la hemodiafiltración «on-line» y la hemodiálisis de alto flujo53. El segundo constató una mejor supervivencia en el grupo tratado con hemofiltración «online » con respecto al grupo tratado con hemodiálisis de bajo flujo54; los propios autores y el comentario editorial correspondiente55 reconocen las limitaciones del estudio por el pequeño número de enfermos y el alto índice de abandonos.
La influencia de la técnica convectiva sobre la mortalidad ha sido objeto de análisis en cuatro estudios observacionales realizados a partir de diferentes registros de enfermos56-59. Mientras que en el primero de ellos no hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas, en los otros tres estudios la mortalidad fue menor en el grupo tratado con hemodiafiltración «on-line». Los datos sobre mortalidad de estos estudios observacionales, no aleatorizados, deben ser analizados con cautela por el sesgo de selección anteriormente citado.
Resultados de datos clínicos y analíticos
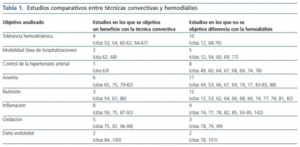
En la tabla 1 se presentan las conclusiones de 47 estudios comparativos. Al analizar las características de la técnica de hemodiálisis hay que resaltar que en 21 la membrana es de bajo flujo, en 17 el dializador tiene menos superficie, en ocho el flujo arterial es menor y en 19 el baño de diálisis no es ultrapuro. Sólo en 12 estudios estos cuatro parámetros son similares con ambas técnicas. Dieciséis de estos trabajos corresponden a estudios observacionales en los que se analizan los efectos del cambio de técnica, sin grupo control. A pesar de estas limitaciones metodológicas que suponen un sesgo a favor de las técnicas convectivas, los resultados no muestran una clara ventaja sobre la hemodiálisis en la mayoría de parámetros analizados.
Estudios iniciales objetivaron una mejor tolerancia hemodinámica; posteriormente se demostró que se debía a la mayor pérdida de calor inducida por la convección sin observarse diferencias cuando se comparaba con la hemodiálisis fría o con biocontrol de temperatura70-72,76.
Donde se detectan más datos a favor de la convección es en los trabajos que estudian el comportamiento de diversos marcadores de inflamación y oxidación, cuya trascendencia clínica está por determinar.
Eficacia de la diálisis
Las técnicas convectivas no aportan un incremento relevante de la eliminación de pequeñas moléculas con respecto a la hemodiálisis, siempre que se mantengan constantes el resto de las variables que intervienen en aclaramiento de las mismas102,103. Es en la eliminación de medianas y grandes moléculas donde la convección es más eficaz. Su mayor capacidad depurativa, reflejada en las tasas de aclaramiento o de reducción de la concentración plasmática posterior al tratamiento, ha sido objetivada con numerosas moléculas49,69,103-107, pero no siempre suele acompañarse de un descenso de las concentraciones sanguíneas.
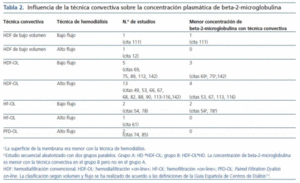
La molécula más estudiada es la beta-2-microglobulina. Publicaciones recientes observan una relación entre su concentración plasmática y mortalidad108-110. En la tabla 2 se exponen los resultados de 24 trabajos que permiten analizar la evolución de la concentración de beta-2-microglobulina con diferentes técnicas convectivas. Puede comprobarse que en la mayoría de los estudios no hay diferencias con la hemodiálisis realizada con membrana de alto flujo.
Seguridad
La seguridad de las técnicas convectivas queda aparentemente garantizada por la ausencia de publicaciones que describan peores resultados clínicos con las mismas. Sin embargo, hay algunos aspectos a tener en cuenta.
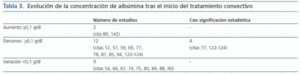
La pérdida de proteínas y aminoácidos es mayor118-121. En la tabla 3 se exponen los datos de 23 trabajos en los que se puede estudiar la evolución de la concentración plasmática de albúmina tras el inicio del tratamiento convectivo. Como puede constatarse, la tendencia es a la disminución, generalmente leve, de la concentración de albúmina.
La infusión directa del baño de diálisis al torrente circulatorio plantea algunos interrogantes sobre la seguridad de la técnica y sus consecuencias a largo plazo. El agua ultrapura contiene gran variedad de oligoelementos125 que, una vez infundidos en la sangre, se unen a las proteínas del plasma y son de difícil eliminación. El posible efecto de su acumulación progresiva está por determinar126,127. Además, es imprescindible garantizar la esterilidad de la solución infundida. La contaminación del filtro de endotoxinas o del circuito hidráulico posterior al mismo provocaría la infusión de un baño no estéril hasta el cambio del filtro o la realización de los controles habituales de endotoxinas. También hay que tener en cuenta que el baño de diálisis puede contener otros productos de contaminación bacteriana que no son detectados con los tests de endotoxinas128,129, que atraviesan los filtros de protección130,131 y que son capaces de inducir y mantener la respuesta inflamatoria in vitro130,132. Estos restos bacterianos son transferidos directamente al torrente sanguíneo durante las técnicas convectivas «on-line», aunque hasta el momento no se ha comprobado que sean capaces de provocar respuesta inflamatoria in vivo.
Se puede alegar que la hemodiálisis con dializadores de alto flujo conlleva un fenómeno de retrofiltración y que tanto los oligoelementos del baño de diálisis como los posibles restos bacterianos pueden alcanzar el compartimento sanguíneo. Pero no hay que olvidar que el revestimiento de la membrana del dializador por proteínas de la sangre representa un límite a la transferencia de productos contaminantes procedentes del baño de diálisis a través del dializador133-135.
ENSAYOS CLÍNICOS EN MARCHA
Para aclarar alguno de estos interrogantes, se están realizando cinco ensayos clínicos aleatorizados y controlados que comparan los resultados de la hemodiafiltración «on-line» con la hemodiálisis convencional (tabla 4). Llama la atención que en dos de ellos la membrana utilizada en la hemodiálisis convencional sea de baja permeabilidad. Los resultados de estos estudios ayudarán a dilucidar aspectos de la controversia actual. De momento sólo se conocen datos, recientemente publicados, de uno de ellos (Estudio CONTRAST): la hemodiafiltración «on-line» provoca una activación plaquetaria más intensa y prolongada que la hemodiálisis; la trascendencia clínica de este hallazgo está por determinarse141.
CONCLUSIONES
Podemos concluir que las técnicas de diálisis basadas en la convección son procedimientos con aspectos interesantes, pero que hasta el momento no han podido demostrar una evidente superioridad clínica sobre la hemodiálisis con membrana biocompatible de alta permeabilidad y líquido ultrapuro. La seguridad está avalada por la ausencia de publicaciones que muestren peores resultados, aunque quedan algunos interrogantes por aclarar. Hasta la publicación de los resultados de los ensayos clínicos que se están realizando, habrá que utilizar las técnicas de convección según la propia experiencia o el deseo de adquirirla, y las disponibilidades de cada centro. El momento del cambio todavía no ha llegado.
Tabla 1.
Tabla 2.
Tabla 3.
Tabla 4.