The relationship between diabetes and the development of kidney complications is well known, but the understanding of prediabetes and insulin resistance with impaired kidney function has been scarcely assessed. Various factors could explain this phenomenon, from the lack of standardization in the definitions of prediabetes, to the erratic and inconsistent evidence in large-scale epidemiological and cohort studies. It seems that the pathophysiological pathway of prediabetes could be related to inflammation and neurohormonal hyperactivation, factors present even before the onset of diabetes, which might be the main drivers of glomerular hyperfiltration, albuminuria, and impaired glomerular filtration rate. It is possible that existing treatments for the management of diabetes, as metformin or SGLT2 inhibitors may also be useful in patients with prediabetes with evidence of functional and structural kidney damage. The purpose of this review is to summarize the evidence regarding the relationship between prediabetes (preDM) and the development of CKD.
La relación entre diabetes y el desarrollo de complicaciones renales es bien conocida; sin embargo la asociación entre prediabetes y la resistencia a la insulina con el daño en la función renal apenas ha sido evaluada. Varios factores podrían explicar este fenómeno, desde la falta de estandarización en las definiciones de prediabetes, hasta la errática e inconsistente evidencia en estudios epidemiológicos y de cohortes a gran escala. Parece que las vías fisiopatológicas en la prediabetes podrían estar relacionadas con inflamación y la hiperactivación del sistema neuro-hormonal, factores presentes incluso antes de la aparición de la diabetes, que podrían ser los principales impulsores de la hiperfiltración glomerular, albuminuria y alteración de la tasa de filtración glomerular. Es posible que los tratamientos existentes para el control de la diabetes, como metformina o los inhibidores SGLT2 también pueden ser útiles en pacientes con prediabetes con evidencia de daño renal funcional o estructural. El propósito de esta revisión es resumir la evidencia sobre la relación entre la prediabetes (preDM) y el desarrollo de la ERC.
Prediabetes (preDM) is a condition defined as an intermediate state in the alteration of glucose metabolism that is part of the continuum from normoglycemia to diabetes mellitus (DM).1 The criteria for identifying patients with preDM are based on changes in glucose, measured by fasting plasma glucose (FPG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) or two-hour post-load plasma glucose level (2hBG).1 There is growing data suggesting that preDM may be associated with increased risk of developing cardiovascular (CV) and chronic kidney disease (CKD).2,3 However, it has not been easy to link these conditions, in part due to the absence of systematized criteria for the diagnosis of preDM, which has had an impact on the incidence and prevalence.
Currently, there is sufficient evidence to confirm that, in patients with CKD who are at high risk for presenting a CV event, the identification of modifiable factors is an element of great clinical relevance that will be helpful in decreasing the incidence of complications.4 Therefore, an early diagnosis of patients with preDM that are prone to develop CKD could help in elaborating screening, prevention, and risk mitigation strategies4; this is very similar to what happens in the DM population. The purpose of this review is to summarize the evidence regarding the relationship between preDM and the development of CKD, as well as its correlation with adverse cardiovascular outcomes and mortality, with a brief commentary on available therapeutic strategies.
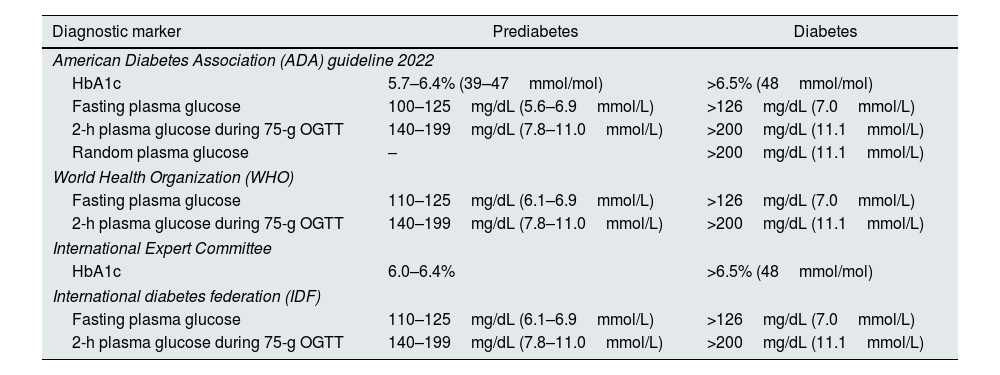
Definition and epidemiology of prediabetesThe American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) differ in the definition of preDM; the ADA uses 100mg/dL of FPG as the lower limit, while the WHO uses a lower limit of 110mg/dL. The lack of standardized criteria makes difficult to establish the real incidence and prevalence of preDM5–7 (see Table 1).
Criteria for the screening and diagnosis of prediabetes and diabetes.
| Diagnostic marker | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|
| American Diabetes Association (ADA) guideline 2022 | ||
| HbA1c | 5.7–6.4% (39–47mmol/mol) | >6.5% (48mmol/mol) |
| Fasting plasma glucose | 100–125mg/dL (5.6–6.9mmol/L) | >126mg/dL (7.0mmol/L) |
| 2-h plasma glucose during 75-g OGTT | 140–199mg/dL (7.8–11.0mmol/L) | >200mg/dL (11.1mmol/L) |
| Random plasma glucose | – | >200mg/dL (11.1mmol/L) |
| World Health Organization (WHO) | ||
| Fasting plasma glucose | 110–125mg/dL (6.1–6.9mmol/L) | >126mg/dL (7.0mmol/L) |
| 2-h plasma glucose during 75-g OGTT | 140–199mg/dL (7.8–11.0mmol/L) | >200mg/dL (11.1mmol/L) |
| International Expert Committee | ||
| HbA1c | 6.0–6.4% | >6.5% (48mmol/mol) |
| International diabetes federation (IDF) | ||
| Fasting plasma glucose | 110–125mg/dL (6.1–6.9mmol/L) | >126mg/dL (7.0mmol/L) |
| 2-h plasma glucose during 75-g OGTT | 140–199mg/dL (7.8–11.0mmol/L) | >200mg/dL (11.1mmol/L) |
PreDM is considered an intermediate stage of progression in the development of DM. In several cohorts, an annual conversion rate of 5–10% has been described, with a similar behavior for reversion to states of normoglycemia.8 A recently published registry from China analyzed the prognosis of different subgroups of patients with preDM and different degrees of CKD, finding a higher risk of progression to DM in those with both diseases, preDM and CKD. With a mean follow-up of 3.1 years, 3615 and 1020 participants with prediabetes developed T2DM and CKD, respectively. Additionally, those patients with highest levels of FPG, 2h PG, and HbA1c had a higher risk of developing CKD (OR, 2.22; 95% CI, 1.80–2.75).9
The prevalence of preDM varies between reports from different countries, ranging from 9% to 40%.5 We surmise that one of the explanations for this variability of prevalence is the definition used. In the 2005–2008 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys registry, a total of 3627 adults were classified according to their condition of preDM status using HbA1c, FPG, or 2hBG, and differences in prevalence could be seen with 14.2% for HbA1c, 26.2% for FPG, and 13.7% for 2hBG.10 In addition, these differences could also be affected by conditions such as age, gender or ethnic group.11 Furthermore, individuals with preDM were found to have an increased risk of all-cause mortality, CV, and microvascular complications,11–15 as is the case with CKD. CKD is a silent disease and recent studies have demonstrated that if assessed properly by the estimated GFR and albuminuria its prevalence is higher than previously reported. As an example, the recent paper published by Cobo Marcos et al. demonstrated that the incidence of CKD in 13 heart failure clinics from Spain is up to 70%,16 indicating that its prevalence maybe higher in some diseases if the KDIGO criteria for diagnosis is implemented.17,18
Prediabetes and cardiovascular riskEvidence is increasing regarding the association between preDM and an increase in comorbidities that increase CV risk. A post hoc analysis of the 2011–2014 NHANES cohort reported that individuals with preDM presented more frequently hypertension (36.6%), dyslipidemia (51.2%), albuminuria (7.7%), or reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (4.6%).19
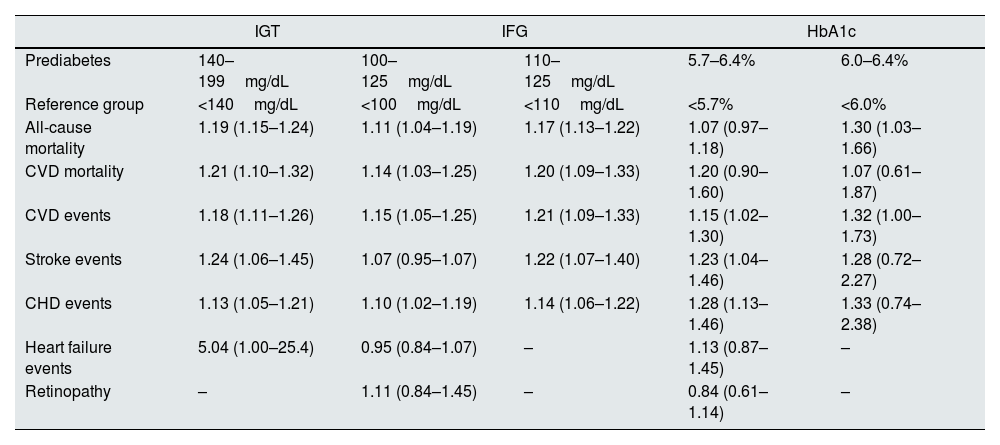
A meta-analysis that included 52 prospective cohort studies, with a total of 1,611,339 individuals followed for 9.5 years, reported that preDM, regardless of definition, was consistently associated with an increase in the following risks when compared with normoglycemia: 25% composite CV event, 17% coronary heart disease, 15% stroke, and 20% all-cause mortality.20 However, this association has not always been reported. In a cohort that included 5791 older adults in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study, after adjustment for other CV risk factors, preDM was not significantly associated with a higher risk of all-cause or CV mortality.21 Therefore, although some studies indicate that preDM condition increase the risk of CV events, its association with increased CV risk and mortality remains unclear and further studies are needed (see Table 2).
Associations between prediabetes and outcomes of interest.
| IGT | IFG | HbA1c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediabetes | 140–199mg/dL | 100–125mg/dL | 110–125mg/dL | 5.7–6.4% | 6.0–6.4% |
| Reference group | <140mg/dL | <100mg/dL | <110mg/dL | <5.7% | <6.0% |
| All-cause mortality | 1.19 (1.15–1.24) | 1.11 (1.04–1.19) | 1.17 (1.13–1.22) | 1.07 (0.97–1.18) | 1.30 (1.03–1.66) |
| CVD mortality | 1.21 (1.10–1.32) | 1.14 (1.03–1.25) | 1.20 (1.09–1.33) | 1.20 (0.90–1.60) | 1.07 (0.61–1.87) |
| CVD events | 1.18 (1.11–1.26) | 1.15 (1.05–1.25) | 1.21 (1.09–1.33) | 1.15 (1.02–1.30) | 1.32 (1.00–1.73) |
| Stroke events | 1.24 (1.06–1.45) | 1.07 (0.95–1.07) | 1.22 (1.07–1.40) | 1.23 (1.04–1.46) | 1.28 (0.72–2.27) |
| CHD events | 1.13 (1.05–1.21) | 1.10 (1.02–1.19) | 1.14 (1.06–1.22) | 1.28 (1.13–1.46) | 1.33 (0.74–2.38) |
| Heart failure events | 5.04 (1.00–25.4) | 0.95 (0.84–1.07) | – | 1.13 (0.87–1.45) | – |
| Retinopathy | – | 1.11 (0.84–1.45) | – | 0.84 (0.61–1.14) | – |
CHD, coronary heart disease; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c; IFG, impaired fasting glucose; IGT, impaired glucose tolerance.
To our knowledge, the mechanisms that promote the development and progression of CKD in people with preDM are unknown. Until the date, scarce number of publications have been focused on the binomials preDM and CKD, and the majority of studies have suggested that the pathohistological pathways involved are, in part, shared with the ones described in people with DM. The existing relationship between preDM and CKD suggests that the deterioration of kidney function does not only depend on a glycemic threshold and that other multiple metabolic pathways of damage are also involved, similar to what occurs with other micro- or macrovascular complications.2 Up to 30% of people with recently diagnosed DM have some degree of kidney damage, which would suggest that, amongst other things, the injury effects of dysglycemia on the kidneys can start very early, before these values reach the glucose threshold of DM criteria.22–24
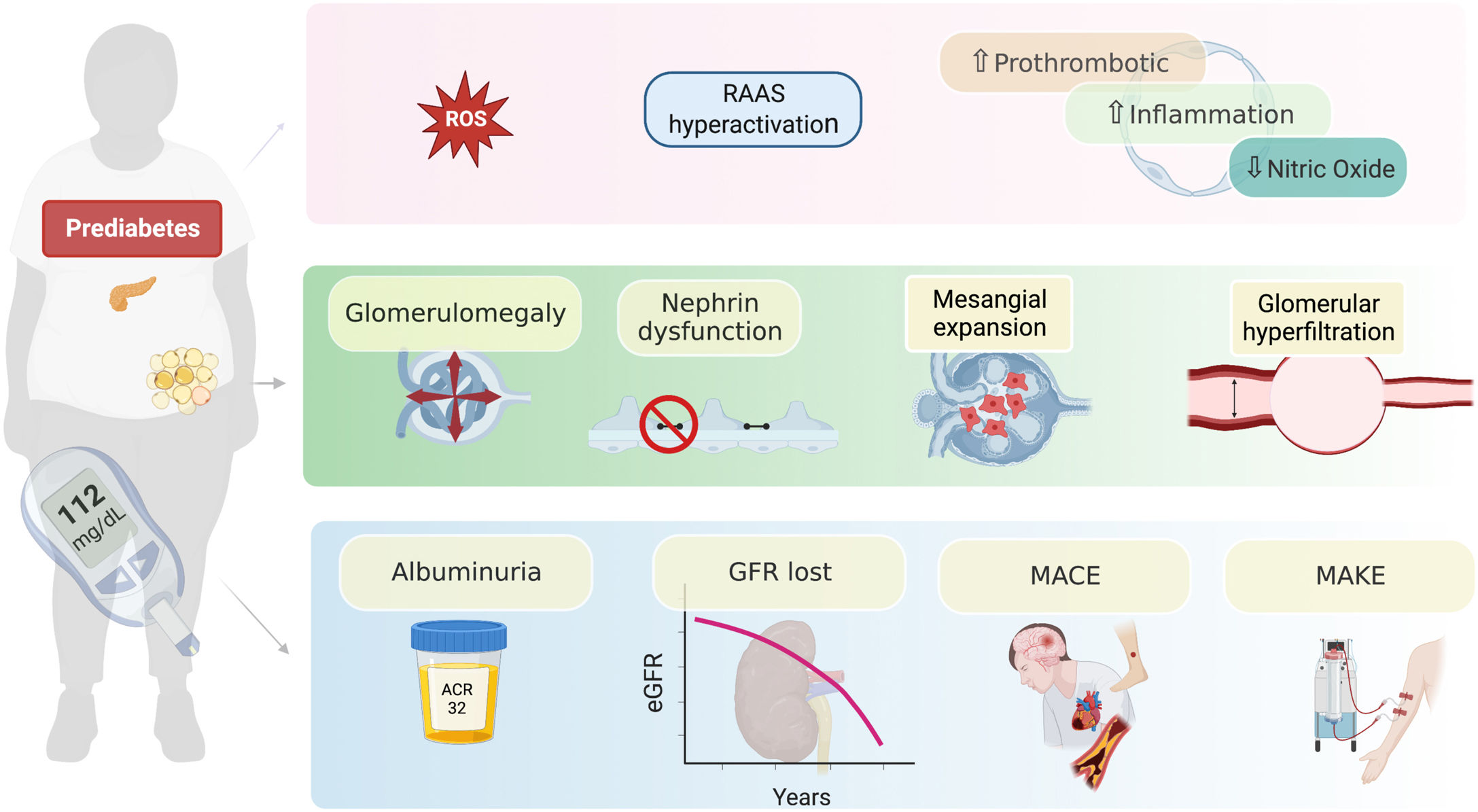
The role of dysglycemia in the development of CKD is not completely understood.25 It could be associated with increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), that promote the accumulation of advanced glycation end products, activate intracellular signaling molecules such as protein kinase C, and stimulate the renin–angiotensin system.26–28 These proposed alterations may favor glomerular hyperfiltration, mesangial expansion, thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, damage to podocytes and generation of glomerular sclerosis, which would favor the development of albuminuria and the progression of CKD.27,28 These alterations have been related to renal functional and structural changes such as glomerulomegaly, expansion of the mesangial matrix, and increased plasma flow, which becomes evident with histological patterns of focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis as it has been seen in obesity-related chronic kidney disease29 (Fig. 1).
Possible mechanisms by which prediabetes can result in kidney dysfunction. Prediabetes generates a state of neurohormonal and inflammatory activation that has functional consequences such as glomerular hyperfiltration, as well as structural injury in different segments of the nephron such as, glomerulomegaly, dysfunction of the permeability barrier and mesangial expansion. The most common clinical expression of these alterations is the appearance of albuminuria, loss of eGFR and the incidence of major cardiorenal events. RAAS: renin-angiotensin aldosterone system; MACE: major adverse cardiovascular events; MAKE: major adverse kidney events; GFR: glomerular filtration rate; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Overweight and obesity are comorbidities that usually concur in people with preDM and both diseases could be synergistic and additive to the increased risk of developing CKD. Even with only a “healthy overweight” (absence of hypertension, DM or dyslipidemia), the risk of developing CKD is increased by 30%.30 In a cohort of 176,420 patients followed for 22 years, the relationship between obesity and CKD was in part ascribed to insulin resistance, in up to 50% of patients.31
Glomerular hyperfiltration has been identified as the first sign of kidney damage in people with DM and preDM.22,32 It has been postulated that hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance occurs due to an increase in the expression of the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) and subsequently, the reabsorption of glucose and insulin favor hyperfiltration. In addition, with the increase of SGLT2 at the proximal tubule, there is an increase in the sodium reabsorption that is detected by macula densa followed by a decrease in the adenosine synthesis that produces afferent glomerular arteriole vasodilation, increasing intraglomerular pressure. Hyperfiltration “per se” has been considered as a maladaptive response of the nephron against alterations associated with dysglycemia (Fig. 1). It has been already demonstrated that glucose alterations promote hemodynamic changes at the single nephron level that include alteration of the renal plasma flow, transmembrane hydraulic pressure gradient, and the ultrafiltration coefficient leading to intraglomerular hypertension. Together with vascular inflammation, it may lead to elevated GFR and microalbuminuria.22
Insulin resistance also causes podocyte dysfunction,33 because insulin signaling is required for the proper functioning and expression of nephrin, which becomes dysfunctional, leading to the appearance of albuminuria. On the other hand, a greater expression of SGLT2 secondary to dysglycemia has been shown, which would lead to greater reabsorption of glucose and sodium, ultimately leading to the macula densa sensing low intratubular sodium values, which would alter tubuloglomerular feedback.34
Prediabetes and alteration of kidney function markersThere is robust evidence supporting how DM impacts the course and progression of CKD. However, the role of preDM is far more uncertain.
Prediabetes and the risk of glomerular hyperfiltrationThe most frequently identified kidney abnormality in patients with preDM has been the development of glomerular hyperfiltration, a finding that should not be surprising when considering the hemodynamic and neurohormonal changes that this pathology generates on the renal arterioles.
The prospective cohort studies RENIS-T6 and RENIS evaluated 1261 patients with preDM defined by FPG and HbA1c according to levels suggested by the preDM ADA and the International Expert Committee (preDM IEC). During follow-up, preDM was associated with an increased risk of glomerular hyperfiltration and high-normal urine to albumin–creatinine ratio, with ORs of 1.95 (95% CI, 1.20–3.17) and 1.83 (95% CI, 1.04–3.22), respectively.35 A subsequent and larger cohort, which included 24,524 participants without diabetes, CKD, glomerular hyperfiltration or antihypertensive treatment at baseline, found that preDM IEC was significantly associated with the risk of incident glomerular hyperfiltration, with an aHR of 1.9 (95% CI, 1.32–2.71), whereas preDM ADA was not, after a follow-up period of 5.3 years. These findings exemplify the inconsistencies over time in the different studies regarding the appearance of glomerular hyperfiltration in patients with preDM, which would even be influenced by the criteria used for its diagnosis,32 in addition to ethnic differences, limited population, and lack of availability in the reference ranges in relation to age, sex and race for eGFR estimation.22 In a Japanese cohort, when analyzing 5003 patients with preDM, the risk of developing glomerular hyperfiltration was approximately 25% higher. Notably, both HbA1c and FPG were considered, both being associated to increased glomerular hyperfiltration.36
Along the same lines, a study investigating the association between preDM and glomerular hyperfiltration in a cohort that included 1031 patients, who were separated into groups of normoglycemia, preDM and DM according to the ADA, and with glomerular hyperfiltration defined as eGFR>95th percentile of age and gender, reported a higher prevalence of glomerular hyperfiltration in patients with preDM as compared with the normoglycemic group, with almost a 3-fold increased risk (OR 2.83, 95% CI 1.24–6.45, p=0.013).22 Glomerular hyperfiltration has been associated with a 5-fold increase in the risk of developing albuminuria35 and with a 61% increase in CV risk,37 a finding that has been confirmed in a meta-analysis of 19 cohort studies.38 This condition could represent an early stage in the course of CKD; therefore, its identification and monitoring could be used to define populations at risk and with potential benefits of an early intervention in the prevention of DM and CKD22(Table 3). One should be aware of the important limitations of measuring hyperfiltration using methods other than radioactive isotopes or iohexol, and this may be considered a major limitation in the results of the studies described where hyperfiltration has been measured using equations or 24h creatinine clearance measurement.39
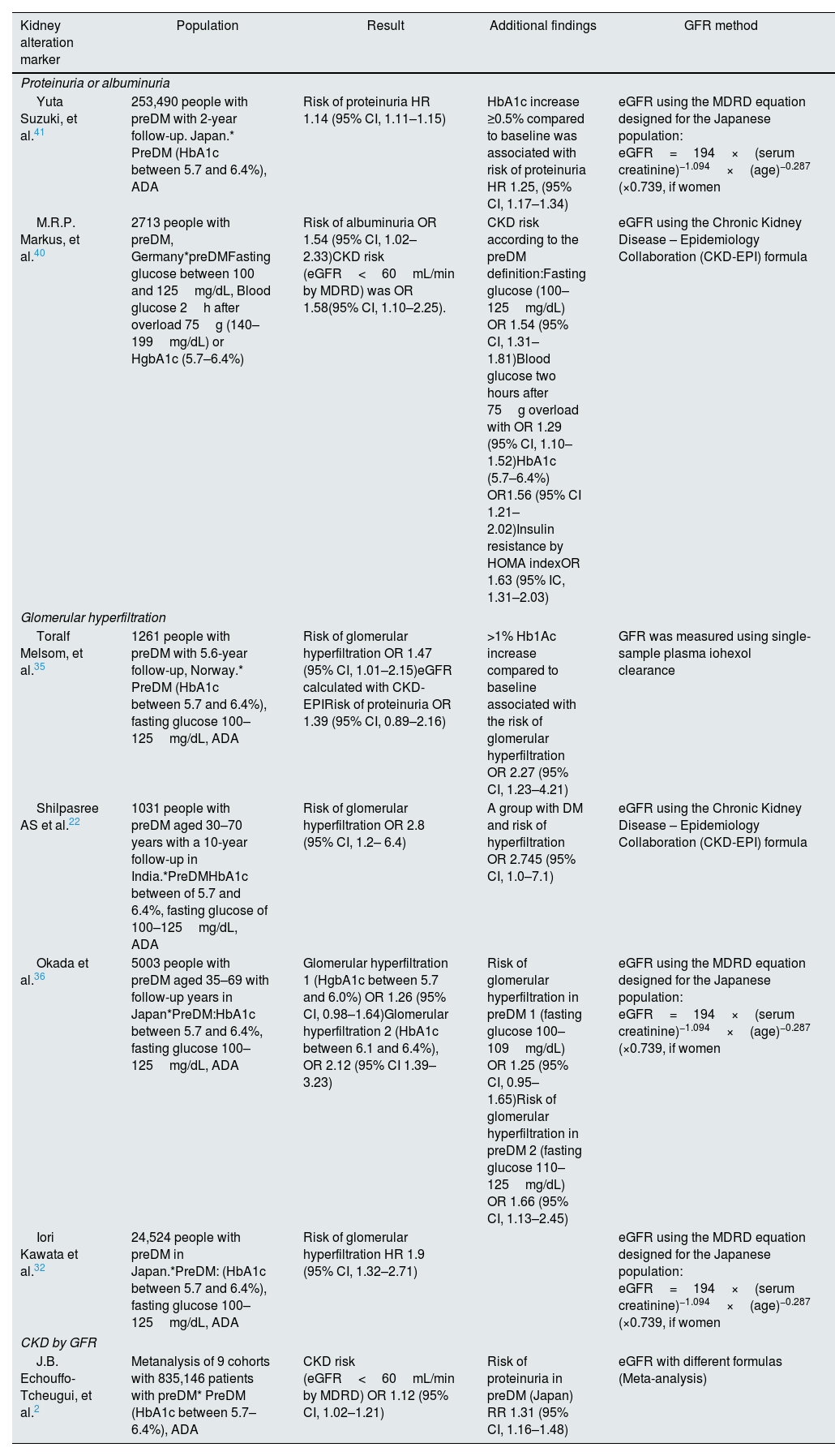
Prediabetes and the association with markers of kidney dysfunction.
| Kidney alteration marker | Population | Result | Additional findings | GFR method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proteinuria or albuminuria | ||||
| Yuta Suzuki, et al.41 | 253,490 people with preDM with 2-year follow-up. Japan.* PreDM (HbA1c between 5.7 and 6.4%), ADA | Risk of proteinuria HR 1.14 (95% CI, 1.11–1.15) | HbA1c increase ≥0.5% compared to baseline was associated with risk of proteinuria HR 1.25, (95% CI, 1.17–1.34) | eGFR using the MDRD equation designed for the Japanese population: eGFR=194×(serum creatinine)−1.094×(age)−0.287 (×0.739, if women |
| M.R.P. Markus, et al.40 | 2713 people with preDM, Germany*preDMFasting glucose between 100 and 125mg/dL, Blood glucose 2h after overload 75g (140–199mg/dL) or HgbA1c (5.7–6.4%) | Risk of albuminuria OR 1.54 (95% CI, 1.02–2.33)CKD risk (eGFR<60mL/min by MDRD) was OR 1.58(95% CI, 1.10–2.25). | CKD risk according to the preDM definition:Fasting glucose (100–125mg/dL) OR 1.54 (95% CI, 1.31–1.81)Blood glucose two hours after 75g overload with OR 1.29 (95% CI, 1.10–1.52)HbA1c (5.7–6.4%) OR1.56 (95% CI 1.21–2.02)Insulin resistance by HOMA indexOR 1.63 (95% IC, 1.31–2.03) | eGFR using the Chronic Kidney Disease – Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) formula |
| Glomerular hyperfiltration | ||||
| Toralf Melsom, et al.35 | 1261 people with preDM with 5.6-year follow-up, Norway.* PreDM (HbA1c between 5.7 and 6.4%), fasting glucose 100–125mg/dL, ADA | Risk of glomerular hyperfiltration OR 1.47 (95% CI, 1.01–2.15)eGFR calculated with CKD-EPIRisk of proteinuria OR 1.39 (95% CI, 0.89–2.16) | >1% Hb1Ac increase compared to baseline associated with the risk of glomerular hyperfiltration OR 2.27 (95% CI, 1.23–4.21) | GFR was measured using single-sample plasma iohexol clearance |
| Shilpasree AS et al.22 | 1031 people with preDM aged 30–70 years with a 10-year follow-up in India.*PreDMHbA1c between of 5.7 and 6.4%, fasting glucose of 100–125mg/dL, ADA | Risk of glomerular hyperfiltration OR 2.8 (95% CI, 1.2– 6.4) | A group with DM and risk of hyperfiltration OR 2.745 (95% CI, 1.0–7.1) | eGFR using the Chronic Kidney Disease – Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) formula |
| Okada et al.36 | 5003 people with preDM aged 35–69 with follow-up years in Japan*PreDM:HbA1c between 5.7 and 6.4%, fasting glucose 100–125mg/dL, ADA | Glomerular hyperfiltration 1 (HgbA1c between 5.7 and 6.0%) OR 1.26 (95% CI, 0.98–1.64)Glomerular hyperfiltration 2 (HbA1c between 6.1 and 6.4%), OR 2.12 (95% CI 1.39–3.23) | Risk of glomerular hyperfiltration in preDM 1 (fasting glucose 100–109mg/dL) OR 1.25 (95% CI, 0.95–1.65)Risk of glomerular hyperfiltration in preDM 2 (fasting glucose 110–125mg/dL) OR 1.66 (95% CI, 1.13–2.45) | eGFR using the MDRD equation designed for the Japanese population: eGFR=194×(serum creatinine)−1.094×(age)−0.287 (×0.739, if women |
| Iori Kawata et al.32 | 24,524 people with preDM in Japan.*PreDM: (HbA1c between 5.7 and 6.4%), fasting glucose 100–125mg/dL, ADA | Risk of glomerular hyperfiltration HR 1.9 (95% CI, 1.32–2.71) | eGFR using the MDRD equation designed for the Japanese population: eGFR=194×(serum creatinine)−1.094×(age)−0.287 (×0.739, if women | |
| CKD by GFR | ||||
| J.B. Echouffo-Tcheugui, et al.2 | Metanalysis of 9 cohorts with 835,146 patients with preDM* PreDM (HbA1c between 5.7–6.4%), ADA | CKD risk (eGFR<60mL/min by MDRD) OR 1.12 (95% CI, 1.02–1.21) | Risk of proteinuria in preDM (Japan) RR 1.31 (95% CI, 1.16–1.48) | eGFR with different formulas (Meta-analysis) |
eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate.
As patients with preDM present profound metabolic alterations, it is fully expected to result in the appearance of albuminuria or proteinuria, either as a marker of kidney dysfunction or associated with systemic inflammation. A correlation has been established between preDM and the development of albuminuria. In a German population, individuals with preDM had an increase of more than 50% of albuminuria and 39% of proteinuria.40 This was in agreement with a Japanese cohort, where an increase in the risk of being diagnosed with proteinuria was appreciated 2 years after the diagnosis of preDM (HR 1.14).41 In a cohort of 405,487 participants followed for 2 years, 1.7% developed proteinuria, 4.7% presented eGFR decline, and only 0.2% showed both. In addition, preDM was independently associated with proteinuria (OR 1.23; 95%, CI 1.17–1.30) but not with eGFR decline.42Table 3 summarizes the studies performed in preDM and its association with markers for kidney dysfunction.
Prediabetes and the risk of chronic kidney disease by eGFRA prospective cohort of 8188 patients found that 41.7% of patients without diabetes had CKD; amongst them, 17.7% had preDM.43 Very similar to the descriptive cross-sectional study that evaluated 91 patients with CKD not associated with DM, the authors found that 41% of the study subjects met the criteria for preDM; amongst them, 18.7% had impaired FPG, 7.7% had impaired glucose tolerance, and 15.4% presented both. These studies are clear examples of the high prevalence of preDM within the population of patients with CKD.44 One explanation of these findings could be that uremia may predispose patients to preDM as previous studies showed that the uremic milieu itself induced molecular changes related to insulin resistance. In addition, urea is at the origin of the generation of cyanate, ammonia and carbamylated compounds, which have all been linked to negative biological changes. Carbamylation is responsible for posttranslational protein modifications that are involved in atherogenesis. In observational clinical studies, these carbamylated compounds were associated with higher CV morbidity and overall mortality.45,46
PreDM has also been linked to an increased risk of developing CKD. In the Chinese REACTION study that included 250,752 patients over 40 years of age, preDM was a risk factor for the development of CKD in men (OR 1.15, 95% CI 1.02–1.32).47 This association has been confirmed in two meta-analyses. The first included 9 cohorts which reported that preDM was associated with an increased risk of developing CKD (1.12, 95% CI 1.02–1.21).2 The second included 16 publications, and found an increased risk of developing CKD of 10–25% and an increased risk of CV complications ranging from 6% to 101%.48 Nevertheless, an analysis of the CRIC study26 observed that preDM was not associated with increased composite renal outcome (defined as either the development of ESRD (renal transplantation or dialysis initiation), a 50% decline in baseline eGFR (CKD-EPI equation) to ≤15mL/min/1.73m2, or doubling of urine protein to creatinine ratio to ≥0.22g/g creatinine) but was related to the onset and progression of proteinuria (aHR 1.23; 95% CI, 1.03–1.47), the development of composite cardiovascular events (aHR 1.38; 95% CI, 1.05–1.82) and only a tendency toward increased all-cause mortality.
One my surmise that the differences regarding the association between preDM and CKD in the different studies may be in part depending on the criteria used for preDM diagnosis (see Table 1). In this sense, a meta-analysis that included 106 prospective studies, comprising nearly 1.85 million people from 27 countries, found that HbA1c and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) in the preDM ranges increased the risk of onset of new CKD, as opposed to the FPG criteria of the ADA and/or WHO, which showed no association.11 The correlation between preDM and CKD, although plausible and rational, has not yet been fully clarified, but preDM appears to be a strong predictor of major CV events and mortality26 (Table 3). In addition, the lack of differences in terms of CKD progression may be also ascribed to the different GFR methods used in the studies, being the ones that measure radioactive isotopes or iohexol the more accurate ones.49
Therapeutic interventions for CKD preventionEarly and accurate identification of people with preDM and DM2 at risk of progressing to CKD is essential to prevent its complications.50 Different studies have been conducted with the intention to reduce the new onset of DM and the subsequent reduction of CV risk associated.1 Management strategies include both pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches.
Amongst the non-pharmacological strategies, lifestyle modifications consisting of increased physical activity, improved diet patterns, smoke cessation, and weight reduction have been proposed. These interventions would be related to a reduction in complications such as diabetic retinopathy, amputation, stroke, and coronary artery disease and a 38% decrease in the risk of CKD.5,51 Some of these strategies have demonstrated to decrease the new-onset of DM, as shown by a meta-analysis that included 16 studies, where lifestyle changes in people with preDM decreased the probability of developing DM after 1 and 3 years (RR 0.46; CI 0.32, 0.66, and RR 0.64; CI 0.53, 0.77].52 Accordingly, another study, the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) Research Group, also demonstrated that lifestyle interventions decreased the risk of progression from preDM to DM even more efficiently than metformin. In this trial, patients assigned to the lifestyle modification group reduced the risk of developing DM by 59% compared with 31% in the metformin group.53
Regarding the relationship between lifestyle changes and CV mortality in preDM, a meta-analysis of 11 clinical trials comparing lifestyle changes with usual care showed that these interventions did not reduce CV or all-cause mortality. Therefore, these strategies may not be sufficient to reduce the burden associated with preDM, making it necessary to consider complementing them with additional interventions.54,55
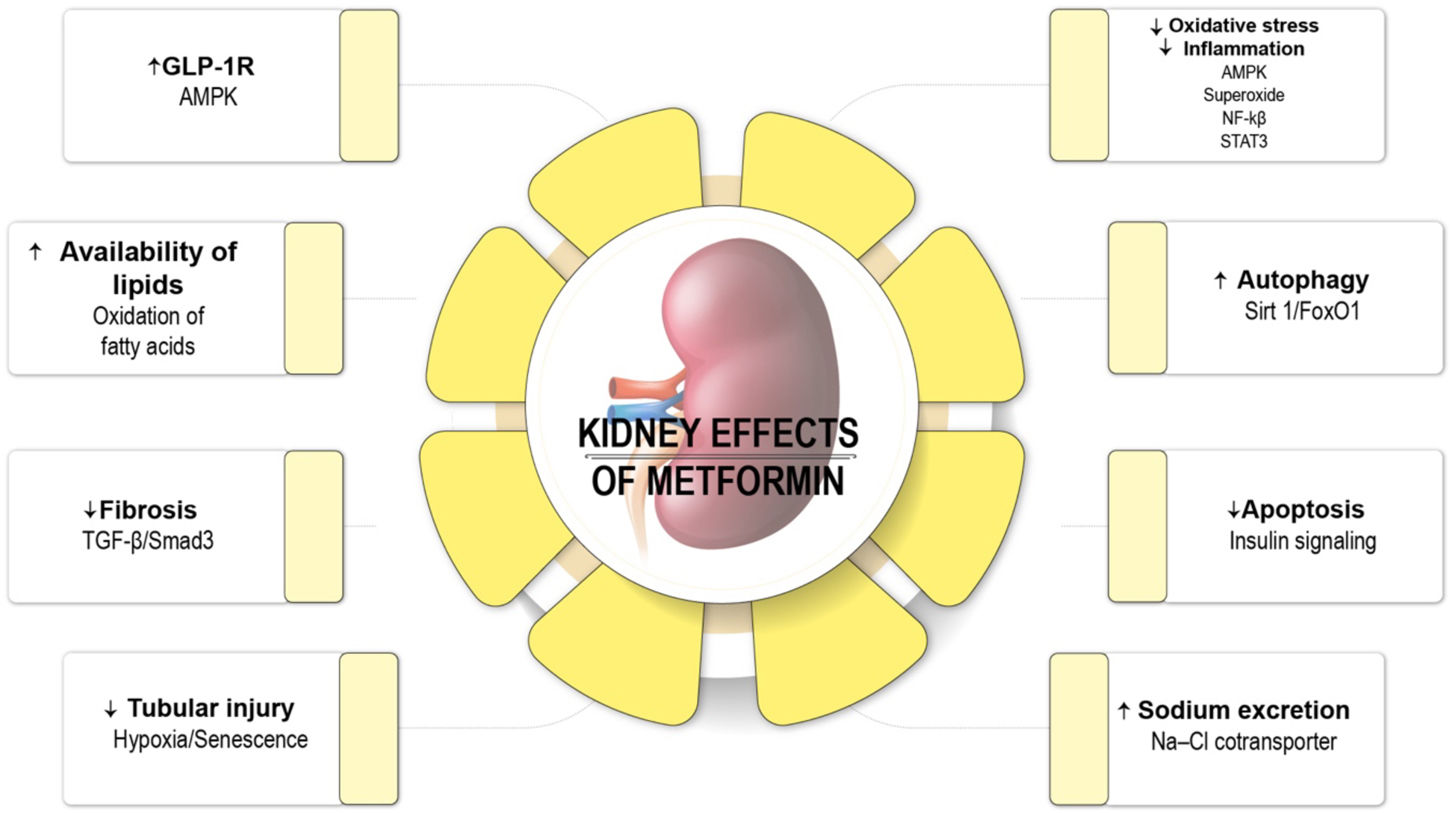
Many pharmacological alternatives are available for treating preDM and DM, including metformin, acarbose, a-glucosidase inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide analog receptor agonists, thiazolidinediones and the anti-obesity drug orlistat.5,56–60 Metformin is the only pharmacological agent recommended by the ADA to prevent DM61 (Fig. 2). During the DPP study, metformin reduced the risk of overt DM by 31% when compared with the placebo.53 In a secondary analysis of the DPP study with 10-year of follow-up, the authors showed a reduction in the onset risk of DM by 18%, demonstrating a sustained long-term benefit.62 In addition, in animal models of kidney injury, metformin has demonstrated renoprotective effects in terms of decreasing inflammation, apoptosis, reactive oxygen stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, epithelial–mesenchymal transition via AMPK activation.29
Nephroprotective effects of metformin. AMPK: AMP kinase; AMP: adenosine monophosphate; NF-κβ: nuclear factor kappa B; GFR-β: transforming growth factor β; GLP-1R: glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor.76
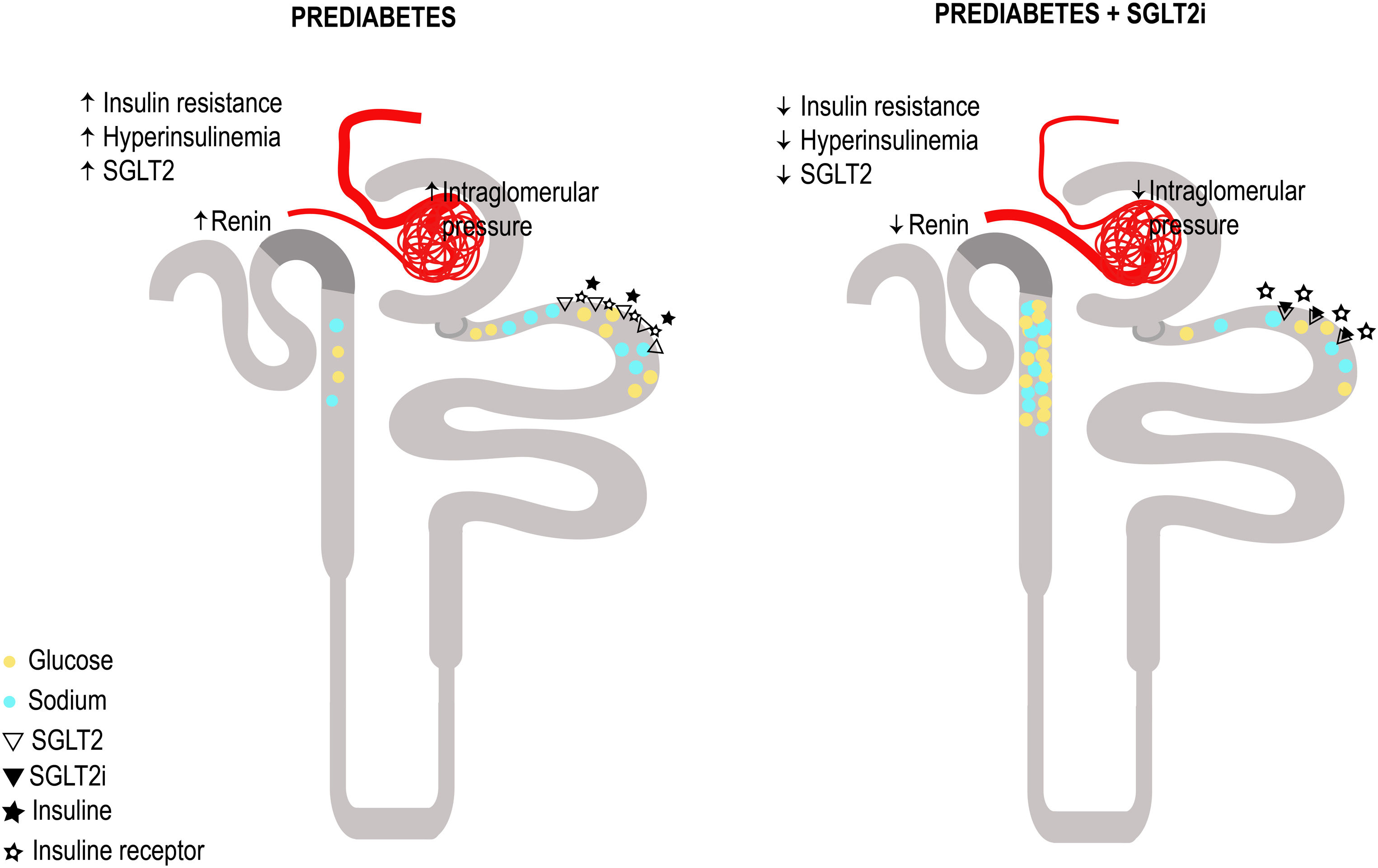
SGLT2i have proven to be innovative drugs in the treatment and reduction of the progression of CKD in both patients with and without DM.63,64 From the perspective of its action mechanism and kidney effects, the idea of the impact of SGLT2i in conditions of glomerular hyperfiltration such as preDM and insulin resistance sounds attractive. By blocking the reabsorption of glucose and sodium, SGLT2i would lead to a decrease in blood glucose levels, which reduces serum insulin levels and thus the negative effects of a hyperinsulinemic state. Additionally, by increasing sodium in the tubular flow of the distal nephron, tubuloglomerular feedback is restored, and two effects are obtained: preglomerular vasoconstriction and a higher sodium concentration in the macula densa which decreases the release of intrarenal renin and therefore the activation of the renin–angiotensin system. A proof of this is the decrease in the angiotensinogen/creatinine urine ratio.65 The suggested mechanisms of glomerular hyperfiltration and the effect of SGLT2i in patients with preDM and kidney disease are summarized in Fig. 3. In agreement, a study with dapagliflozin (an SGLT2i) has demonstrated a renoprotective effect by ameliorating obesity-induced renal inflammation, fibrosis, ER stress, apoptosis and lipid accumulation in rats with preDM.66
Proposed plausible mechanisms of glomerular hyperfiltration and the effect of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition (SGLT2i) in patients with prediabetes and kidney disease. Panel A: Postulated mechanisms for glomerular hyperfiltration in prediabetes and kidney disease. Prediabetes implies insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia, sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) overexpression, increased glucose and sodium reabsorption, decreased intratubular sodium concentration reaching the macula densa, increased renin release and activation of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) cascade, resulting in an increased production of angiotensin II leading to vasoconstriction of the efferent arteriole, decrease in adenosine and this ultimately causes glomerular hyperfiltration. In panel B, the proposed effect of SGLT2i on Prediabetes and kidney disease: Decreased glucose and sodium reabsorption, decreased intrarenal glucotoxicity and the phenomenon of insulin resistance, and lower expression of the SGLT2. With the decrease in the intratubular sodium concentration that reaches the macula densa, there is less renin and Angiotensin II, this will lead to vasodilatation of the efferent arteriole and vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole, due to the restoration of tubuloglomerular feedback, resulting in, improvement of glomerular hyperfiltration.
A secondary analysis of the DAPA-CKD study evaluated 1398 patients without DM and found that dapagliflozin reduced the risk of newly-onset DM by 32% compared with placebo.67 In terms of evaluating the efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin according to baseline glycemic status in 4304 participants of the DAPA-CKD study, which included patients with preDM, dapagliflozin was associated with a 63% reduction in the renal composite primary outcome (sustained decrease in eGFR≥50%, end-stage CKD or renal or CV death), with no increase in adverse effects, such as hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis.63,68
In a meta-analysis that included 4 clinical trials with SGLT2i (DAPA-HF, DAPA-CKD, EMPEROR-Reduced, and EMPEROR-Preserved) and 5655 participants with preDM, the authors analyzed the global and individual effect of SGLT2i on the prevention of new-onset DM, demonstrating a 21% reduction (RR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.68–0.93) and finding no difference between dapagliflozin and empagliflozin (P-for-heterogeneity=0.14), thus favoring the hypothesis of a pharmacological class effect. These results suggest favorable effects of the use of SGLT2i in the prevention of DM in patients with heart failure or CKD in the presence of preDM.63,69–71 However, in this metanalysis the renal endpoints were not assessed in patients with preDM. The mean eGFR (mL/min per 1.73m2) in patients with preDM and DM in the different randomized clinical trials was DAPA-HF (67.1±18.8 vs 65.8±19.5), DAPA-CKD (41.6±11.8 vs 43.1±12.4), EMPEROR-Reduced (61.8±20.7 vs 62.0±21.6), without data available in the EMPEROR-Preserved trial. In addition, there is no data available in terms of proteinuria and albuminuria between the DM and the preDM groups. As obesity and preDM are currently increasing, studies with the new drugs focused on people with preDM with kidney disease as primary endpoint are needed.69
It is interesting to mention that in the studies that included patients with advanced CKD, the impact of SGLT2i on the HbA1 was limited. For that reason, additional renoprotective mechanisms of SGLT2i have been proposed, that may be partially extrapolated to people with preDM.72 Amongst the renoprotective mechanisms that are not directly related to HbA1 control, the improvement of pancreatic β-cell function, hepatic glucose metabolism, upregulation of the membrane-associated protein 17 and muscle insulin sensitivity through amelioration of glucose toxicity. Studies are needed to validate these proposed alternative mechanisms in the setting of preDM.69,73–75
ConclusionsPreDM is a metabolic condition that is part of the DM continuum. Its presence implies profound biological and pathophysiological changes that place the individual at risk of metabolic complications such as the development of DM, as well as increasing the risk of CV events. Although there are multiple data that relates the presence of prediabetes to the incidence of CKD, there are data in several studies that demonstrate the opposite. This maybe in part related to the differences in GFR methods used (measured and estimated). Large-scale clinical studies with measured radioactive isotopes or iohexol are the clue to demonstrate whether there is a causal or real association between PreDM and CKD. This clinical research strategy may help to delay and prevent CKD, especially in patients with preDM. Currently, preDM is not considered an indication for CKD screening, but it remains a big question of whether these patients at risk for CV disease should or not be included as a target risk population for CKD.
FundingM.J.S. is funded by ISCIIII-FEDER and ISCIII, ERA PerMed JTC2022 grant number AC22/00029, Río Hortega CM23/00213, Marató TV3 421/C/2020, Marató TV3 215/C/2021, and RICORS RD21/0005/0016. Enfermedad Glomerular Compleja del Sistema Nacional de Salud (CSUR), enfermedades glomerulares complejas.
Conflict of interestsJ.R.F received honoraria as a speaker and consulting fees from Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Bayer, Sanofi, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Merck and MSD.
M.J.S. received honoraria as a speaker and consulting fees from Novo Nordisk, Jansen, Mundipharma, AstraZeneca, Esteve, Fresenius, Eli Lilly, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Vifor, ICU, Pfizer, Bayer, Travere Therapeutics, GE Healthcare, GSK and Otsuka. She is also one of the former Editors-in-Chief of CKJ. Current editorial board of American Society of Nephrology (ASN) journals.
R.D.A received honoraria as a speaker and consulting fees from Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Bayer and Boehringer-Ingelheim.
The other authors have no conflict of interest.