To the Editor:
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) has increased globally, primarily type 2.1 One of the main complications of this disease, diabetic nephropathy (DN), is the primary global cause of terminal chronic kidney disease (TCKD), and affects approximately one-third of all DM patients.2 The diagnosis of this condition is usually established based on clinical criteria in diabetic patients with albuminuria and/or diabetic retinopathy.
However, it is also common to encounter non-diabetic kidney disease in diabetic patients, which necessitates the indication for renal biopsies in patients with DM and nephropathy, especially those with a rapid progression or atypical forms of disease.2,3
In our study, we describe the characteristics of patients with DN confirmed by renal biopsy. We analysed the motives described for indicating the renal biopsy and the moment in the evolution of disease when the biopsy was taken.
During the study period of 2004-2011, a total of 156 native renal biopsies were performed at the Hospital General de Segovia. In 17 of these (10.9%), a final diagnosis of DN was made.
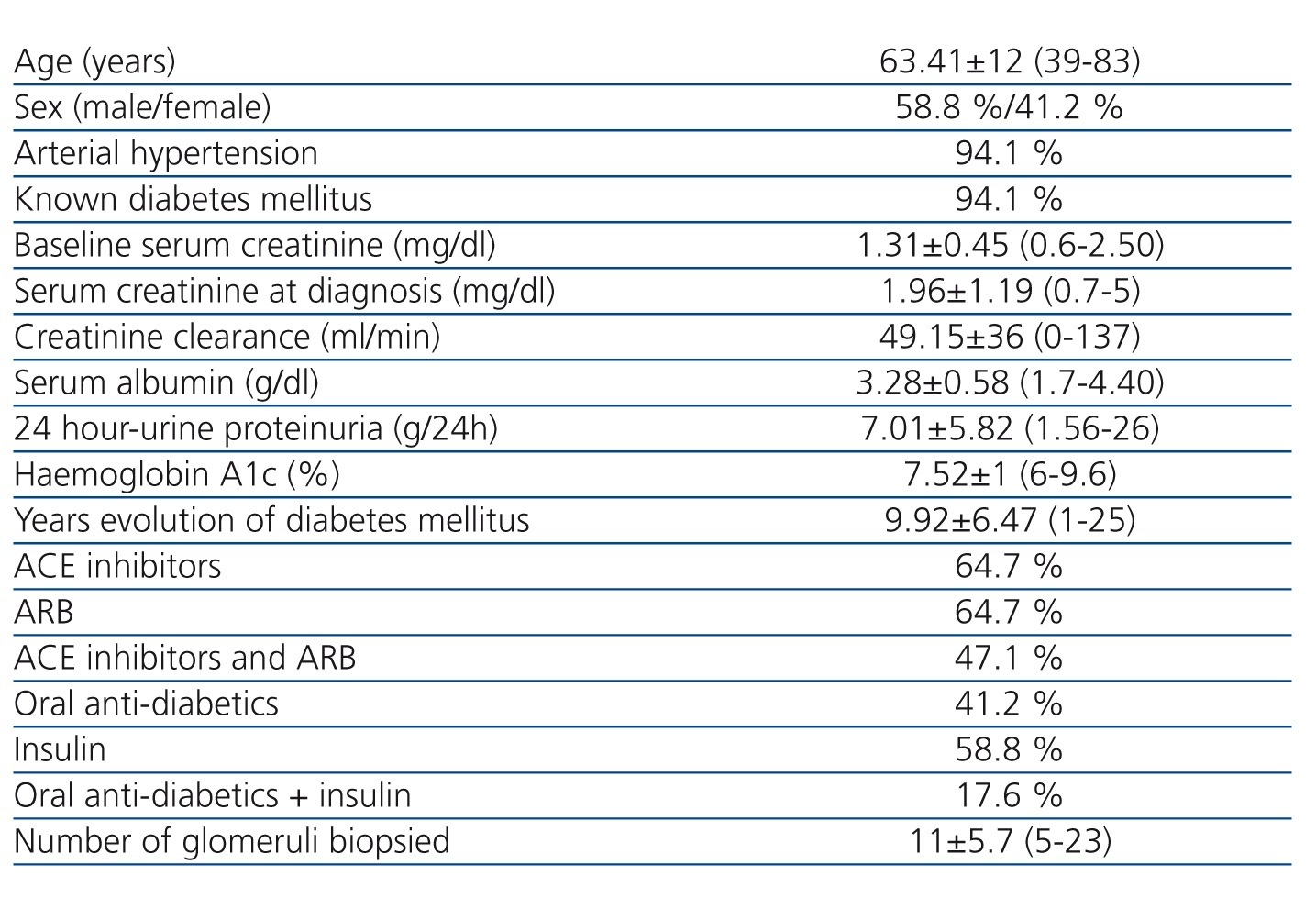
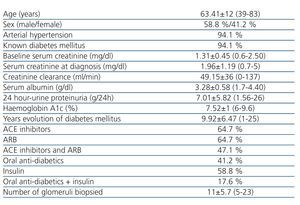
Table 1 describes the socio-demographic characteristics, pathological history, treatments given, and laboratory results for all of these patients prior to the renal biopsy.
As regards the motive for indicating the renal biopsy, 82.4% of cases were due to nephrotic range proteinuria or nephrotic syndrome, 5.9% were due to acute renal failure, another 5.9% were due to persistent urinary alterations, and the final 5.9% were due to other indications. In 16 patients, the diagnosis was established based on the first renal biopsy, and the other patient required a second biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
In two patients, the diagnosis of DN was confirmed when the patient had TCKD, while on a dialysis programme.
Lin et al. performed a retrospective analysis of 50 renal biopsies in patients with type 2 DM, showing that in patients with type 2 DM of at least 10 years evolution and retinopathy, the presence of non-diabetic kidney disease cannot be ruled out. In their study, elevated serum albumin levels and low urinary protein losses served as indications for renal biopsies in order to exclude the possibility of non-diabetic kidney disease.4 In our study however, the primary motive for indicating renal biopsy was severe, persistent, or increasing proteinuria in patients that had already been treated with anti-proteinuric drugs, in which the diagnosis of DN was confirmed.
To conclude, our patients with DN as confirmed by renal biopsy had nephrotic range nephropathy or severe nephrotic syndrome, with DM of long evolution and associated with poor metabolic control.
Conflicts of interest
The authors state that they have no potential conflicts of interest related to the content of this article.
Table 1. Sociodemographic characteristics, pathological history, laboratory results, and treatments given prior to renal biopsy