Dear Editor:
Mechanical complications in peritoneal dialysis (PD) are common, particularly the appearance of abdominal herniae dependent on a sustained increase of intra-abdominal pressure.1 The presence of anomalous pleuroperitoneal communication results in the appearance of massive pleural effusion.2
Diagnosis is usually clinical, although there are various available imaging techniques for confirming this.3 In our centre we have available the Tc-99 scintigraphy, and have used it as a simple and innocuous method for confirming clinical suspicions.
We present the case of a 52 year old patient who began a CAPD programme in April 2008 following five years in haemodialysis. No pathological history of interest, except nephroangiosclerosis as cause of renal failure.
The PD catheter was fitted using a laparoscopic technique (Techknoff swan neck, rectum) without complication. At two months the patient was following a routine of APD with no problems. The course was completed on a humid day at low volume due to abdominal discomfort.
Four months after fitting the catheter the patient suddenly complained of general discomfort and intense epigastric pain with no vomiting, depositional alterations or fever. Orthopnoea and pain in the right ribcage with a dry cough. Increase in weight of 2kg during previous days, apparently without loss of UF.
On examination, global hypoventilation of the right lung was apparent. There was no oedema and the abdomen was normal.
A chest x-ray showed a massive right pleural effusion.
A thoracentesis was performed and one litre of liquid was obtained which had properties similar to dialysis liquid, with high glucose content. Negative cultures.
With a diagnosis of pleural drainage, we proceeded to peritoneal rest.
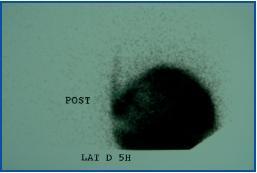
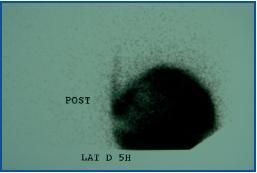
A scintigraphy was carried out, which showed the presence of a right pleuroperitoneal leak (figure 1). The patient remained on haemodialysis for three months, then resumed APD without relapse. The scintigraphy was repeated and showed no leak. During the following two months, the patient continued on APD until receiving a transplant.
The presence of dyspnoea compels us to rule out the most common pathology in our patients (hydrosaline retention, heart failure, etc.) but we must not forget about mechanical complications.4
The diagnosis will primarily be clinical, and on analysing the effusion we can test the properties of the dialysis liquid.
We stress the Tc-99 scintigraphy as a simple and safe technique for confirming a diagnosis.
It is carried out by means of a manual exchange with 2mCi Tc-99. The first reading is taken after 10 to 15 minutes, and after 3-4 hours delayed images are taken in different positions. Finally, all liquid is drained and destroyed according to nuclear medicine department protocol.
Figure 1.