Unilateral nephrectomy (Uni-Nx) produces compensatory hypertrophy of the remnant kidney. In this anabolic process, the upregulation of renal insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) plays a key role, which has inspired numerous studies considering the potential regenerative actions of the IGF-1 and the subsequent increase in the glomerular filtration rate. Thus, IGF-1 administration has shown to be able to induce renal hypertrophy, increase glomerular size and enhance glomerular filtration rate, without reaching glomerulosclerosis. Moreover, protein uptake also contributes to renal hypertrophy by increasing renal and circulating IGF-1 levels. In this respect, circulating IGF-1 concentration has been used as a marker of the nutritional status in end-stage CKD patients and has been associated with hormones that participate in the regulation of appetite. Moreover, IGF-1 regulate mineral metabolism, participating in phosphate resorption and calcitriol production by increasing 1-α-hydroxylase activity. Furthermore, IGF-1 is key for bone growth in pediatric patients, acting directly in chondrocytes, osteoblasts and, in a lesser manner, in osteoclasts. In addition, IGF-1 is an important inductor of erythroid proliferation, being able to maintain erythrocytic homeostasis in anephric patients. Nevertheless, the actions of the IGF-1 are attenuated in the context of renal disease, which may be promoted by the presence of inhibitory factors, such as the IGF binding proteins, and inability to trigger intracellular downstream signaling despite of normal IGF-1 receptor expression in cell surface. This review highlights the importance of the IGF-1 in the context of CKD and its potential contribution to renal and also systemic disorders.
La nefrectomía unilateral (Uni-Nx) produce hipertrofia compensatoria del riñón remanente. En este proceso anabólico, la regulación positiva del factor de crecimiento similar a la insulina 1 (IGF-1) juega un papel clave, lo que ha inspirado numerosos estudios considerando las posibles acciones regenerativas del IGF-1 y el consiguiente aumento de la tasa de filtración glomerular. Así, la administración de IGF-1ha demostrado ser capaz de inducir hipertrofia renal, aumento del tamaño glomerular y un consecuente aumento de la tasa de filtración glomerular, sin llegar a desarrollar glomeruloesclerosis. Además, la ingesta de una dieta alta en proteínas también contribuye a la hipertrofia renal mediante el aumento de los niveles de IGF-1, tanto a nivel renal como en la circulación. En este sentido, la concentración sérica de IGF-1 se ha utilizado como marcador del estado nutricional en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica (ERC) terminal y se ha asociado con hormonas que participan en la regulación del apetito. Además, el IGF-1 regula el metabolismo mineral, participando en la resorción de fósforo y la producción de calcitriol al aumentar la actividad de la 1-α-hidroxilasa. Además, el IGF-1 es clave para el crecimiento óseo en pacientes pediátricos, actuando directamente en condrocitos, osteoblastos y en menor medida en osteoclastos. Además, el IGF-1 es un importante inductor de la proliferación eritroide, pudiendo mantener la homeostasis de los eritrocitos en pacientes anéfricos. No obstante, las acciones del IGF-1 se atenúan en el contexto de la enfermedad renal, que puede deberse a la presencia de factores inhibidores, como las proteínas de unión al IGF, y a la incapacidad de activar la señalización intracelular a pesar de una expresión normal del receptor de IGF-1 en la superficie celular. Esta revisión destaca la importancia del IGF-1 en el contexto de la ERC y su potencial contribución a los trastornos renales y también sistémicos.
The insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is a hormone widely expressed throughout the body that plays a crucial role in promoting anabolic processes. By binding to the IGF-1 receptor (IGF1R), IGF-1 initiates the phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol 2-phosphate (PIP2) to phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3), which activates downstream signaling pathways involving AKT and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Thus, the IGF-1 signaling is essential for processes such as cell proliferation, survival, and metabolic regulation, impacting various organs and systems. The kidney expresses both, IGF-1 and IGF1R, where they contribute significantly to renal function and disease. IGF-1 is particularly abundant in the medullary collecting ducts, with lower expression in the cortical collecting ducts, proximal tubular cells, and the glomerulus. The binding sites for IGF-1 are widely distributed across the kidney, with higher concentrations observed in the inner medulla.1
Importantly, unilateral nephrectomy (uni-Nx) induces an increase in IGF-1 production in contralateral kidney, which promotes compensatory renal hypertrophy.2 Similarly, both the exogenous administration of recombinant growth hormone (GH), a major stimulus for IGF-1 synthesis during development, and uni-Nx compensatory renal hypertrophy by both, exogenous administration of recombinant GH, which is a principal stimulus for IGF-1 synthesis during development, or uni-Nx result in enhanced renal IGF-1 expression, a critical factor in renal hyperplasia.3 The kidney also produces a variety of IGF-1 binding proteins (IGFBPs), which bind and capture free soluble IGF-1, inhibiting its mitogenic effects.4 To date, six closely related high-affinity IGFBPs have been identified, and all are expressed in the kidney. These include IGFBP-1 to IGFBP-6, each expressed at different sites. Among them, IGFBP-5 is the most abundant in renal tissue, while IGFBP-3 is the most prevalent in circulation. In contrast, IGFBP-6 exhibits the lowest renal expression.5 Notably, although IGFBP-7 is minimally expressed in healthy kidney and has low affinity for IGF-1, its production is significantly upregulated in renal biopsies from CKD patients, making it a potential marker for acute kidney injury.6,7
In addition to its regulatory binding proteins, serum IGF-1 levels decline with aging in the general population.8 This reduction may also contribute to the decreased renal anabolic capacity observed in older adults, as well as the progressive decrease of the kidney function.
In this review, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the renal actions of IGF-1 signaling, highlighting its role in the pathophysiological complications associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD) at systemic level. This review in structured into two main sections: the first one explores the effects of IGF-1 on renal physiology and pathophysiology and the second one highlights the key role of IGF-1 in systemic complications associated with renal dysfunction.
IGF effects on renal pathophysiologyIGF-1 in normal kidney function and compensatory renal hypertrophyThe GH is a key stimulus for both, whole-body and renal growth. Studies in rats have shown that administration of recombinant GH or carrying a GH-producing tumor results in increased body weight and kidney size compared to control animals. Additionally, rats under high GH conditions showed increased serum levels and renal expression of IGF-1, with sclerotic glomeruli. These findings suggest that overproduction of renal IGF-1 may contribute, at least in part, to kidney abnormalities observed in acromegaly.9 In a similar context, mutant mice with GH overproduction develop renal hypertrophy, increased glomerular size and mesangial sclerosis. This condition progresses to glomerulosclerosis and albuminuria, along with interstitial infiltration, further emphasizing the role of excessive GH and IGF-1 signaling in renal pathophysiology. However, mutant mice overproducing IGF-1 do not develop glomerulosclerosis, despite exhibiting increased kidney size and mild glomerular hypertrophy. This suggesting that activation of the renal IGF-1 signaling may not be directly involved in the GH-induced pathological effects on the kidney.10,11 The mild glomerular changes observed, such as cell proliferation, could be mediated directly by renal IGF-1, since mesangial and other glomerular cells express the IGF1R.12 Interestingly, other studies have observed increased kidney weight following IGF-1 or GH administration in rats. This anabolic effect of the GH is partially mediated through stimulation of renal IGF-1, leading to enhanced glomerular and tubular cell proliferation; although, the increase in kidney size was only significant in IGF-1 treated animals when expressed relative to total body weight.13
In healthy human subjects, the stimulatory effects of GH on renal plasma flow and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) exhibits a significant delay following exogenous GH administration. This delay is likely due to the time required for subsequent increases in renal IGF-1 levels, suggesting that locally produced IGF-1 may play a crucial role as a mediator of GH's renal effects.14 Of note, IGF-1 injection alone is sufficient to induce renal actions in animals with pituitary gland ablation, further supporting the importance of IGF-1 in this context.15,16 Additionally, IGF-1 administration led to an increase in GFR in healthy volunteers while simultaneously decreasing GH levels and insulin secretion. This observation contrasts with the typical effects of GH, which usually induces hyperinsulinemia.17
Compensatory renal hypertrophy induced by contralateral nephrectomy is accompanied by increased expression of IGF-1 in the remnant kidney, but not by serum or liver expression;18 suggesting that the renal anabolic effects of IGF-1 are likely triggered locally, through binding to specific receptors in the kidney. This compensatory mechanism is highly sensitive to changes in renal function, as even partial unilateral infarction, induced by ligation of one-half of the renal arteries, can be sufficient to increase IGF-1 expression in the contralateral kidney.19 Mechanistically, the upregulation of renal IGF-1 expression is stimulated by epidermal growth factor (EGF) in the renal collecting ducts, indicating a paracrine regulatory mechanism, as both, IGF-1 and EGF, are produced locally within the kidney.20 Moreover, the renal anabolic effects of IGF-1 are partly mediated through activation of the AKT-calcineurin-NFATc1 signaling pathway, which is involved in the regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).21,22
More recently, studies using single-cell RNA sequencing, have revelated that renal hypertrophy in mice activates sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2) and increases cholesterol biosynthesis in medullary thick ascending limb cells. This signaling pathway is essential for the hypertrophic effects of IGF-1.23 Notably, IGF-1 has also been shown to promote intracellular lipid accumulation in mesangial cells, a phenotype similar to foam cells, which leads to reduced contractility in response to angiotensin-II.24,25 Furthermore, kidney samples from patients with advanced CKD and mouse models with renal fibrosis have defective fatty acid oxidation and higher lipid accumulation than controls without fibrosis. Interestingly, restoring fatty acid metabolism has been found to prevent tubulointerstitial fibrosis in mouse models of renal injury.26
Recent studies have demonstrated that upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) plays a crucial role in renal hypertrophy,27 highlighting the importance of lipid metabolism on renal hyperplasia. Notably, compensatory renal hypertrophy following Uni-Nx is prevented in mice over-expressing α-klotho. This fact is associated with the reduction in renal IGF-1 production, while plasma IGF-1 levels remain unaffected. Moreover, the study shows that in vitro over-expressing of α-klotho in human proximal tubular cells decreases IGF-1-induced AKT phosphorylation, indicating that the inhibitory effects of α-klotho on compensatory renal hypertrophy may be mediated, at least in part, through reduced IGF-1 signaling.28
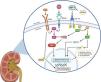
Notably, inhibition of the GH receptor by the specific antagonism G120K-PEG blocks renal IGF-1 upregulation and subsequent kidney hypertrophy in Uni-Nx animals. Despite this, total body weight, food intake and serum levels of GH and IGF-1 remain similar to those in the vehicle-treated Uni-Nx group, suggesting direct renal effects.29 In contrast, continuous infusion of IGF-1 during one-week results in increased glomerular volume and decreased renal vascular resistance, leading to a higher GFR. Inhibition of the GH-releasing hormone, however, does not promote kidney growth or glomerular volume, but reduces renal plasma flow and vascular resistance.30 In Fig. 1 are shown the main regulatory factors of the IGF-1 signaling, as well as the principal downstream pathways related to kidney hypertrophy.
Schematic illustration depicting IGF-1 regulatory factors in the kidney and its downstream interaction pathways leading to renal hypertrophy. Binding of IGF-1 to the IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) results in phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) activation, increasing phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to generate phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3), which in turn results in the AKT and mTOR phosphorylation, as well as NFATc1 nuclear translocation, and subsequent transcription of genes related to cell survival and proliferation. In contrast, IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) capture free IGF-1 and inhibits IGF-1 binding to IGF-1R. Growth hormone (GH) and epidermal growth factor (EGF) bind to their specific receptors and increase RAS-mediated ERK phosphorylation, which also activates the transcription of genes involved in proliferation and survival. Activation of the IGF-1 signaling interacts with EGF and GH downstream signaling by enhancing MEK signaling and ERK phosphorylation, thereby stimulating their anabolic effects. Furthermore, activation of the GH signaling increases IGF-1 gene transcription through phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of STAT5, which further stimulates IGF-1 signaling. Altogether, IGF-1 signaling produces renal hypertrophy and increases glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Created in BioRender. Domínguez Coral, J. (2025) https://BioRender.com/ah5z7kc.
Of note, sex differences in renal characteristics have been observed, with male mice having larger kidneys and glomerular area compared to females. In terms of renal hypertrophic capacity, female mice exhibit larger kidney size and weight, as well as greater glomerular area, despite similar levels of renal IGF-1 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) expression.31 These sex differences in kidney size were attenuated in female mice lacking the estrogen receptor; although their glomerular area remained similar to that of wild-type females. Interestingly, the loss of estrogen receptor function did not affect compensatory renal hypertrophy following Uni-Nx in male mice.
Role of IGF-1 in renal ischemiaPost-ischemic regeneration leads to increased renal IGF-1 expression, promoting proliferation of tubular and non-tubular cells at the kidney regenerative zones by binding IGF1R.32 Studies using animal models of ischemic acute renal injury have shown that IGF-1 administration is useful to reduce renal protein catabolism, resulting in enhanced renal cell proliferation, accelerated recovery of renal function, and improved kidney histology.33,34 These regenerative effects after ischemia-induced acute tubular necrosis are also achieved by exogenous administration of recombinant IGF-1, resulting in a lower mortality in comparison with animals treated with vehicle or GH.34,35
However, despite these promising results in animal models, administration of recombinant IGF-1 (100μg/12h; sc) did not improve renal outcomes in patients with acute renal failure, compared to placebo, after a mean period of 10 days.36 To account for co-founding factors in acute renal injury, recombinant IGF-1 administration was also tested in transplant patients receiving a cadaveric kidney allograft.37 In these patients, treatment with IGF-1 similarly failed to significantly improve renal function compared to placebo, suggesting that the regenerative effects of IGF-1 observed in animal models of renal ischemia may not be directly scalable to patients with acute renal failure.
Subsequent studies in rats have shown that subcutaneous administration of recombinant IGF-1 may be associated with exacerbation of the ischemic renal damage through stimulation of neutrophil infiltration and inflammation.38 This mechanism could be related to the unfavorable results in patients with acute renal failure.
IGF-1 in renal cancerThe anabolic effects of IGF-1 signaling activation can be particularly negative in the context of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). In vitro studies have demonstrated that RCC cells exhibit high expression of both IGF-1 and IGFBP-3, which have opposing effects: inhibition of IGF-1 reduces RCC cell proliferation, while blocking IGFBP-3 increases it.39 This response occurs because IGF-1 signals through IGF1R triggering proliferative effects and promoting IGFBP-3 expression, the latter modulating the IGF-1 actions. Importantly, IGF1R expression also determine RCC aggressiveness, while patients with clear-cell RCC shown kidney IGF1R expression higher than 50% have shorter survival time, a difference that becomes particularly significant after two years of follow-up.40
Moreover, after adjustment for age and stage at diagnosis, those patients with renal IGF1R expression higher than 50% had a 4.2 increased risk of death compared to those with lower renal IGF1R expression. Similarly, other studies have demonstrated a direct association between kidney IGF1R expression and the severity of RCC.41,42In vitro studies using RCC cell lines have shown that treatment with neutralizing antibodies against IGF1R can reduce IGF1R expression and inhibit cell proliferation. This effect is enhanced when combined with the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus.43
Importantly, loss-of-function mutations in the gene encoding the tumor suppressor Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) are commonly observed in RCC.44 These mutations have been associated with increased activation of renal IGF-1 signaling and elevated IGF1R expression, resulting in a more aggressive tumor phenotype compared to RCC with wild-type VHL. This mitogenic response is directly induced by upregulation of IGF1R transcription and occurs independently of VHL's role in suppressing the hypoxia pathway.45–47
Despite of the clear association between activation of renal IGF-1 signaling and RCC occurrence and progression, low circulating IGF-1 levels have been linked to an increased risk of renal cancer, particularly in a cohort of male smokers after at least five years of follow-up.48 This finding raises doubts about the utility of circulating IGF-1 as a reliable biomarker for renal cancer risk.
In addition, discordant (oppositive) differential mRNA expression of genes associated to the IGF-1 signaling pathway has been observed in kidney samples from mice undergoing post-ischemic renal repair, compared to gene expression profiles reported in human renal cell carcinoma. Particularly, IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-3 are upregulated in cancer, while IGFBP-8 and IGFBP-10 (which has lower affinity for IGF-1).49 Thus, whereas 77% of differentially expressed genes were similarly regulated in both renal regeneration and cancer, some genes related to IGF-1 signaling follow divergent molecular pathways in these contexts. This differential response suggests that IGF-1 signaling may not play a common role in both physiological and pathophysiological proliferative processes in the kidney.
Implication of IGF-1 in other renal pathologiesThe beneficial effects of IGF-1 treatment have also been observed in rats with acute renal tubulointerstitial injury induced by ureteral obstruction.50 Likewise, in vivo studies in this mouse model of obstructive nephropathy have demonstrated that IGF-1 administration reduces apoptosis, an effect that was abolished by inhibition of the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway.51
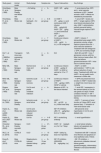
Of particular interest, renal hypertrophy in diabetes is also associated with elevated kidney IGF-1 production, similar to the compensatory hypertrophy observed in the contralateral kidney following Uni-Nx.52 In fact, while rats subjected to Uni-Nx show increased size of the remnant kidney by 30%, animals undergoing streptozotocin-induced diabetes show a 32% increase in renal size, reaching a 46% increase when the diabetic rats were subjects to Uni-Nx, which was consistent with the increased kidney IGF-1 expression.53 These effects of IGF-1 on compensatory renal growth are reduced by administration of an IGF1R antagonism in both, diabetic and Uni-Nx rats,54 as well as ex-vivo compensatory hyperfiltration in kidney samples from Uni-Nx rats.55 Similar results have been observed in non-obese diabetic mice treated with an antagonist of the GH receptor.56 These studies demonstrate that diabetes is an inductor of renal hypertrophy through activation of the kidney IGF-1 levels. Table 1 shows the main renal effects of IGF-1 in studies with animal models.
Studies in animal models on the renal actions of IGF-1.
| Study (year) | Animal model | Study design | Sample size | Type of intervention | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hirschberg R., et al. (1989) | Male Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats | ∼3 d fasting | n=6–8 | rhIGF-1 (25μg/kg; i.v.) | - ↑ renal plasma flow, GFR and ↓ renal vascular resistance in IGF-1 treated animals- rhIGF-1 effects are mediated by eicosanoids |
| Hirschberg R., et al. (1991) | Male Wistar rats | (1) 12h fasting(2) ∼3 d fasting | n=6–8 per group | (1) rhIGF-1 (75μg/kg; i.v.) and continuous rhIGF-1 infusion (250μg/kg/h)(2) rhIGF-1 (25μg/kg; i.v.) and continuous rhIGF-1 (75μg/kg/h) | - ↑ serum IGF-1 levels and GFR- ↑ single nephron GFR, renal blood and plasma flow rate- rhIGF-1 administration partially prevents fasting-induced single nephron GFR reduction |
| Hirschberg R., et al. (1992) | Male Wistar rats | N/A | n=7 per group | Continuous infusion of rhIGF-1 (125μg/24h; s.c.) or GH antagonist | - rhIGF-1 infusion ↑ kidney/total body weight, GFR, glomerular volume, single nephron plasma flow and ↓ renal vascular resistance- Treatment with GH antagonist ↓ GFR, but not kidney weight |
| Doi T., et al. (1988)Doi T., et al. (1990) | Transgenic mice over-expressing GH and IGF-1 | N/A | n=2–36 | N/A | - Both GH and IGF-1 mice ↑ glomerular volume, with the latter having a lesser effect- GH mice had severe glomerulosclerosis- IGF-1 mice had no sclerotic lesions |
| Miller SB., et al. (1990) | Male Sprague-Dawley rats | Normal renal mass and 5/6Nx | n=3–8 per group | Continuous infusion of 200μg/day of rhIGF-1 or rbGH or vehicle for 10 or 17 days | - rhIGF-1 or rbGH administration ↑ GFR in rats without reduction of renal mass- Treatment with rbGH nor rhIGF-1 do not modify inulin clearance in 5/6Nx rats |
| Miller SB., et al. (1992) | Male Sprague-Dawley rats | Ischemic acute tubular necrosis | n=7–9 per group | Continuous infusion of rhIGF-1 (100μg/day), rbGH, rhEGF or vehicle | - ↑ GFR and preserved renal function in rhIGF-1 treated rats- ↓ weight lost, renal injury and mortality |
| Rogers SA., et al. (1993) | Male Sprague-Dawley rats | Uni-Nx and partial unilateral infarction | n=4–8 | Measure of IGF-1 in the tissue infarcted | - ↑ renal IGF-1 expression in the remnant kidney of Uni-Nx rats (peak at 3 days)- Partial unilateral infarction ↑ IGF-1 expression in the non-infarcted kidney |
| Ding H., et al. (1994) | Male Sprague-Dawley | Ischemic acute renal failure | n=14 per group | rhIGF-1 (50μg/100g; s.c.) three times daily | - rhIGF-1 ↑ recovery of renal function at 3 days (GFR, renal plasma flow)- ↑ formation of new renal tubular cells |
| Haylor JL., et al. (JASN 2000) | Male Wistar rats | Uni-Nx and streptozotocin-induced diabetes | IGF-1R inhibition (JB3, 10μg/kg/day) for 4 or 11 days | - JB3 prevents renal hypertrophy in Uni-Nx and diabetic rats | |
| Haylor JL., et al. (NDT 2000) | Male Wistar rats | Uni-Nx | n=4–8 per group | IGF-1 neutralizing antibody | - ↓ renal hyperfiltration |
| Chevalier RL., et al. (2000) | Sprague-Dawley neonatal rats | UUO | n=21–24 per group | rhIGF-1 (2mg/kg/d; s.c.) for 3 or 7 days | - ↓ renal tubular atrophy, tubular cell apoptosis and interstitial fibrosis |
| Wu Z., et al. (2016) | C57BL/6 mice | UUO | n=10 per group | rhIGF-1 (daily/i.p.; dose non-reported) | - Treatment with IGF-1 reduces renal fibrosis and apoptosis of renal epithelial cells (↑Bcl2) |
| Dong R., et al. (2019) | Male C57BL/6J mice | Streptozotocin-induced diabetic kidney disease | n=8–10 per group | IGF-1R inhibition (GSK4529, 30mg/kg/day; i.p.) | - IGF-1R inhibition ↓ albuminuria, diabetes-induced kidney growth, glomerulomegaly, inflammatory infiltration and tubulointerstitial fibrosis |
Abbreviations. rhIGF-1: recombinant human IGF-1; Uni-Nx: unilateral nephrectomy; GFR: glomerular filtration rate; GH: growth hormone; bGH: recombinant bovine growth hormone; EGF: epidermal growth factor; GH-rh: growth hormone-releasing hormone; UUO: unilateral ureteral obstruction; IGF-1R: IGF-1 receptor; Bcl2: B-cell lymphoma 2 (apoptosis regulator).
In clinical studies, treatment with recombinant IGF-1 improved renal function in patients with moderate renal insufficiency or end stage renal disease (ESRD), as evidenced by increased GFR, lower plasma creatinine and BUN levels, and enhanced inulin clearance. Additionally, IGF-1 administration has been associated with increased tubular phosphate reabsorption.57,58 In the same way, other clinical studies have reported beneficial effects of recombinant IGF-1 on GFR in ESRD patients scheduled to begin renal replacement therapy or patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis.59,60
In vitro studies have supported the renal protective effects of IGF-1. Specifically, treatment with IGF-1 prevented etoposide-induced podocyte apoptosis, whereas these protective actions were blocked by inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway, highlighting the critical role of this signaling pathway as a key downstream mechanism.61 Moreover, in vitro studies have shown that IGF-1 signaling is crucial for mesenchymal stem cell-mediated recovery of renal function and tubular cell structure following cisplatin-induced damage.62 Notably, mesenchymal stem cells over-expressing IGF-1 significantly improved outcomes in a rat model of acute kidney injury, enhancing renal function and preventing apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation.63
Based on the studies mentioned above, treatment with IGF-1 appears to be beneficial for renal function. However, the mechanisms underlying IGF-1 signaling seem to be complex. To note, aged rats with GH inhibition, which leads to reduced plasma IGF-1 levels, exhibit improved age-associated renal changes, including lower glomerulosclerosis, altered myofibroblast, reduced collagen content and less macrophage infiltration.64 Additionally, it has been observed that blocking IGF-1 signaling by inhibition of the IGF1R results in prevention of renal inflammation, tubular damage and fibrosis in a mouse model of diabetic kidney disease.65 These findings emerge the controversy regarding potential negative effects of IGF-1, suggesting that its role in kidney disease may not be entirely protective.
Studies in rats undergoing subtotal nephrectomy (5/6Nx) have shown that IGF-1 administration failed to increase GFR in this model of renal insufficiency.66 Close to this finding, recombinant IGF-1 administration induces a dose-dependent decrease in plasma levels of insulin, C-peptide, amino acids and glucose in patients undergoing hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis; however, this response was blunted compared to normal subjects, despite higher plasma IGF-1 concentrations, indicating partial resistance in advanced CKD.67 This reduced response is likely due to a decrease in the distribution and shortened half-life of the IGF-1 in dialysis patients.68 Furthermore, resistance to the GH-mediated bioactive IGF-1 stimulation has been demonstrated in non-diabetic hemodialysis patients, suggesting the presence of additional inhibitory mechanisms.69 In predialysis patients, increased production of IGFBPs has been observed, which may bind free IGF-1 and contribute to the attenuation of its renal effects.70 Therefore, as previously mentioned, elevated levels of renal IGFBPs in conditions of renal insufficiency may act as inhibitors of IGF-1 contributing to resistance in the proximal tubular cells.4
On the other hand, the renal anabolic actions of IGF-1 can be detrimental in the context of polycystic kidney disease (PKD), as it promotes renal cell proliferation and kidney enlargement. Studies have shown that renal epithelial cells from patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) exhibit increased sensitivity to IGF-1 compared to those from healthy individuals, indicating the involvement of this signaling pathway in cyst formation.71 In addition, increased expression of IGF-1-related genes, such as IGF-1, IGF1R, and IGFBP-5, along with the metalloproteinase Pregnancy-Associated Plasma Protein A (PAPPA), has been detected in kidney samples from PKD1 mutant mice, a model of PKD, compared to wild-type controls. PAPPA levels were also elevated in kidney samples from ADPKD patients, where it was found to cleave IGFBP-4, an inhibitor of the IGF-1, producing a consequent overactivation of the IGF-1 signaling. This overactivation contributes to increased cyst number and area.72
Despite the controversy surrounding the various actions of the IGF-1, lower serum IGF-1 levels have been associated with shorter survival rates in patients undergoing one year on dialysis,73 whereas hemodialysis patients with low serum IGF-1 levels had a higher mortality rate, an association that remained significant after adjusting for demographic factors, inflammatory markers, co-morbidities, and biomarker of renal function.74 These studies suggest that, systemic IGF-1 may play a role in preventing mortality in ESRD patients, and could serve as an useful circulating marker of survival in this population.
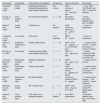
Clinical trials investigating the renal effects of recombinant human IGF-1 are shown in Table 2. It is important to highlight that numerous studies in small groups of patients with kidney disease have demonstrated significant improvements in GFR following recombinant IGF-1 administration; however, these benefits are not observed in clinical studies with larger numbers of kidney patients. Since this discrepancy could be due, at least in part, to the heterogeneity of kidney patients in larger studies, there is a possibility that a particular profile of kidney patients may benefit from IGF-1 treatment.
Clinical studies on the effects of IGF-1 on glomerular filtration rate and survival in CKD patients.
| Study (year) | Study design | Sample size | CKD stage of participants | Type of intervention | Key findings | Potential side effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O'Shea MH., et al. (1993) | Longitudinal study | n=4 | Moderate chronic renal insufficiency (CrCl 2560mL/min) | rhIGF-1 (100μg/kg; 12h; s.c.) for 4 d | - ↑ circulating IGF-1- ↑ inulin clearance- ↑ kidney size | - Tachycardia |
| Miller SB., et al. (1994) | Longitudinal study | n=9 | CrCl less than 20mL/min/1.73m2 | rhIGF-1 (100μg/kg; 12h; s.c.) for 4 d (short-term) and for 13–27 d (long-term) | - ↑ GFR- ↓ plasma creatinine and BUN levels- ↑ inulin clearance during short-term administration | - Pericardial rub- Nasal congestion- Jaw pain |
| Fouque D., et al. (1995) | Longitudinal study | n=18 | Stage 5 | rhIGF-1 (50 or 100μg/kg; s.c.; twice) | Dose-dependent effects:- ↓ plasma levels of insulin- ↓ serum C-peptide, amino acids and glucose levels- Partial resistance to IGF-1 in advanced CKD | Not reported |
| Hirschberg R., et al. (1999) | Multicenter clinical trial, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | n=72 | Acute renal failure, CKD stage 5 | rhIGF-1(100μg/12h; s.c.) | rhIGF-1 did not improve renal outcomes in patients with acute renal failure | Not reported |
| Vijayan A., et al. (1999) | (a) Prospective open-labeled trial; (b) randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial | (a) n=5(b) n=10 | End-stage renal disease | rhIGF-1 (50μg/kg; 24h; s.c.) for (a) 24 d or (b) 31 d | - ↑ GFR during the 3rt and 4th week in both studies | - Peripheral edema- Local irritation at the site of drug injection |
| Frystyk J., et al. (1999) | Cross-sectional case–control study | n=38 | CrCl: 3–59 and 89–148mL/min/1.73m2 | Overnight fasting serum samples | - ↑ production of IGFBPs- Low serum levels of IGF-1 | Not reported |
| Hladunewich MA., et al. (2003) | A randomized, placebo-controlled trial | n=47 | Acute renal failure with GFR less than 20mL/min | rhIGF-1 (100μg/kg; 12h; s.c.) for 6 d | Treatment failed to improve renal function compared to placebo | Not reported |
| Jia T., et al. (2014) | Cohort study | n=365 | CKD stage 5 | Measurement of serum IGF-1 and other biochemical markers | - ↓ serum IGF-1 levels are associated with body composition and CKD-MBD parameters- Serum IGF-1 levels predict increased mortality risk. | Not reported |
| Nilsson E., et al. (2016) | Cohort study | n=265 | CKD stage 5 | Analysis of serum biochemistry and IGF-1 levels | - ↓ serum IGF-1 levels associate with increased mortality in HD patients | Not reported |
Abbreviations. rhIGF-1: recombinant human IGF-1; CrCl: creatinine clearance; GFR: glomerular filtration rate; ESRD: end-stage renal disease; HD: hemodialysis; CKD: chronic kidney disease; IGFBPs: IGF-1 binding proteins; CKD-MBD: CKD-associated mineral and bone disorders.
Protein intake is an important stimulus for renal growth. In rats, kidney size increases according to protein consumption and it acts synergically with compensatory renal hypertrophy following Uni-Nx.75 Of relevance, switching to low- or high-protein diet leads to decreased or increased renal IGF-1 production, respectively, being directly associated with renal growth. These effects are observed even in rats deficient in GH or vasopressin.76 Uni-Nx-induced renal enlargement occurs similarly in both normal and GH-deficient rats when fed a diet with moderate protein content. However, when provided a high-protein diet, only normal rats showed further renal growth. This is because GH-deficient rats on the moderate-protein diet had lower baseline renal and plasma IGF-1 levels, but their IGF-2 levels increased similarly after Uni-Nx. In contrast, a high-protein diet enhanced renal IGF-1 levels only in normal rats, suggesting that the additional effects of a high-protein intake on compensatory renal hypertrophy are partially mediated by GH signaling.77 In fact, the renal anabolic effects of the high-protein diet are attenuated by the inhibition of the GH receptor.78
Particularly, protein and energy wasting (PEW) is commonly observed in hemodialysis patients and likely associated with a lower protein and caloric intake.79 In this respect, circulating IGF-1 has been well-established as a marker for nutritional deficiency in hemodialysis patients for decades.80,81 Thus, patients undergoing hemodialysis with decreased muscle mass and a history of infections often show decreased serum IGF-1 levels, showing high sensitivity (77%) and moderate specificity (52%) as a marker of nutritional status.82
Compared to controls on a low-protein diet, rats fed a high-protein diet showed increased IGF-1 levels in the serum, liver and glomerulus, but not in the renal cortex, which resulted in higher total body and kidney weight but not liver. In addition, high protein intake also increased renal flow and GFR as compared with rats fed a low-protein diet, while decreased renal vascular resistance, actions that were associated with the higher serum IGF-1 levels.83 As previously mentioned, the glomerular hemodynamic effects of IGF-1 are mainly due to increased glomerular ultrafiltration coefficient and decreased efferent arteriolar resistance. However, these effects are prevented in fasted animals due to a reduction in the increment of the glomerular transcapillary hydrostatic pressure.15 Additionally, a protein-rich diet also stimulates VEGF signaling, which promotes glomerular hypertrophy.84 In contrast, low-protein diet leads to reduced serum GH and IGF-1 levels in rats, which could help preventing glomerulosclerosis.85
It is important to note that appetite-regulating endocrine factors, such as leptin, a hormone that induces satiation, may be linked to IGF-1 production in renal patients. Thus, serum IGF-1 levels correlates with the circulating leptin concentration in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis, but not in patients treated with conservative therapy.86 Interestingly, administration of recombinant IGF-1 decreases serum leptin concentration in patients undergoing hemodialysis; however, when recombinant IGF-1 is co-administrated with recombinant GH, circulating leptin levels are unexpectedly elevated, likely due to GH stimulatory effects on insulin production.87 Moreover, treatment with recombinant GH increases IGF-1 levels in patients undergoing hemodialysis with low protein intake, resulting in a positive nitrogen balance and suggesting an anabolic response, which may also contribute to increase the leptin levels.88 Of note, among the multiple factors, circulating IGF-1 concentration is strongly associated with loss of appetite in dialysis patients, a condition linked to poor clinical outcomes.89 However, very low IGF-1 levels have been associated with a higher mortality in CKD patients with poor muscle strength, whereas those with higher muscle strength showed improved survival despite of the reduced IGF-1 concentration.90 This suggests that muscle effects, potentially influenced by physical exercise habits or muscle-derived cytokines (myokines), may play a role in these outcomes.
In addition, ghrelin, a stomach-derived hormone that is involved in appetite stimulation, increases renal IGF-1 levels and improves renal function in a mouse model of ischemia-reperfusion.91 Consequently, the effects of the treatment with a ghrelin receptor agonist has been studied in patients undergoing hemodialysis, being efficient in increasing serum IGF-1 levels after three months of treatment, suggesting that the ghrelin receptor activation should be useful to prevent PEW in these patients.92
IGF-1 and CKD-MBDGH induces increased tubular phosphate reabsorption and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 production, which should be at least partially induced by the subsequent renal IGF-1 production. Thus, continuous administration of exogenous IGF-1 in rats with pituitary gland ablation showed enhanced renal phosphate reabsorption, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin production, reduces renal sodium excretion and increases GFR. These effects of the IGF-1 persisted even in thyroparathyroidectomized rats, suggesting a PTH-independent mechanism.93 In addition, 1-alpha hydroxylase activity is synergically increased by IGF-1 administration in rats fed a phosphorus deficient diet, which suggests also distinct mechanisms.94In vitro experiments with renal proximal tubular cells have demonstrated the direct stimulatory effects of IGF-1 and P depletion on calcitriol synthesis.95
In patients undergoing hemodialysis, recombinant GH administration results in a subsequent increase in plasma IGF-1 concentration, accompanied by reductions of the blood urea nitrogen (BUN), urea generation, protein catabolic rate, phosphate, and intact parathyroid hormone plasma (iPTH) concentrations,96 likely reflecting improved renal function. In prepubertal children with advanced CKD and severe growth retardation, GH administration has shown significant benefits, leading to increased serum IGF-1 levels.97 However, despite improved growth in children treated with GH and the non-apparent progression of renal damage, bone maturation seems to be unaffected despite of the increased plasma IGF-1 levels after 6 months, maybe due to the concomitant decrease of IGFBP-1 and increase of IGFBP-3, which occurred in a lower extent that the IGF-1 changes.98 In the same way, circulating levels of IGF-1 are not correlated with bone formation parameters in non-dialysis CKD patients, which apparently excludes a role of the IGF-1 in bone turnover.99
Recent studies have demonstrated that low serum IGF-1 levels are associated with lower weight and bone mineral density in pediatric CKD patients.100 Importantly, a combination of recombinant GH and IGF-1 has been found to be more effective in preventing growth retardation than GH alone, suggesting an impaired response to the GH effect on IGF-1 stimulation.101 In a study of young rats with renal insufficiency, despite having similar serum GH levels, exhibited lower IGF-1 concentrations, which may contribute to bone growth retardation. This reduced bone response to the stimulatory effects of GH via IGF-1 has been linked to decreased VEGF expression and diminished vascularization in the primary ossification zone of rats with renal insufficiency.102 In the same way, intensive treadmill exercise improves linear bone growth in a rat model of renal insufficiency (5/6Nx). This effect was associated with increased expression of IGF-1 and VEGF in the primary ossification zone.103
Altogether, the bone anabolic actions of the GH can be, at least in part, mediated by paracrine IGF-1 signaling, which enhances osteoblast activity.104 In fact, the only administration of recombinant IGF-1 to healthy participants results in an increase in circulating levels of bone remodeling markers. In these participants, GH administration increased circulating phosphate levels by enhancing phosphate resorption, while IGF-1 treatment did not significantly modify phosphate concentrations.105 These effects of recombinant IGF-1 on bone remodeling and calcitriol production have been also observed in patients with GH deficiency, being more notable on osteoblast activity than in bone resorption.106
Furthermore, calcium influx from the bone store appears to be an important regulator of IGF-1 production, since patients with pycnodysostosis, who have a loss-of-function mutation of the Cathepsin K gene and develop osteosclerosis, show low levels of IGF-1, which may be associated with impaired osteoclastic activity.107 In addition, continuous infusion of PTH or PTH-related protein (PTHrP) increase circulating IGF-1 levels, along with plasma levels of calcium and calcitriol, as well as bone resorption.108 Of interest, the osteoanabolic effects of PTH are reduced in mice with IGF-1 knockout mice, as well as in osteoblasts derived from this mutant strain, while administration of exogenous recombinant IGF-1 increased in vitro proliferation.109 In contrast, total parathyroidectomy abolishes the effects of high dietary protein supplementation on the stimulation of renal and liver IGF-1 expression, as well as its actions on the compensatory kidney hypertrophy. However, administration of calcitriol or activation of renal calcium reabsorption by a retinoid derivate restored plasma IGF-1 levels.110
Importantly, chondrocytes isolated from rats with renal insufficiency also show decreased response to the anabolic effects of IGF-1 compared to chondrocytes from rats with normal renal function,111 suggesting that intracellular alterations as causing factors for IGF-1 resistance. Moreover, rats undergoing subtotal nephrectomy (5/6Nx), which impairs long bone growth, show reduced IGF-1 expression in the growth plate. The exacerbation of secondary hyperparathyroidism due to high dietary phosphate further worsens bone alterations and decreases growth plate width. These bone defects are associated with a reduced expression of both IGF-1 and PTH receptor expression in the growth plate.112 Altogether, these studies suggest a connection between mineral metabolism parameters and bone IGF-1 signaling.
In humans, the bone effects of IGF-1 have been demonstrated in elderly women,113 where treatment with a low dose of recombinant IGF-1 led to increased osteoblast activity with only a minor increase in bone resorption, also decreased serum phosphate after 3 weeks. Similarly, associations among serum IGF-1 concentration and serum levels of phosphate, calcium, FGF23 and bone mineral density have been shown in patients with advanced CKD, which also supports the link between mineral metabolism and IGF-1 regulation in CKD patients.73
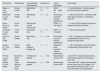
In patients with acromegaly, higher renal IGF-1 is associated expression with increased serum and urinary calcium levels, elevated serum phosphate and calcitriol concentrations, along with decreased serum PTH levels. In these patients, treatment with the diuretic agent furosemide decreases serum IGF-1 concentration and normalizes mineral parameters, but did not further increase urinary calcium excretion, suggesting that these effects are mediated by IGF-1.114 Another factor that reduces IGF-1 levels is metabolic acidosis that often may accompany CKD,115 highlighting the complexity of the IGF-1 regulation. Studies demonstrating the effects of IGF-1 in mineral and bone metabolism are shown in Table 3.
Evidence on the involvement of IGF-1 in mineral and bone metabolism.
| Study (year) | Study design | Characteristics of participants | Sample size | Type of intervention | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caverzasio J., et al. (1990) | Animal models | Hypophysectomized and thyroparathyroidectomized male Sprague-Dawley rats | 5–8 animals | rhIGF-1 continuous infusion (10μg/h) for 6 days | - ↑ max. TRPi, 1,25-(OH)2D3 and GFR- ↓ urinary Na excretion |
| Coen G., et al. (1991) | Cross-sectional study | Non-dialysis CKD patients | n=28 | Serum IGF-1 quantification | - Inverse association between serum IGF-1 and MAR |
| Nesbitt T., et al. (1993) | Animal models | C57BL/6J mice | Not reported | rhIGF-1 continuous infusion (0.1–10μg/h) for 24h | - ↑ renal 1-α-hydroxylase |
| Condamine L., et al. (1994) | In vitro study | Kidney cells | 5–10 replicates | rhIGF-1 (25ng/mL) | - ↑ renal 1-α-hydroxylase |
| Ghiron LJ., et al. (1995) | Prospective interventional study | Healthy elderly women | n=16 | rhIGF-1 (15 or 50μg/kg/12h; s.c.) or GH for 28 days | - ↑ markers of bone turnover- ↑ urinary Ca excretion- ↓ urinary P excretion |
| Mak RH., et al. (1996) | In vitro study | Chondrocytes from 5/6Nx male Sprague-Dawley rats | n=6 | rhIGF-1 (1–100ng/mL) for 3 days | - ↓ growth response to rhIGF-1 in chondrocytes from 5/6Nx rats |
| Johansson AG., et al. (1996) | Randomized, crossover study | Idiopathic osteoporosis men | n=12 | rhIGF-1 (80μ/kg; s.c.) for 1 week | - ↑ markers of bone turnover |
| Bianda T., et al. (1997) | Randomized, crossover study | Healthy young adults | n=7 | rhIGF-1 continuous infusion (8μg/kg/h) for 2 weeks | - ↑ markers of bone turnover- ↑ urinary Ca excretion- ↑ calcitriol (free) |
| Bianda T., et al. (1998) | Randomized, crossover study | GH-deficient adults | n=8 | Continuous infusion of rhIGF-1 (5μg/kg/h) | - ↑ markers of bone turnover- ↑ 1,25-(OH)2D3- ↓ serum creatinine |
| Miyakoshi N., et al. (2001) | Animal models | IGF-1 deficient mice | n=5–6 | rhPTH (1–34) (160μ/kg; s.c.) for 10 days | - Lack of IGF-1 blocks PTH osteoanabolic effects |
| Karava V., et al. (2021) | Cross-sectional study | CKD children and adolescent patients | n=46 patients | Serum IGF-1 quantification | - Association between serum IGF-1 and lumbar BMD |
Abbreviations. rhIGF-1: recombinant human IGF-1; Max TRPi: maximal tubular reabsorption of phosphate; GFR: glomerular filtration rate; BMD: bone mineral density; MAR: mineral apposition rate; 5/6Nx: 5/6 nephrectomized; GH: growth hormone; CKD: chronic kidney disease; rhPTH: recombinant human parathyroid hormone; TRPi: tubular reabsorption of phosphate; PTH: parathyroid hormone.
Most studies have reported a protective effect of IGF-1 on cardiovascular health in CKD. In hemodialysis patients, higher circulating levels of IGF-1 are independently associated with a lower ventricular mass and an improved ejection fraction.116 However, under hypertensive conditions, increased IGF-1 expression is observed in the left ventricle but not in the right ventricle. The highest IGF-1 expression occurs in the subendocardial layer, where the wall stress is more pronounced,117 suggesting a possible role as a mediator of left ventricular hypertrophy. In the same way, left ventricular IGF-1 expression is increased in the early stages of hypertrophy,118,119 which may raise the possibility of an involvement of the IGF-1 anabolic actions in the exacerbation of cardiac insufficiency. Remarkably, while recent studies have reported an association between low serum IGF-1 levels and all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients, serum IGF-1 concentration was not useful as a predictor of cardiovascular events.120
In the vasculature, studies in animal models have shown that IGF-1 induces vasodilatory effects mediated by increasing nitric oxide synthesis in vascular endothelial cells.121,122 Moreover, in vitro studies with rat vascular smooth muscle cells have demonstrated that treatment with recombinant IGF-1 directly reduces the endogenous production of nitric oxide induced by exogeneous administration of interleukin-1β or TNF-α, suggesting a role of IGF-1 on the regulation of nitric oxide synthase at the sites of vascular injury.123 A list of preclinical and clinical studies on the actions of IGF-1 in cardiovascular diseases is shown in Table 4.
Studies demonstrating an involvement of IGF-1 in cardiovascular diseases.
| Study (year) | Study design | Characteristics of participants | Sample size | Type of intervention | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haylor J., et al. (1991) | Animal models | Male Wistar rats | n=11–13 | rhIGF-1 (50μg/kg; i.v.) | - ↑ renal blood flow- ↓ blood pressure and renal vascular resistance |
| Wåhlander H., et al. (1992) | Animal models | Male Wistar rats | n=10 | Renal artery occlusion-induced hypertension | - ↑ left ventricular IGF-1 expression after renal artery occlusion, in association with LVH |
| Schini VB., et al. (1994) | In vitro study | Rat vascular smooth muscle cells | rhIGF-1 (1–100; ng/mL) | - ↓ IL1β and TNF-induced production of nitrate and citrulline formation | |
| Tsukahara H., et al. (1994) | In vitro study | Endothelial cells | n=4–14 | rhIGF-1 (1–20; ng/mL) | - ↑ nitric oxide production |
| Guron G., et al. (1996) | Animal models | Male Wistar rats | n=5–8 | Renal artery occlusion-induced hypertension | - ↑ IGF-1 expression in the left ventricle of hypertensive rats with LVH in comparison with Sham |
| Huang CY., et al. (2003) | Animal models | Male Sprague-Dawley rats | n=4 | Abdominal aorta occlusion- induced hypertension | - ↑ IGF-1 expression in the left ventricle of hypertensive rats precedes LVH |
| Prelevic V., et al. (2020) | Multicentric cohort study | Hemodialysis patients | n=102 | Measurement of serum IGF-1 | - Serum IGF-1 levels associate directly with left-ventricular EF and inversely with LVMI |
| Nakaya R., et al. (2022) | Cross-sectional cohort study | Hemodialysis patients | n=506 | Measurement of serum IGF-1 | - Low serum IGF-1 levels are associated with all-cause and CVD mortality.- No association among serum IGF-1 and new CVD events or hospitalization |
Abbreviations. rhIGF-1: recombinant human IGF-1; IL1β: interleukin-1β; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; LVH: left ventricular hypertrophy; EF: ejection fraction; LVMI: left ventricular mass index; CVD: cardiovascular disease.
Anemia is a common complication in CKD patients, primally caused by decreased renal erythropoietin (EPO) production. Standard treatments typically are focused on exogenous administration of recombinant EPO or EPO-stimulating agents. However, the erythropoietic activity of IGF-1 has been recognized since 1985.124 Despite of this evidence, the potential role of the IGF-1 in the development of anemia within the context of CKD remains insufficiently explored.
In hemodialysis patients with severe secondary hyperparathyroidism, Ureña et al., observed that hematocrit values correlated more strongly with serum IGF-1 levels than with serum EPO levels.125 Interestingly, residual hematopoietic function has been observed in some anephric patients, suggesting the involvement of stimulators beyond renal EPO. Serum IGF-1 has been identified as a major contributor to hematopoiesis in anephric patients with normal hematocrit. Furthermore, treatment with recombinant IGF-1 enhanced erythroid colony formation in in vitro culture of bone marrow cells.126 In the same way, end-stage CKD patients undergoing hemodialysis and presenting erythrocytosis showed elevated serum IGF-1 levels, while EPO levels were variable. Serum from these CKD patients showed a greater ability to enhance proliferation of erythroid progenitors in normal marrow cultures than serum from non-CKD controls. This effect was diminished after IGF-1 neutralization with a specific antibody. Of note, serum from anemic CKD patients showed similarly variable EPO levels but lower serum IGF-1 concentration than CKD patients with erythrocytosis and their uremic serum was not able to induce erythroid progenitor proliferation in normal bone marrow culture, being these effects unaffected by IGF-1 neutralization.127 These findings underscore the significant role of IGF-1 in the erythrocytic homeostasis in CKD, particularly in those with low EPO levels.
However, a negative association between circulating IGF-1 levels and the hematocrit has been also observed in predialysis patients, suggesting that the presence of uremic inhibitors could impair the effects of IGF-1 on erythroid cell proliferation, which could be restored in patients undergoing hemodialysis.128
In renal transplant recipients, patients developing erythrocytosis have similar serum levels of IGF-1 and EPO than those without erythrocytosis; however, elevated levels of serum IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-3 were found higher in the transplant patients with erythrocytosis, which have been related to decreased degradation of IGF-1.129
In addition, recombinant EPO administration increased IGF-1 levels in hemodialysis patients, along with higher serum collagen telopeptide concentration, in comparison with untreated patients. This suggests a potential link between EPO, IGF-1, and bone resorption in CKD.130
More recently, the association between low IGF-1 and anemia in hemodialysis patients has been also demonstrated,131 which support the principal role of the IGF-1 in hematocrit homeostasis, being a relevant topic of current research interest. Table 5 shows key studies demonstrating a role of IGF-1 signaling in the development of anemia.
Studies suggesting a key role of IGF-1 deficiency in the development of anemia.
| Study (year) | Study design | Characteristics of participants | Sample size | Type of intervention | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kurtz A., et al. (1985) | In vitro study | Fetal mouse liver cells | n=21 | Administration of FBS, rat or human serum and IGF-1 antiserum | - ↑ erythroid colonies formation in cells treated with IGF-1-containing serum |
| Ureña P., et al. (1992) | Cross-sectional study | Hemodialysis patients with severe SHPT | n=17 | Measurement of serum EPO, IGF-1 and hematocrit values | - Positive association between serum IGF-1 levels and hematocrit |
| Geffriaud-Ricouard C., et al. (1993) | Cross-sectional study | Non-dialysis patients with CKD | n=12 | Analysis of serum IGF-1 levels and anemia parameters | - Inverse association between serum IGF-1 and hematocrit |
| Brox AG., et al. (1998) | Cross-sectional study | Renal transplant recipients with/out erythrocytosis | RT-E n=18RT-nE n=23Control n=15 | Measurement of serum EPO, IGF-1, IGFBP-1, and IGFBP-3 | - ↑ IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-3 levels in CKD patients with erythrocytosis |
| Shih LY., et al. (1999) | Cross-sectional study | ESRD patients with erythrocytosis | n=8 | Measurement of serum EPO, IGF-1 and hematocrit values | - No correlation between serum EPO and hematocrit- ↑ IGF-1 and ↓ EPO serum in ESRD patients with erythrocytosis- ↑ in vitro erythropoietic effects of serum from ESRD patients with erythrocytosis. |
| Małyszko J., et al. (2002) | Interventional study | Hemodialysis, CAPD and renal transplant patients | HD n=79CAPD n=34RT n=46 | rhEPO or no treatment | - ↑ serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels in rhEPO-treated patients- Association of serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 with serum Crosslaps |
| Xu S., et al. (2023) | Cross-sectional study | Hemodialysis patients | n=165 | Measurement of serum IGF-1 and routine biochemistry | - ↓ Serum IGF-1 levels are associated with anemia |
Abbreviations. FBS: fetal bovine serum; SHPT: secondary hyperparathyroidism; ESRD: end stage renal disease; rhEPO: recombinant human erythropoietin; HD: hemodialysis; CAPD: continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis; RT: renal transplant patients; CKD: chronic kidney disease; RT-E: renal transplant recipients with erythrocytosis; RT-nE: renal transplant recipients without erythrocytosis; EPO: erythropoietin; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor 1; IGFBP-1: insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1; IGFBP-3: Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3.
Aerobic exercise, a condition known to prevents renal disease progression in CKD models,132 has been linked to elevated plasma IGF-1 levels, which may partially contribute to the improved renal outcomes.133 Moreover, IGF-1 plays a significant role in the development of CKD-associated sarcopenia. Attenuation of the IGF-1/AKT pathway in muscle satellite cells from CKD mice leads to reduced levels of myogenic markers, resulting in poor muscle regeneration, fibrosis, and the consequent muscle wasting.134
In hemodialysis patients, it has been recently demonstrated that the association between plasma IGF-1 and muscle strength is comparable to that of the myostatin, a well-known inhibitor of muscle growth, and both similarly predict mortality in this population.135 In this regard, the relationship between higher plasma IGF-1, muscle strength and survival could be expected; however, the association with plasma myostatin is surprising and should be related to dialysis conditions, since these patients commonly have higher myostatin levels than general population.136
Similar to other organs, the anabolic response to IGF-1 in skeletal muscle cells is decreased in the context of renal insufficiency.137 This resistance is associated with both, decreased local IGF-1 production and resistance to recombinant IGF-1 administration. Despite of the increased expression of the IGF1R in the skeletal muscle cells of uremic animals, intracellular phosphorylation and downstream signaling activation is attenuated, suggesting additional inhibitory mechanisms. Studies in animal models of renal insufficiency have demonstrated that GH or work overload-induced upregulation of IGF-1 expression in the skeletal muscle is partially reduced in animals with renal insufficiency.138 In the same way, a complementary study has shown that IGF-1, IGF-2 and IGF-1 receptor gene expressions are reduced in skeletal muscle from patients treated with hemodialysis as compare with normal control participant; however, at protein level, the amounts of IGF-1, IGF-2 and TNF-α in the skeletal muscle of hemodialysis patients were found elevated in comparison to the control group,139 which may suggest impaired IGF-1 signaling activation as observed in animal models of renal insufficiency,137 considering the decreased muscle strength in the hemodialysis group. In Table 6 are presented principal studies showing evidences for a role of IGF-1 signaling in sarcopenia.
Evidences for a role of IGF-1 in sarcopenia.
| Study (year) | Study design | Characteristics of participants | Sample size | Type of intervention | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ding H., et al. (1994) | Animal model | Male Sprague-Dawley with ischemic acute renal failure | n=14 per group | rhIGF-1 (50μg/100g; s.c.) three times daily | - ↑ synthesis and ↓ degradation of skeletal muscle protein |
| Ding H., et al. (1996) | Animal model | Male Sprague-Dawley | n=10–35 | 5/6Nx and Sham rats | - ↓ serum and skeletal muscle IGF-1 levels in rats with renal insufficiency.- ↑ IGF-1 receptor expression in skeletal muscle, but impaired IGF-1 signaling in rats with renal failure. |
| Wang H., et al. (2005) | Cross-sectional study | Hemodialysis patients and normal control participants | HD n=51Control n=21 | Skeletal muscle biopsy and IGF-1 expression analysis | - ↓ IGF-1, IGF-2 and IGF-1 receptor mRNA expression in skeletal muscle of HD patients vs controls.- ↑ serum levels of IGF-2 and TNF-α in HD patients vs control. |
| Sun DF., et al. (2006) | Animal model | Male Sprague-Dawley rats | 5/6Nx n=14Sham n=11 | 5/6Nx and Sham rats and unilateral work overload of the plantaris muscle | - ↑ skeletal muscle IGF-1 production in rats subjected to WO.- ↓ skeletal muscle IGF-1 production in response to WO in CKD rats. |
| Zhang L., et al. (2010) | In vitro and in vivo studies with animal models | Primary cultures of muscle cells and 5/6Nx mice (C57/BL6) | n=3–5 | Inducible IGF-1 receptor ablation in estrogen receptor-expressing cells | - IGF-1 increases myogenesis, while inhibition of the IGF-1 signaling impairs satellite cell function. |
| Delanaye P., et al. (2019) | Observational multicenter prospective study | Hemodialysis patients | n=204 | Measurement of serum markers of muscle function an IGF-1 | - Serum IGF-1 levels associate with muscle strength and muscle mass. |
Abbreviations. WO: work overload; HD: hemodialysis; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor 1; rhIGF-1: recombinant human insulin-like growth factor 1; IGF-2: insulin-like growth factor 2; CKD: chronic kidney disease.
IGF-1 exhibits a wide range of functions that are significantly altered in the context of CKD. In spite of the numerous studies on the renal actions of IGF-1, most of them conducted decades ago, emphasizing its potential role on renal regeneration, mineral and bone metabolism and red blood cell homeostasis, as well as its association with patient survival, nowadays its relevant functions are underestimated. Recent findings demonstrating the key role of fatty acid oxidation for renal cell proliferation and compensatory hypertrophy may help to understand the complex mechanisms involved in this process and whether abnormal lipid metabolism in the injured kidney may contribute to IGF-1 resistance. Moreover, the implication of a defective IGF-1 signaling in the development of adynamic bone disease or EPO-resistant anemia in CKD should be considered.
In summary, the wide-ranging actions of IGF-1 make it a compelling molecule for studying various pathological complications associated with renal disease. Understanding the IGF-1 downstream pathways could reveal novel mechanisms underlying multiple conditions, offering the potential for the development innovative therapeutic strategies.
FundingThis work has been funded by the Spanish Society of Nephrology (Grant for Research in Nephrology, 2021) and it is submitted as a benefit for this grant. It is also supported by the I+D+I project in health by the Carlos III Health Institute (ISCIII), call 2021, co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), grant number PI21/01099 and the Personalized Precision Medicine research projects, call 2021, funded by the ISCIII and co-financed by the ERDF, grant number PMP21/00109.
Conflict of interestAll authors declare no conflicts of interest.
JMDT received a Research Grant from the Spanish Society of Nephrology (2021). JDDC maintains a PFIS contract (FI22/00167) funded by the ISCIII and co-financed by the ERDF.