Recurrent uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs) are frequent among healthy young women.1 In some women, there is a clear relationship with sexual activity; the frequency of is sexual intercourse described as an important contributing factor, and it has even been reported that women having sexual intercourse on a daily basis are at 9 times’ greater risk.2–4 While changes in sexual partner during the previous year is a known risk factor, it is unusual to studied the couple.
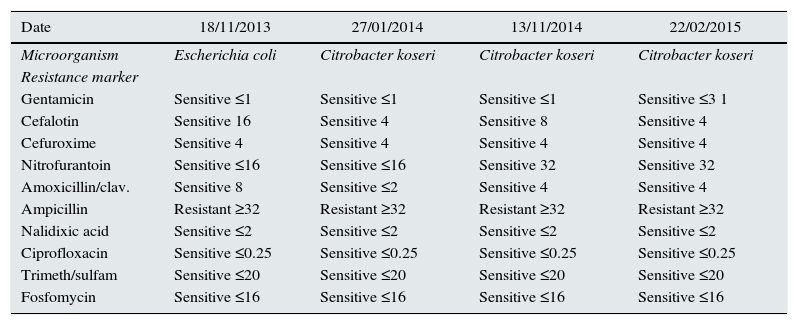
We present the case of a 39-year-old woman with a stable partner who presented with post-coital voiding syndrome. She had no prior relevant medical history, nor repeated UTIs, and did not take oral contraceptives or use spermicide. It was discovered to have positive culture for Escherichia coli culture. She therefore received treatment with ciprofloxacin and became asymptomatic. Two months later, she again presented with post-coital voiding syndrome; this time, it was caused by Citrobacter koseri. She received treatment with fosfomycin and nutritional-hygienic measures that included post-coital voiding. After 10 months without symptoms, she again presented with post-coital voiding syndrome, again with the Citrobacter koseri culture. She therefore began another course of antibiotics with fosfomycin and compliance with hygienic measures was stressed.
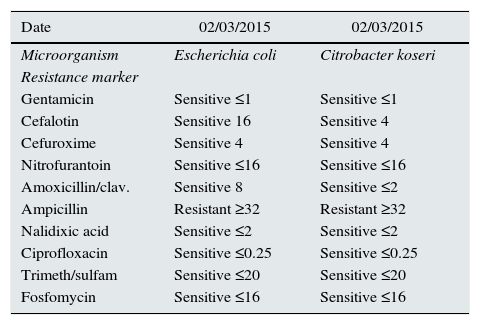
Three months later, when the voiding syndrome occurred again, a new culture was requested and her asymptomatic partner was studied, using a glans swab. The man's culture showed 2 germs, Escherichia coli and Citrobacter, with identical sensitivity to the patient's cultures (Tables 1 and 2). Both started treatment with single-dose fosfomycin and no further new infections developed.
Bacteria in female urine cultures.
| Date | 18/11/2013 | 27/01/2014 | 13/11/2014 | 22/02/2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microorganism | Escherichia coli | Citrobacter koseri | Citrobacter koseri | Citrobacter koseri |
| Resistance marker | ||||
| Gentamicin | Sensitive ≤1 | Sensitive ≤1 | Sensitive ≤1 | Sensitive ≤3 1 |
| Cefalotin | Sensitive 16 | Sensitive 4 | Sensitive 8 | Sensitive 4 |
| Cefuroxime | Sensitive 4 | Sensitive 4 | Sensitive 4 | Sensitive 4 |
| Nitrofurantoin | Sensitive ≤16 | Sensitive ≤16 | Sensitive 32 | Sensitive 32 |
| Amoxicillin/clav. | Sensitive 8 | Sensitive ≤2 | Sensitive 4 | Sensitive 4 |
| Ampicillin | Resistant ≥32 | Resistant ≥32 | Resistant ≥32 | Resistant ≥32 |
| Nalidixic acid | Sensitive ≤2 | Sensitive ≤2 | Sensitive ≤2 | Sensitive ≤2 |
| Ciprofloxacin | Sensitive ≤0.25 | Sensitive ≤0.25 | Sensitive ≤0.25 | Sensitive ≤0.25 |
| Trimeth/sulfam | Sensitive ≤20 | Sensitive ≤20 | Sensitive ≤20 | Sensitive ≤20 |
| Fosfomycin | Sensitive ≤16 | Sensitive ≤16 | Sensitive ≤16 | Sensitive ≤16 |
Swab culture from male glans.
| Date | 02/03/2015 | 02/03/2015 |
|---|---|---|
| Microorganism | Escherichia coli | Citrobacter koseri |
| Resistance marker | ||
| Gentamicin | Sensitive ≤1 | Sensitive ≤1 |
| Cefalotin | Sensitive 16 | Sensitive 4 |
| Cefuroxime | Sensitive 4 | Sensitive 4 |
| Nitrofurantoin | Sensitive ≤16 | Sensitive ≤16 |
| Amoxicillin/clav. | Sensitive 8 | Sensitive ≤2 |
| Ampicillin | Resistant ≥32 | Resistant ≥32 |
| Nalidixic acid | Sensitive ≤2 | Sensitive ≤2 |
| Ciprofloxacin | Sensitive ≤0.25 | Sensitive ≤0.25 |
| Trimeth/sulfam | Sensitive ≤20 | Sensitive ≤20 |
| Fosfomycin | Sensitive ≤16 | Sensitive ≤16 |
The study and treatment of couples with post-coital UTI in women may be helpful in managing recurrent UTIs.
Please cite this article as: Pavone MA, Aguilera Peralta A. Estudio y tratamiento de la pareja en ITU poscoital de la mujer. Nefrologia. 2017;37:662–663.