To the Editor:
Renovascular hypertension (RVH) is the most common form of secondary hypertension, with renal arteriography being the gold standard study for confirming diagnosis.1 It presents clinically with arterial hypertension (AHT) that does not respond to treatment (three antihypertensive drugs including a diuretic) and progressive deterioration of renal function due to ischaemic renal atrophy.2 Angioplasty is the technique of choice in cases of renal artery fibromuscular dysplasia; but there is the possibility of performing nephrectomy, back table procedure and autotransplantation in cases that cannot be treated with angioplasty.3
We report the case of a 59-year-old female, without harmful habits, a history of dyslipidaemia, obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and chronic iron deficiency anaemia, followed up in the Nephrology outpatient service for about 20 years due to AHT unresponsive to treatment (5 drugs).
Physical examination was normal except for sustained AHT (170/90mmHg under antihypertensive medical treatment), including funduscopic examination, where no retinopathy was observed. Ambulatory monitoring of arterial pressure was carried out on various occasions and confirmed resistant AHT. One of these measurements showed the following readings:
Mean systolic blood pressure (SBP): 143mmHg (110-168), mean diastolic blood pressure (DBP): 80mmHg (62-90), mean heart rate: 61 (64-67). SBP load: 70.7%, DBP load: 25.9%. NON-DIPPER night-time pattern (lower night-time SBP: -1.15%, lower night-time DBP: 0%).
The blood test showed haemoglobin: 11.7g/dl, haematocrit 37.1%, creatinine: 1.22mg/dl, urea: 40mg/dl, glucose: 88mg/dl, total cholesterol: 249mg/dl and normal urinary sediment without microalbuminuria. Thyroid hormones, catecholamines and metanephrines were normal.
The electrocardiogram showed signs of left ventricular hypertrophy which was not confirmed by Doppler echocardiography.
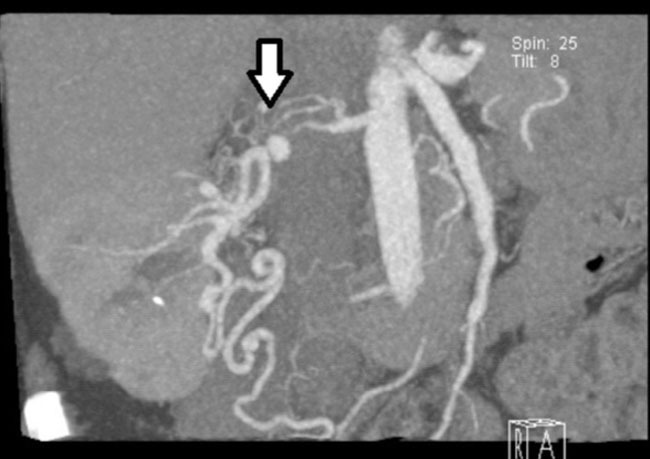
Imaging studies showed normal chest X-ray and renal ultrasound with right kidney with no structural abnormalities, except for the presence of two simple cysts in the upper pole and it was not possible to visualize the left kidney. Subsequently, renal artery CT angiography was performed and we observed almost complete stenosis of the right renal artery, 1.3cm long, at a distance of approximately 2cm from its outlet, with an 8mm aneurysm subsequent to stenosis and the presence of smaller aneurysmal dilatation. There was also left renal atrophy (Figure 1). This finding was confirmed by renal arteriography.
As treatment, several antihypertensive drugs were required throughout follow-up including diuretics, beta blockers, alpha blockers, calcium channel blockers and angiotensin II receptor blockers, with high levels of arterial pressure being sustained. This was properly controlled by treatment with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, which was suspended due to acute impairment of renal function.
Given the situation of resistant hypertension and the possibility of complications, the patient was offered surgical treatment with renal autotransplantation, as she was not a candidate for a vascular interventional procedure due to vascular anatomical abnormalities.
Ipsilateral renal autotransplantation was performed at the right iliac fossa by extraction of the graft with ex-vivo pedicle reconstruction, and repair of main trunk and secondary branch of right renal artery and subsequent renal autotransplantation with internal iliac artery and aneurysmorrhaphy.
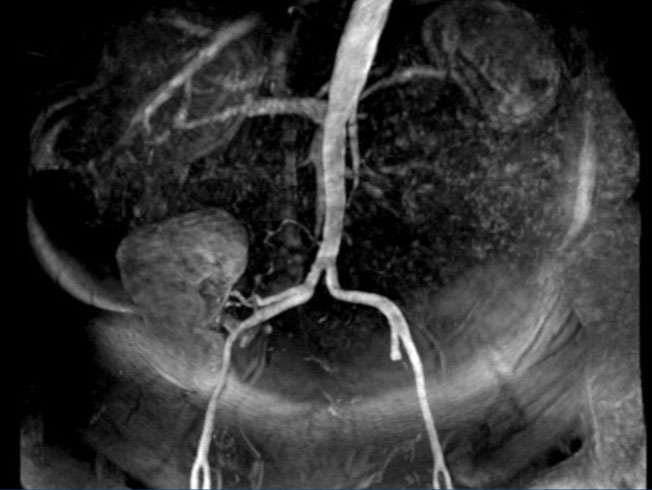
Following surgery, the blood pressure normalised and since then maintained around 120/80mmHg without drugs. In the postoperative imaging study (renal MRA) (Figure 2), normal kidney graft was observed with new vascularisation.
RVH is one of the most common forms of secondary hypertension, with a prevalence ranging from 5-15%. The importance of its diagnosis is mainly due to the fact that it is a potentially curable form of hypertension with stenosis correction.1 There are two main types of renovascular disease: that which is produced by fibromuscular dysplasia, more prevalent in women under the age of 30 and atherosclerosis, observed in males over 60 years of age, especially in patients with vascular risk factors.2 The medical management of hypertension is the preferred therapeutic resource of patients with atherosclerosis, since renal function loss due to progressive obstruction is not common.4 However, interventional treatment is reserved for those patients in whom, despite multiple drugs being indicated, it is not possible to control hypertension.
If renal artery stenosis is due to perimedial and intimal fibroplasia, it usually progresses to ischaemic renal atrophy. In these cases, interventional treatment is recommended. Angioplasty is the technique of choice in cases of fibrodisplasia.5 However, 30% of patients may require surgical revascularisation, which generally takes place in situ. There is the possibility of performing back table surgery and then autotransplantation; this is carried out in complex cases, where in situ repair may be a challenge.
In our case, back table surgery was a complicated procedure with pedicle reconstruction aneurysmorrhaphy, which led to the solution of the problem.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest related to the contents of this article.
Figure 1. CT angiogram of renal arteries
Figure 2. Renal magnetic resonance angiography