The increased incidence of carpal tunnel syndrome among hemodialysis patients in the 1980s led to the identification of dialysis-related amyloidosis, attributed to tissue deposits of B2-microglobulin (β2m).1 Dialysis vintage and chronic inflammation were identified as the primary contributors to this disorder. The introduction of high-flux membranes and ultrapure water have drastically reduced the incidence of this disease.2 Currently, there is no specific treatment for this pathology, except for renal transplantation or enhancing β2m clearance through high permeability membranes and the use of convective techniques. Some studies have reported a favorable clinical response with doxycycline use.3 However, despite these therapeutic interventions, the prognosis remains poor.
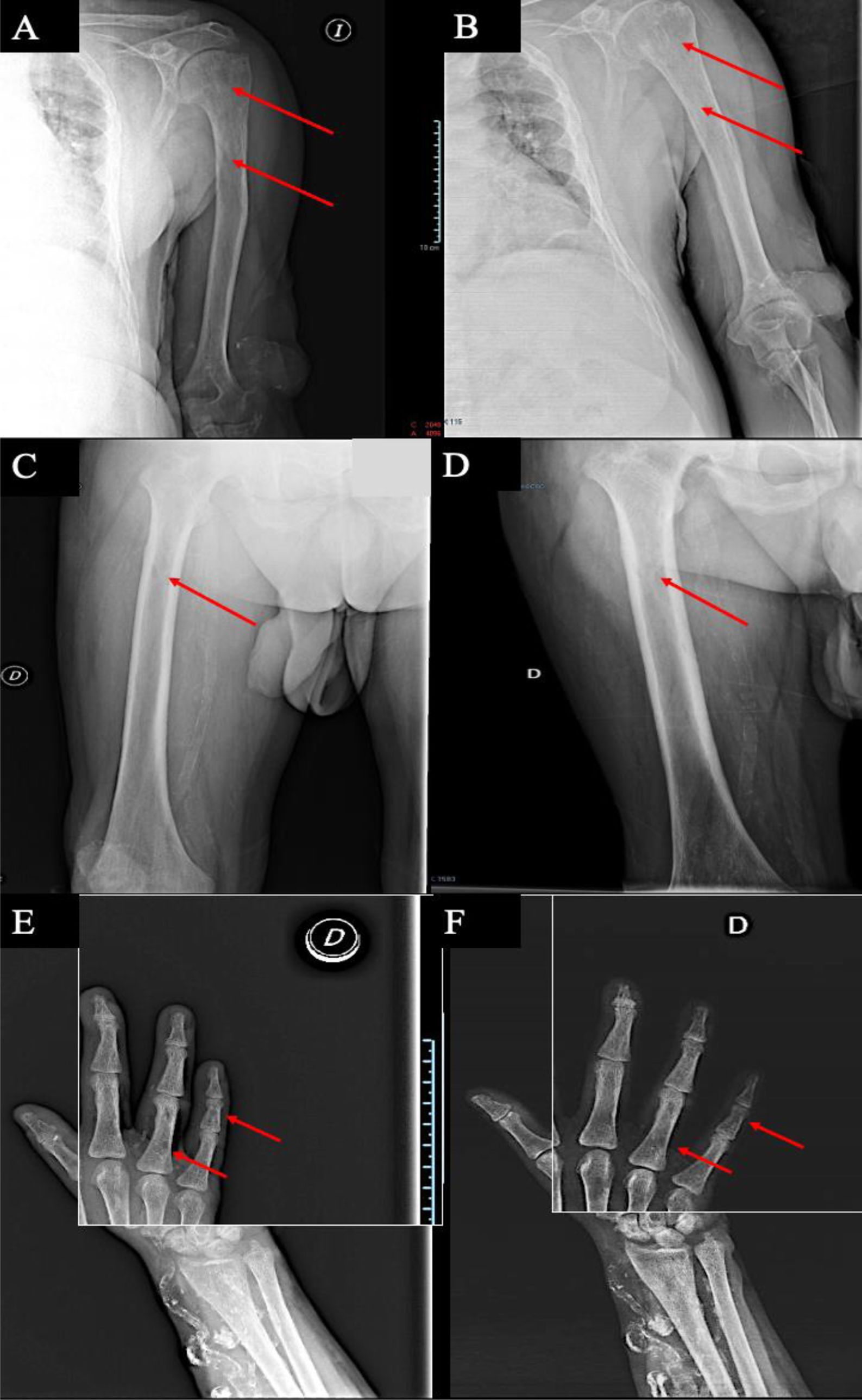
We describe the case of a 52-year-old man with musculoskeletal pain predominantly in the shoulder girdle and both hands that was exacerbated during hemodialysis sessions. The patient had multiple cardiovascular risk factors and chronic kidney disease secondary to vesicoureteral reflux. He had undergone renal transplantation on two occasions, with chronic dysfunction of both grafts. In addition, he had persistent tertiary hyperparathyroidism. Subtotal parathyroidectomy was performed in 2012, followed by resection of a hyperplastic gland in 2021 and thermal ablation of left upper parathyroid hyperplasia in 2022. Yet, PTH increased again. We introduced Etelcalcetide, and after 5 months PTH levels decreased from 831 to 286 pg/mL. He was diagnosed with carpal tunnel syndrome, which required surgical intervention. Considering the characteristics of the pain, the accumulated dialysis vintage of 22 years and the presence of carpal tunnel syndrome, a radiological evaluation was performed, revealing radiolucent lesions in the diaphysis of long bones, accompanied by evidence of subperiosteal resorption (Fig. 1).
Based on these findings, β2m amyloidosis concomitant with a high remodeling metabolic bone disease was suspected. However, histologic diagnosis could not be confirmed due to the unavailability of bone tissue samples. Treatment was initiated with low-dose doxycycline and the frequency of on-line hemodiafiltration sessions was increased to four sessions per week ; the patient refused to undergo additional sessions beyond this. The patient presented a favorable clinical course, with the Visual Analog Scale decline from 9 to 6. One month after the increase in on-line hemodialysis sessions, the pre-dialysis serum concentration of β2m decreased from 41.7 to 32.2 mg/L, a decrease of 22%. After 12 months of intensified post-dilution hemodiafiltration, and 13 months of doxycycline, radiographic examination of the left humerus (Fig. 1A and B), right femur (Fig. 1C and D) and middle phalanx of the fifth finger of the right hand (Fig. 1E and F) revealed improvement and even resolution of bone lesions.
Amyloidosis β2m is caused by accumulation and tissue deposition of β2m fibrils that affect different structures, including the bone.4 The β2m is a component of the major histocompatibility complex I, present in nearly all nucleated cells of the body. End-stage renal disease significantly reduces the renal clearance of β2m. Furthermore, during hemodialysis, contact between the patient's blood and the dialyzer membrane stimulates complement activation and proinflammatory cytokine release, increasing β2m production. In vitro studies indicate that β2m directly activates osteoclasts, promoting bone resorption.5 The prevalence of this disease is unknown because definitive diagnosis requires bone tissue biopsy, which israrely performed. A clinical algorithm has been proposed to improve diagnostic accuracy.6 Major diagnostic criteria are the presence of polyarticular pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, trigger fingers, bone cysts or vertebral lesions. Minor diagnostic criteria are the presence of bone fractures, colitis or other lesions. Renal transplantation is the treatment of choice for reducing circulating β2m levels and improving or resolving the symptoms. Clinical symptoms tipically improve rapidly after transplantation, but may recur if graft failure occurs. Analgesia plays a fundamental role. Surgical approach to lesions by open surgery or arthroscopy has been proposed, with initial clinical improvement but subsequent recurrence of pain.7 For patients who are not candidates for renal transplantation, the primary therapeutic approaches include high-permeability dialysis membranes, increased dialysis dose, and online hemodiafiltration, all of which enhance β2m8 clearance. Doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic, has been shown in vitro to reduce the synthesis of β2m.9 Additionally case series have reported symptomatic improvement with doxycycline, including reduced pain and increased joint range of motion.10 In our case, these combined interventions may have contributed to a decrease in plasma β2m levels.
ConclusionThe enhanced clearance efficacy of the dialysis regimen together with doxycycline treatment modified the course of this patient's disease, with clear improvement of his symptomatology and radiological bone lesions.
FundingThis work was supported by EUTOX, RICORS20240 from the ISCIII and Cost action PerMedik (CA21165). The funders of this study had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, interpretation, writing of the report, or decision to submit for publication.
AcknowledgmentC.R.H is a clinician researcher (B Action Program) from Consejería de Salud-Servicio Andaluz de Salud (Junta de Andalucía). All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.