Hypouricemia is defined when a serum urate concentration is less than or equal 2.0mg/dl. Differential diagnosis is made by fractional uric acid excretion with the identification of urate transporters and intracellular proteins involved in the tubular transport of uric acid. This review examines current knowledge on uric acid tubular transport and the various clinical situations of hypouricemia.
La hipouricemia se diagnostica cuando los niveles plasmáticos de ácido úrico son menores o iguales a 2,0 mg/dl. El diagnóstico diferencial de la hipouricemia se realiza en función de la excreción fraccional de ácido úrico, y se han identificado varios transportadores y proteínas implicados en el manejo del ión urato en el túbulo proximal. En este artículo se revisan los conocimientos actuales sobre el manejo tubular renal del ácido úrico y las distintas situaciones clínicas asociadas con hipouricemia.
INTRODUCTION
Hypouricemia has no recognisable symptoms, and therefore requires no treatment. However, it is a biochemical finding that deserves attention since it may be associated with primary or secondary tubulopathies and other underlying conditions. Traditionally, hypouricemia has not been given the same importance as hyperuricemia, perhaps because of its lower incidence rate. However, hypouricemia is now increasingly common in nephrology consultations, as a greater number of patients with diabetic nephropathy are seen, and because it is increasingly common to see patients from different races and countries. Moreover, from a physiological standpoint, there have been new contributions on the mechanisms of uric acid transport in the renal proximal tubule. Therefore, new therapies to block or stimulate these transport mechanisms may become available in the coming years.
NORMAL uric acid Plasma values and urinary excretion
Serum urate concentrations are higher in men than in women. Thus, hyperuricemia is defined as the existence of values above 7mg/dl in men and higher than 6mg/dl in women. Urate excreted in the urine accounts for approximately 70% of that produced daily, with the rest excreted in the faeces. Normal uricosuria values in adults are 620±75mg/day.1,2 Urate elimination is best studied as an excretion index (normal: 0.40±0.09mg/100ml)3 or preferably as fractional excretion (normal: 7.25±2.98%).4,5
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND HISTORICAL BACKGROUND OF RENAL TUBULAR HANDLING OF URIC ACID. NEW DEVELOPMENTS
In the early twentieth century, it was assumed that uric acid was filtered by the kidney, and thus excreted in the urine. However, in 1950, Berliner et al. tried to find an explanation for the finding that uric acid clearance was lower than that of creatinine. To explain this “incomprehensible phenomenon”, the authors induced hyperuricemia in a group of healthy subjects by an overload of lithium carbonate. Studying the clearances of inulin and urate, they came to the conclusion that “urate is excreted by glomerular filtration and active tubular reabsorption”.6 That same year, Praetorius and Kirk described the case of a patient with a severe hypouricemia in which the clearance of uric acid was higher than creatinine. This led them to assume that this individual’s kidney secreted uric acid. It was the first reported case of renal tubular hypouricemia.7
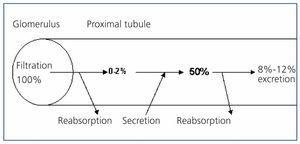
The existence of a tubular secretion phase for uric acid was again proposed in 1957 when Gutman and Yu studied 300 patients with gout and concluded that a reduction in the tubular secretion of uric acid could explain the reduction of uricosuria found.8 Four years later, those same authors published their 3-component theory. Uric acid circulating in the blood is passively filtered at the glomerulus. It is later actively reabsorbed in the proximal tubule and then secreted into the tubular lumen.9 In the early 70s, Diamond and Paolino, through the sequential combination of various uricosuric medications (sulphinpyrazone, probenecid and salicylates at high doses) and pyrazinamide in healthy subjects, reported the existence of a reabsorption of urate in an area distal to secretion (postsecretory reabsorption).10 The 3-component hypothesis had thus become 4. The proportion of filtered urate reabsorbed in the proximal tubule was 99%-100%, leaving 0%-2% of filtered urate in the tubular lumen. Subsequently, a tubular secretory phase is produced, with 50% of the urate initially filtered remaining in the tubular lumen. Finally, this leads to proximal tubular reabsorption, quantified at 80% of that secreted. This explains how the amount of uric acid excreted in the urine is approximately 10% of the amount of urate filtered (Figure 1). Thus, defects in the tubular handling of uric acid associated with hypouricemia could be caused by isolated or combined defects in the presecretory and/or postsecretory reabsorption, or by an increase in tubular secretion. To establish the causal mechanism, pharmacological tests were used with pyrazinamide stimulus (to inhibit tubular secretion) and probenecid or benzbromarone (to inhibit postsecretory tubular reabsorption).11 Currently, these tests are not usually performed in daily practice.
Knowledge of the metabolism of uric acid did not change until the arrival of new developments resulting from the application of molecular biology techniques. These identified several transporters and proteins that have demonstrated the complexity of urate ion handling in the proximal tubule12 (Figure 2).
The URAT1 transporter that reabsorbs the filtered urate was identified by Enomoto et al. in 2002.13 It is located in the apical membrane of proximal tubule cells and is encoded by the gene SLC22A12(URAT1), which belongs to the organic anion transporter (OAT) family.14 In the human kidney, urate is transported via URAT1 through the apical membrane of the proximal tubular cells, in exchange for anions transported towards the tubular lumen to maintain the appropriate electrical balance (Figure 2). Mutations in the SLC22A12 gene encoding URAT1 have been described in Japanese patients suffering from renal tubular hypouricemia.15-17 Mutations in this gene have also been described in Korean patients18 and in 3 Israeli families of Iraqi origin.19 These patients all have very low levels and high fractional excretion of uric acid (approx. 40%-90%) and a low uricosuric response to probenecid and pyrazinamide.15 Both losartan and benzbromarone exert their uricosuric action by inhibiting URAT1.20
Uric acid enters the peritubular space due to basolateral transporters. In 2003, Jutabna et al. identified a new voltage sensitive organic ion transporter, the URATv1 (OATv1), which facilitates the exit of urate from the cell,21 and which is encoded by the gene SLC2A9.22 It was later called GLUT9 as it was known to belong to a family of proteins facilitating the transport of hexoses (fructose, glucose).23 Two variants of the protein have been described: a GLUT9L isoform which is expressed primarily in the basolateral membrane of the proximal tubule cells, and a GLUT9S isoform which is expressed exclusively in the apical membrane of these cells.24 For patients with the latter renal tubular hypouricemia, the urate reabsorption reduction occurs on both sides of the renal proximal tubule cells25,26 (Figure 2). In these patients, fractional excretion of urate exceeds 150%.26 The heterozygous carriers have moderately reduced urate levels.26
GLUT9 is considered the main regulator of urate levels in humans.27 Thus, it has been reported that different polymorphisms in the SLC2A9 gene influence the levels of urate over a wide range of values.28-30 Therefore, in the future this may be a therapeutic target in patients with gout and related cardiovascular diseases.25 Also, the association between certain polymorphisms of the SLC2A9 gene and the development of nephrolithiasis has been described.31
However, the question of renal handling of uric acid is still a complex one. In 1985, Guggino and Aronson suggested that pyrazinamide stimulated the tubular reabsorption of urate by a Na+-dependent cotransporter.32 In other words, contrary to previously thought, they proposed that it inhibited tubular secretion. During the following years, it was confirmed that there was a link between acid and sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule.33 In 2004, a molecular candidate was described for this type of cotransport, SLC5A8, a Na+-monocarboxylate transporter that would carry out a Na+-dependent cotransport of the monocarboxylic anions lactate, butyrate, nicotinate, beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate.34,35 Interestingly, the human gene SLC5A8 has been reported as a tumour suppressor, whose silencing may contribute to carcinogenesis and the progression of various tumours. However, as shown in Figure 2, SLC5A8 acts synergistically with URAT1. This link between the apical tubular reabsorption of urate and the reabsorption of Na+ would explain hyperuricemia induced by ketoacids in diabetic ketoacidosis,36 ethanol intoxication,37 treatment with pyrazinamide38 and the metabolic syndrome.39 It is worth remembering that hyperinsulinemia is known to increase reabsorption of Na+.40 An increase in serum concentrations of these anions, once filtered, would increase their reabsorption in the proximal tubule which, in turn, would enhance the reabsorption of urate by promoting the activity of URAT and the exchange of these anions with filtered urate.41
Finally, excretion by the kidney of a variety of drugs and metabolites which are dicarboxylic organic anions is mediated, via exchange with urate, by a family of multispecific OAT organic anion transporters (OAT genes), which are part of the SLC22 solute transporter family. Different OATs are located in both the apical (OAT2, OAT4) and the basolateral (OAT1 and OAT3) membranes of the renal proximal tubules.42 It has been suggested that the uricosuric effect of probenecid is due to its inhibition of OAT4.12
Therefore, acceptance of the 4-components model (Figure 1) requires an anatomical separation of presecretory reabsorption, tubular secretion and postsecretory reabsorption. At present, in the absence of detailed physiological characterisation and intrarenal location of the various human transporters listed above, the maintenance of this scheme cannot be sustained.
HYPOURICEMIA
Hypouricemia is diagnosed when plasma levels of uric acid are less than or equal to 2.0mg/dl.43 However, Sperling proposed 2.1mg/dl to be used as the normal lower limit for women and 2.5mg/dl in men.44 It is reported to occur in 0.8% of hospitalised patients and 0.2% of the general population.45
An article was published in 1969 from work carried out in hospitals in Toronto (Canada) which examined the clinical usefulness of 1,000 uric acid determinations. These were not requested by the physicians responsible for the patients, but the biochemists included them in the analytical results.46 Serum uric acid levels below 2.6mg/dl were found in 44 patients (4.4% of the sample). Clinical hypouricemia was questioned in only one case, and considered irrelevant in the 43 remaining cases. The diagnoses of these 44 patients were mixed and none was diagnosed with the classic causes of hypouricemia, such as Fanconi syndrome47 or Wilson's disease.
The differential diagnosis of hypouricemia is made based on the fractional excretion of uric acid (Table 1). Hypouricemia with a reduced fractional excretion of uric acid is associated with xanthinuria, treatment with allopurinol, neoplasms and hepatic function abnormalities.48 Rasburicase treatment also produces hypouricemia with reduced fractional excretion of uric acid, as it is a urolithic agent that catalyses the enzymatic oxidation of uric acid into allantoin, a water soluble product easily excreted by the kidneys.
From a nephrological point of view, it is worth highlighting the hypouricemia associated with hereditary xanthinuria (autosomal recessive deficiency of the xanthine oxidase enzyme), as it is a severe hypouricemia of less than 1mg/dl associated with a decreased uric acid fractional excretion and increased xanthine excretion. The confirmation of the diagnosis is made by liver or intestinal biopsy which shows the reduced enzymatic activity.
Hypouricemia with a high fractional excretion of uric acid is mainly caused by renal tubular hypouricemia, either in an isolated15-19,25,26 or complex tubulopathy, such as Toni-Debré-Fanconi syndrome, caused by various conditions such as cystinosis, Lowe syndrome or heavy metal poisoning. Other causes are the use of salicylates, intravenous contrast media, total parenteral nutrition, Hodgkin's disease and other neoplasias, Wilson's disease and other causes of cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus and syndrome of inappropriate secretion of ADH. Finally, an association has been described with hyperparathyroidism,49 thiazide-induced hyponatremia50 and hyperbilirubinemia51 (Table 1). It must also be remembered that oestrogens, losartan, dicumarol, salicylates at high-dose and trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole are drugs that increase uric acid excretion.
Also, from a nephrological point of view, the existence of hypouricemia in diabetes mellitus, hypouricemia associated with hyponatremia and hypouricemia secondary to tubulopathies should be noted.
It has been reported that patients with diabetes mellitus may have hypouricemia.56,57 This is observable in both type 1, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients58 and in type 2, non-insulin-dependent patients.59,60 This implies that the pathophysiology must initially be connected with something common to both conditions. The reduction in plasma uric acid is due to an increase in its renal clearance58,61-63 and it is only observed in patients with normal GFR levels. When uricosuric stimulus tests were performed, a defect in presecretory reabsorption,68 postsecretory62 or a combination of both 62,64 were seen.
In some studies, increased uricosuria has been attributed to glomerular hyperfiltration,59,60 therefore, hypouricemia could be a marker for the onset of diabetic kidney disease.60 In general, though not always, a positive relationship has been described between glycosuria and uricosuria, therefore, there would be interference between the tubular reabsorption of glucose and the tubular capacity to reabsorb urate.61 Hypouricemia would therefore be likely in the case of poor control of the disease. Thus, the hypouricemia would be associated with poor disease control, hyperfiltration or a late onset of nephropathy.69
Regarding the value of hypouricemia in the presence of hyponatremia, hypouricemia secondary to extracellular volume expansion is associated with decreased proximal reabsorption of sodium and urate. It is common in patients receiving large amounts of fluids intravenously, those with psychogenic polydipsia or SIADH. In these situations, water restriction corrects hyponatremia and hypouricemia. However, hypouricemia in patients with intracranial disease associated with cerebral salt wasting syndrome is not corrected by water restriction.
Hypouricemia has no symptoms; the symptoms are those of the causal disease. However, isolated tubular hypouricemia may be associated with nephrolithiasis and acute renal failure induced by exercise in patients with mutations in either the URAT13,15-17 or GLUT925 gene. In these cases, the clinical symptoms are generalised fatigue, nausea or vomiting and diffuse abdominal discomfort; and they often appear at approximately 2 weeks after physical exercise. If the patient has been previously diagnosed with hypouricemia, its diagnosis is simple and treatment can be provided earlier. It is therefore recommended that uric acid levels be determined in routine medical examinations followed by physical exercise, especially in Asians.52 Two mechanisms have been proposed to explain acute renal failure. First, acute urate nephropathy, caused by increased urate production during exercise, culminating in its intratubular precipitation. The second mechanism is ischaemic renal aggression secondary to vasoconstriction of the renal vessels, mediated by the production of oxygen free radicals during exercise.53 It is known that uric acid is the most abundant soluble antioxidant in humans, as it preserves endothelial function in situations of oxidative stress.54 This mechanism is based on histological results showing acute tubular necrosis,55 although it should be considered only as a triggering cofactor, as acute renal failure induced by exercise has not been described in patients with xanthinuria.26 Dinour et al. have proposed a third mechanism, whereby the accumulation of anions not eliminated in patients with URAT or GLUT9 gene mutations exerts a toxic tubular effect leading to acute tubular necrosis.26
Finally, we would like to emphasise that hereditary tubular hypouricemia associated with hypertension is very rare, as only one case has been reported in the medical literature.71
KEY CONCEPTS
1. Hypouricemia is defined when plasma levels of uric acid are less than or equal to 2mg/dl.
2. Differential diagnosis of hypouricemia is usually made by evaluating the fractional excretion of uric acid.
3. Hypouricemia with reduced fractional excretion of uric acid is associated with defects in the production of uric acid.
4. Hypouricemia with increased fractional excretion of uric acid is associated with defects during the proximal tubular transport of uric acid.
5. Currently there has been progress in identifying proximal tubular transporters of uric acid and the genes that encode them.
6. Hypouricemia is a biochemical marker for primary or secondary tubulopathy and other underlying illnesses.
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the 4-component classical hypothesis in proximal tubular handling of urate (% filtered urate).
Figure 2. The exchanger URAT1 reabsorbs the urate filtered at the apical membrane of proximal tubule cells in exchange with anions transported into the tubular lumen to maintain proper electrical balance
10588_108_12814_en_w4777107445tabla_en.doc
Table 1. Differential diagnosis of hypouricemia by fractional excretion of uric acid