To the Editor,
Nefrología has recently published a case of post-denosumab hypocalcaemia and we would like to contribute to this subject1. Denosumab is an anti-RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand) monoclonal antibody used in osteoporosis treatment as an antiresorptive agent. Unlike bisphosphonates, denosumab does not appear to be nephrotoxic2, nor does it require dosage adjustments in kidney failure due to its favourable pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile1,3. However, the qualitative bone changes in osteoporosis patients are not comparable with the wide spectrum of alterations in bone turnover that accompanies chronic kidney disease (CKD)4. For this reason and in relation to the changes in mineral metabolism caused by denosumab, its safety in this population could be questioned. We describe a patient with advanced CKD with extreme hypocalcaemia and hyperparathyroidism following continuous administration of denosumab.
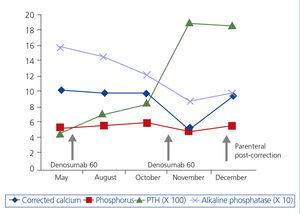
The patient is a 75-year-old female who sought treatment for tremors, muscle spasms and paraesthesia in the limbs. Stage 5 CKD, probably secondary to nephroangiosclerosis and diabetes mellitus, stands out in her medical history. She is allergic to penicillin and is treated with insulin, doxazosin, nifedipine GITS, torsemide, acetylsalicyclic acid, oral iron, erythropoietin, paricalcitol and calcifediol. She was treated, until 7 months before, with 70mg alendronic acid, which was suspended on starting six-monthly subcutaneous 60mg denosumab. Her nephrologist was unaware of the prescription of this drug. She presented the following analysis: creatinine 3.6mg/dl, total corrected calcium 10.06mg/dl, ionic calcium 5.1mg/dl, phosphate 5.1mg/dl, alkaline phosphatase 157U/l, bicarbonate 27.6mmol/l, parathyroid hormone (PTH) 436pg/ml, 25-vitamin D 30.2ng/ml. The evolution of the biochemical parameters until the last analysis 14 days after denosumab is shown in Figure 1. The patient did not attend this last evaluation due to not feeling well. Six days later, she was examined in the Emergency Department: urea 154mg/dl, creatinine 6mg/dl, total corrected calcium 4.36mg/dl, ionic calcium 2.4mg/dl, phosphate 6.7mg/dl, magnesium 1.3mg/dl, alkaline phosphatase 59U/l, bicarbonate 18.6mmol/l, PTH 1900pg/ml. Electrocardiogram (ECG): 440ms corrected QT (QTc). Oral and intravenous calcium replacement and intravenous calcitriol were started, with the disappearance of symptoms. After 15 days of parenteral replacement, the analytical parameters had normalised (Figure 1): ECG: QTc 402ms. PTH remained 1858pg/ml.
The recommendations for the use of denosumab in kidney failure are based on a clinical trial involving very few patients, over a 16 week follow-up period and following only one dose of the drug3. In addition, the authors excluded, in part of the study, those subjects with 1.25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels <30pg/ml, severe renal failure and PTH ≥110pg/ml or kidney failure and PTH ≥300pg/ml. Even so, 22%-25% of the cases with moderate-severe renal failure or patients on dialysis presented hypocalcaemia. The authors recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements for its prevention. In another clinical trial carried out over 36 months in post-menopausal women with CKD and estimated glomerular filtration rate >15ml/min, cases of hypoparathyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, hypercalcaemia and hypovitaminosis D were excluded; PTH levels were not monitored in the study2.
In recent months, cases of hypocalcaemia in chronic nephropathies have continued to be reported1,5-8. Non previous biphosphonate use and kidney failure are risk factors for developing hypocalcaemia8. Consequently, our patient may only have developed hypocalcaemia following the second dose, since she had previously been treated with alendronate.
Denosumab reduces the number of osteoclasts and bone formation rate. Hypocalcaemia would be related to the rapid mineral deposit of calcium in the new bone matrix, which would behave similarly to a hungry bone following parathyroidectomy3. However, as occurred in this case, PTH was not suppressed, but hyperstimulated. In addition to sudden hypocalcaemia following the second denosumab dose, PTH levels were progressively increasing to very high levels following the first dose, despite vitamin D supplements; we also observed a reduction of alkaline phosphatase. For some experts, this inhibition of osteoclastogenesis could favour adynamic bone disease in CKD4,5.
The monitoring of calcium levels 8-14 days after treatment has been advised7. However, this does not guarantee its prevention, since it is not known when the nadir is reached7.
Denosumab can cause potentially fatal short-term adverse effects, as well as other unknown long-term effects, on the bone of CKD patients. For these reasons, some authors recommend not using denosumab in CKD patients or only using it if a bone biopsy has previously been carried out4,6.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest related to the contents of this article.
Figure 1. Evolution of biochemical parameters