To the Editor,
Kidney injury is one of the most important morbidity and mortality factors in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).1,2 Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the best indicator of renal function, and it is important in the diagnosis, determining the stage, gauging treatment response and dosing medications.3
The National Kidney Foundation (NKF) recommends estimating GFR using creatinine-based equations.4,5 On the other hand, the European Consensus of Lupus Glomerulonephritis suggests that renal function in SLE patients should be measured either by serum creatinine levels or by estimating renal function using serum creatinine-based equations, but where GFR is higher than 60ml/min/1.73m2, creatinine clearance should be used (CrCl).6 In a recent publication, we reported on the high frequency of inappropriate sample collection from SLE patients when CrCl is used.7
We took a survey of Mexican rheumatologists to better understand the use of NKF-recommended equations in evaluating renal function in SLE patients.
We used the google.com survey tool to send questionnaires to members of the Mexican College of Rheumatology in September 2010. We evaluated their demographic data, including sex, years practicing medicine, number of SLE patients evaluated per week and the rheumatologist’s method for evaluating renal function in patients with SLE.
We received responses from 45 rheumatologists throughout the country; the mean age of those responding was 40 years, with a mean of 9.5 years practicing medicine. Of those responding, 75.6% were male and 51.2% saw more than 10 SLE patients per week.
Almost half of the rheumatologists (46.7%) use CrCl in all of their patients in order to estimate GFR; 17.8% use it in two-thirds of their patients, and only 13.3% do not use it at all. Only 28.9% of those responding used equations for estimating GFR (MDRD, CKD-EPI, Cockcroft-Gault, others).
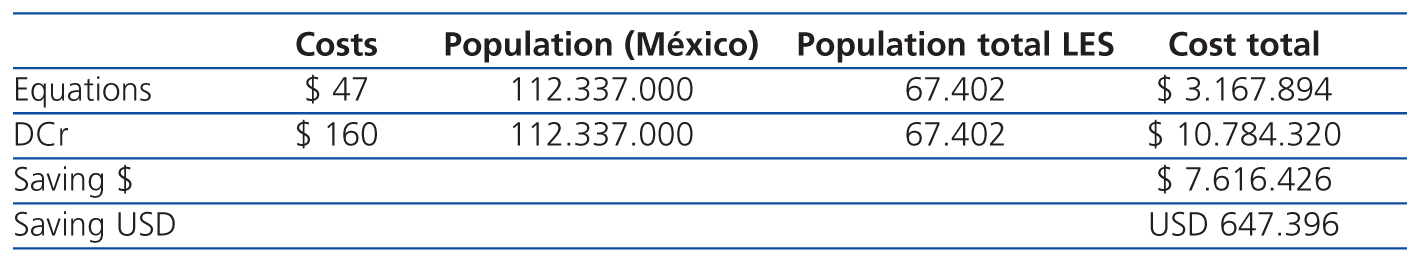
According to INEGI (Mexican National Institute of Statistics and Geography), nearly 112 million people lived in Mexico in 2010. As per the Peláez-Ballestas et al study, the SLE prevalence in Mexico is 0.06%.8 We evaluated the mean cost of CrCl (serum and urinary creatinine in 24 hours) and the mean cost of measuring only serum creatinine (in order to determine GFR by means of equations) in three laboratories in central Mexico. The difference in cost between taking a single GFR measurement by one method or the other is more than 500 000 dollars if the rheumatologist uses CKD-EPI or MDRD instead of 24 hour CrCl (Table 1).
Despite the evidence suggesting a high frequency of inappropriate sample collecting and the recommendation made by the NKF, Mexican rheumatologists continue to use CrCl to estimate GFR. The importance of disseminating studies in other diseases, in addition to the NKF guidelines, is firstly due to the fact that the methods mentioned above do not require 24 hour urine collection and that health care systems would save thousands of dollars if this practice were generalised (worldwide); considering that a number of controlled international clinical trials use CrCl to estimate GFR.9,10
These findings show that although the guidelines suggest the use of more exact, less expensive methods, Mexican rheumatologists continue to use methods that are both more expensive and less reflective of true GFR. We must promote studies among doctors showing the benefits for patients in terms of both economic sustainability and reproducibility. If our results among Mexican rheumatologists were similar on a global level, the savings incurred by using better estimation methods could amount to millions of dollars.
Table 1. Costs associated with a single estimate of GFR in Mexico