Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) is a rare inflammatory neoplasia originating from angiogenic vascular endothelial cells.1 Human herpes virus-8 (HHV-8) is considered as a possible cause. KS is often observed in immunocompromised patients such as organ transplant or acquired immunodeficiency syndromes.2 However, although not typical immunosuppression occurs in uraemic patients, various immunologic abnormalities occur.3
In previous reports, KS was described in dialysis patients with different co-morbidities.4,5 However, our report is the first case detected in the extremity where arterial-venous fistula (AVF) created for haemodialysis (HD).
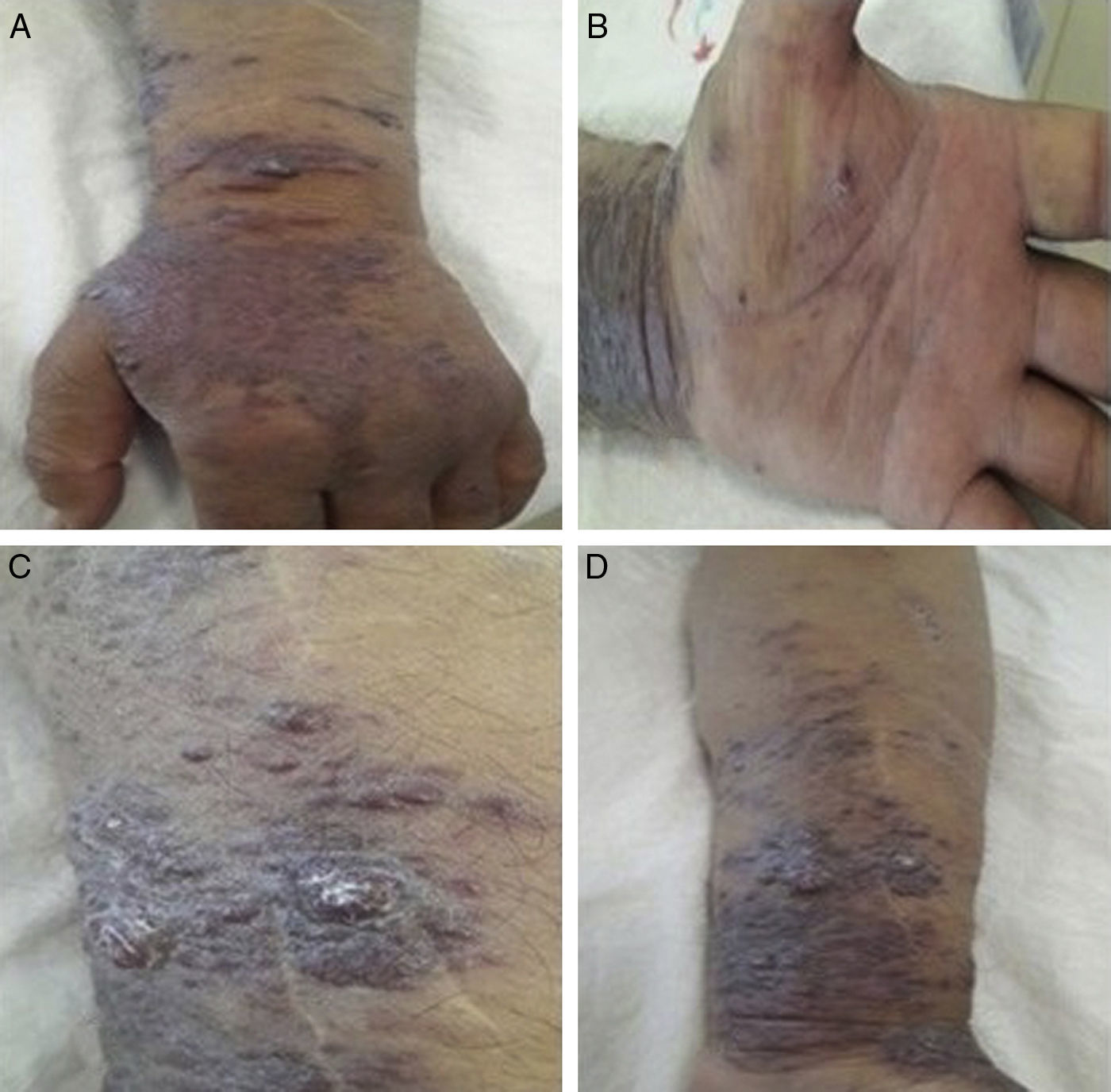
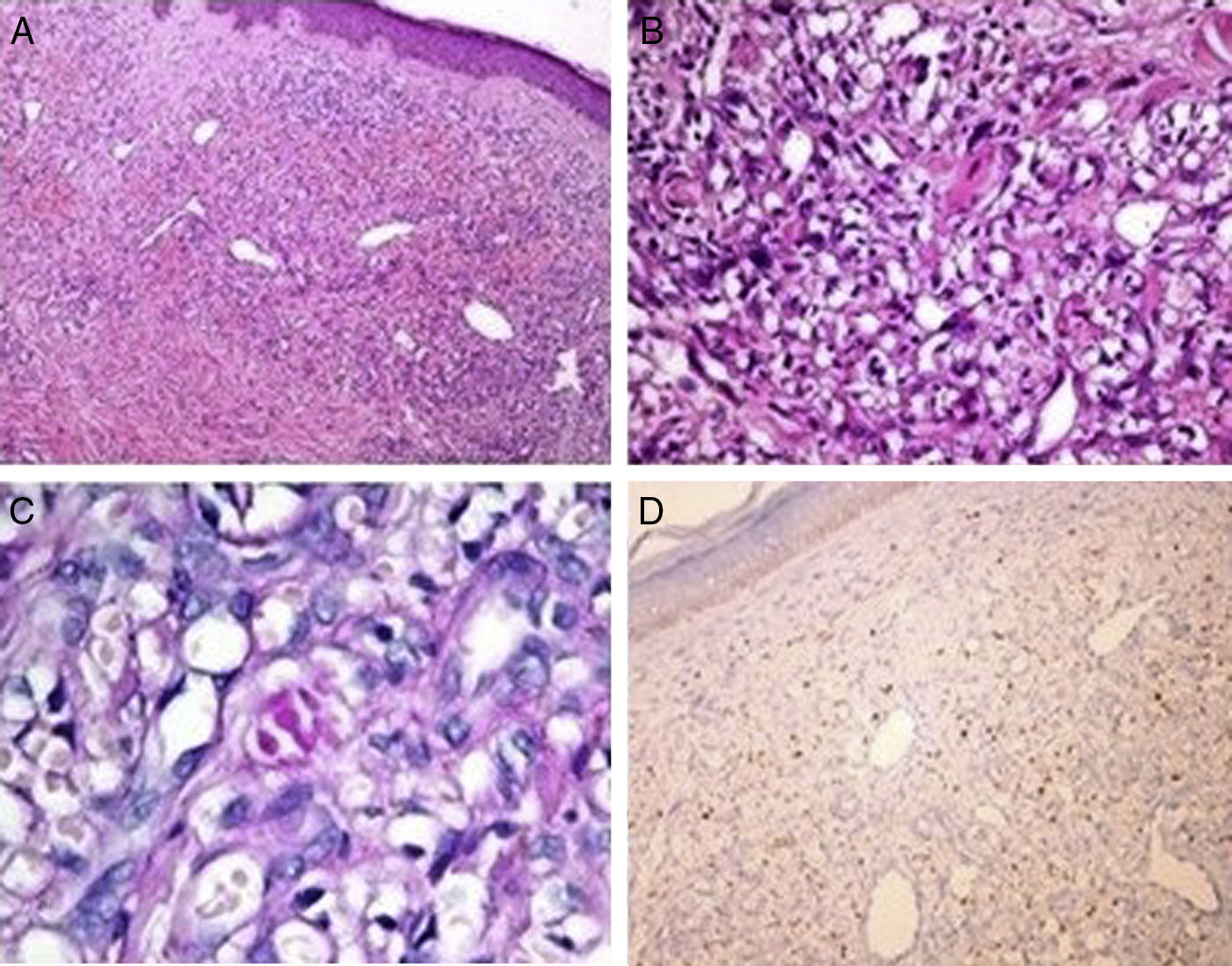
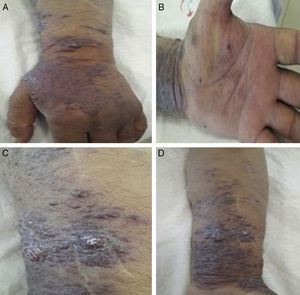
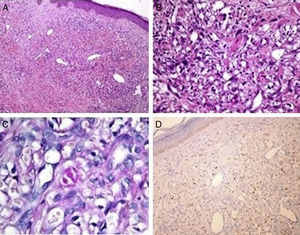
Sixty-nine year's old male patient was on HD treatment for four years. Left arm AVF has been used as vascular access and had swelling for nearly one and half year. The lesions occurred firstly on the dorsal site of the hand. In medical history, there was no significant co-morbidity and history of drug use. In the physical examination deep purple, dark-brown black coloured macular, nodular lesions in the form of plaques starting on the left hand extending proximal forearm and oedema were detected (Fig. 1). In laboratory evaluation, except for blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine levels, all tests were normal. Serological testing of hepatitis B/C and human immune deficiency viruses (HIV) were negative. Complements, immunoglobulins, anti-nuclear antibodies and anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody levels were normal. Chest X-ray and abdominal ultrasonography were normal. In punch biopsy, dilated irregular vascular proliferations surrounding the pre-existing capillaries in the superficial and deep dermis were observed (Fig. 2A). Spindle/oval shaped hyper chromatic atypical cells proliferation forming thin cords around stromal and vascular structures were observed (Fig. 2B). Focally extracellular PAS-positive hyaline globules were noted (Fig. 2C). Immune histochemical examination was positive for HHV-8 (Fig. 2D) and KS was diagnosed.
(A) Dilated irregular vascular channels surround a pre-existing vessel with areas of haemorrhage and variable lymphoplasmacytic infiltration in the dermis (H&E, ×100). (B) Proliferation of spindle-shaped endothelial cells arranged in fascicles in the dermis (H&E, ×400). (C) PAS positive small hyalin globuls are present in the cytoplasm (PAS 1000×). (D) Stromal spindle cells stain with antibody to HHV-8 (immunoperoxidase stain for HHV-8).
This is the first report in the literature in which KS occurred in the extremity where AVF exists. Also KS and HHV-8 co-existence was shown again in CKD.
KS incidence is very low and there are four different variants; classical, African-endemic, immunosuppressive therapy associated and HIV related.6 In our case, lesions localized in the left upper limb, progression rate was slow with no visceral organ involvement. Characteristic features and histopathological findings were consistent with classic KS.1,7
KS is characterized by mutual stimulation of leucocyte and KS cells and cytokine-mediated cell proliferation process. HHV-8 is considered to be a causative agent.5 HHV-8 causes tumour growth by deletion of normal cell cycle and proliferation signal blockage.1 Although the pathogenesis is still unclear, the uraemic toxins accumulated in the CKD may suppress both cellular and humoral immunity.8 Nevertheless, despite the known association between chronic inflammation and KS other malignancies are more prominent in dialysis patients.9 However, chronic inflammation caused by chronic venous stasis (CVS) may contribute to the development of KS in stasis area.10 As in our case, in previously submitted two cases KS is accompanied with venous stasis and this supports this data.4
As a result, in the extremity where AVF exists, HHV-8 and KS existed together. The inflammation and immunosuppression in CKD may contribute to the development and progression of KS.