Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) is a clinical and radiological syndrome described in 1996. Its pathogenesis is still unclear and there are two theories: (1) cerebral hyperperfusion and (2) severe vasospasm.1–3 It is associated with malignant hypertension, eclampsia and other coexisting conditions in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) such as hypertension, vascular or autoimmune diseases, as well as immunosuppressants, erythropoietin and transplantation.2
A higher number of cases have been described in women. Clinical symptoms include seizures (93%), visual disturbances (67%), loss of consciousness (53%) and headache (47%). Between 7 and 13% present aphasia, hemiplegia, hemiparesis or mental impairment.1
In 2010, a large case series (113 adults) was published, among which only 6% were recurrent4: from 2 weeks to 36 months after the initial episode.4,5
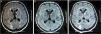
Cranial MRI is the gold standard; it shows symmetrical parieto-occipital white matter abnormalities (cortical or subcortical edema), which are reversible after days or weeks of treatment.1–5
Only a fast and adequate control of triggering events prevents irreversible complications. Sometimes antiepileptics, general anesthesia and mechanical ventilation must be administered; it has not yet been confirmed that corticosteroids reduce vascular edema.2 There is no association between the severity of hypertension and the sequelae.5
In the differential diagnosis, multiple diseases should be considered2 (Table 1).
Differential diagnosis of RPLS.
| Vascular disease | Non-vascular disease |
|---|---|
| Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis | Infectious encephalitis |
| Intracranial hemorrhage | Autoimmune encephalitis |
| Posterior circulation stroke | Metabolic/toxic encephalopathy |
| Primary CNS vasculitis |
RPLS: reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome.
We describe a case that we find interesting because of its unusual clinical presentation and subsequent recurrence:
34-year-old male, on HD with CKD secondary to obstructive uropathy (verumontanum). His hypertension was treated with atenolol 50mg/day. He presented to the emergency department for aphasia and agitation. Fever (38.8°C), BP: 232/124mmHg. No significant findings on physical examination. Blood count: normal leukocytes, slight neutrophilia and lymphopenia. Normal cranial CT and lumbar puncture. Negative blood and CSF cultures, and negative serology. Ocular fundus: hypertensive retinopathy grade III. He was hospitalized to Infectious Disease Service for suspected meningoencephalitis; empirical treatment was initiated with ampicillin, vancomycin, acyclovir, rifampicin and isoniazid.
It remained difficult to control the blood pressure (SBP: 150–200mmHg, DBP: 90–120mmHg); this was initially treated with labetalol via infusion pump, ACE inhibitors and calcium antagonists, but oral minoxidil 10mg and atenolol 100mg and adjustment of dry weight were also needed.
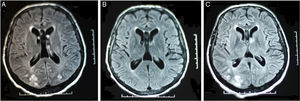
As a result of progressive reduction in the level of consciousness, reaching a score of 4 on the Glasgow scale, he was transferred to ICU. An MRI was ordered and the findings suggested RPLS: bilateral parieto-occipital subcortical white matter hyperintensity in T2 and FLAIR weighted sequences. Ten days later, the follow-up MRI was normal (Fig. 1).
After 22 days in ICU, no neurological sequelae were present and he was transferred to Nephrology with a diagnosis of RPLS, probably hypertensive. Antihypertensive therapy was adjusted at discharge to maintain SBP at ≤150mmHg.
Six months later he was readmitted for right hemiparesis and dysarthria secondary to hypertensive emergency (280/120mmHg), with normal cranial CT. He was admitted to ICU with decreased level of consciousness, motor agitation and poor BP control. The MRI showed similar changes in the previous location, confirming recurrent RPLS in the context of a hypertensive emergency.
Pharmacological treatment was optimized with irbesartan 150mg (0–0–1), carvedilol 25mg (1/2–0–1/2), Carduran neo® 4mg (1–0–1), and enalapril 20mg (1/2–0–1/2).
This is a rare case because it is a male who began with fever and neurological disturbances in the context of hypertensive emergency, and had a recurrence after 6 months.
In the literature, hypertensive crises, CKD and sudden changes in pressure and volume in HD are related as triggers of disease recurrence.5 Early diagnosis through MRI and treatment of risk factors, in this case controlling the blood pressure, are essential for reversing the clinical picture and preventing recurrence. If it persists, it can be fatal or it may result in serious neuropsychological sequelae.
Please cite this article as: Palacios-Parada MA, Acosta-Ochoa MI, Núñez-García JM, Aller-Aparicio C, Sanz-Ballesteros S, Mendiluce-Herrero A. Leucoencefalopatía posterior reversible: un caso recurrente y atípico en hemodiálisis. Nefrología. 2016;36:192–193.