La hiperuricemia se asocia frecuentemente con gota, enfermedad renal, hipertensión arterial y enfermedad cardiovascular. Todos los pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica que presentan un primer episodio de gota deben ser tratados con fármacos hipouricemiantes para conseguir un nivel basal de ácido úrico menor de 6mg/dl (<5mg/dl si presentan tofos). Los fármacos hipouricemiantes de elección en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica son el alopurinol y el febuxostat. El tratamiento se inicia siempre con dosis bajas, que pueden ir aumentándose progresivamente según la tolerancia. La hiperuricemia asintomática aumenta el riesgo de hipertensión arterial, enfermedad cardiovascular y enfermedad renal, pero, en la actualidad, los ensayos clínicos publicados no avalan el tratamiento en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica.
Hyperuricemia is frequently associated with gout, renal disease, arterial hypertension and high cardiovascular disease. All chronic kidney disease patients with a first episode of gout should be treated with hypouricemic drugs to achieve baseline uric acid levels of less than 6mg/dl (<5mg/dl if tophi are present). The hypouricemic drugs of choice in patients with chronic kidney disease are allopurinol and febuxostat, always starting treatment with low doses that can be progressively increased according to tolerance. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia increases the risk of arterial hypertension, cardiovascular disease and renal disease, but at present published clinical trials do not support the treatment of asymptomatic hyperuricemia in patients with chronic kidney disease.
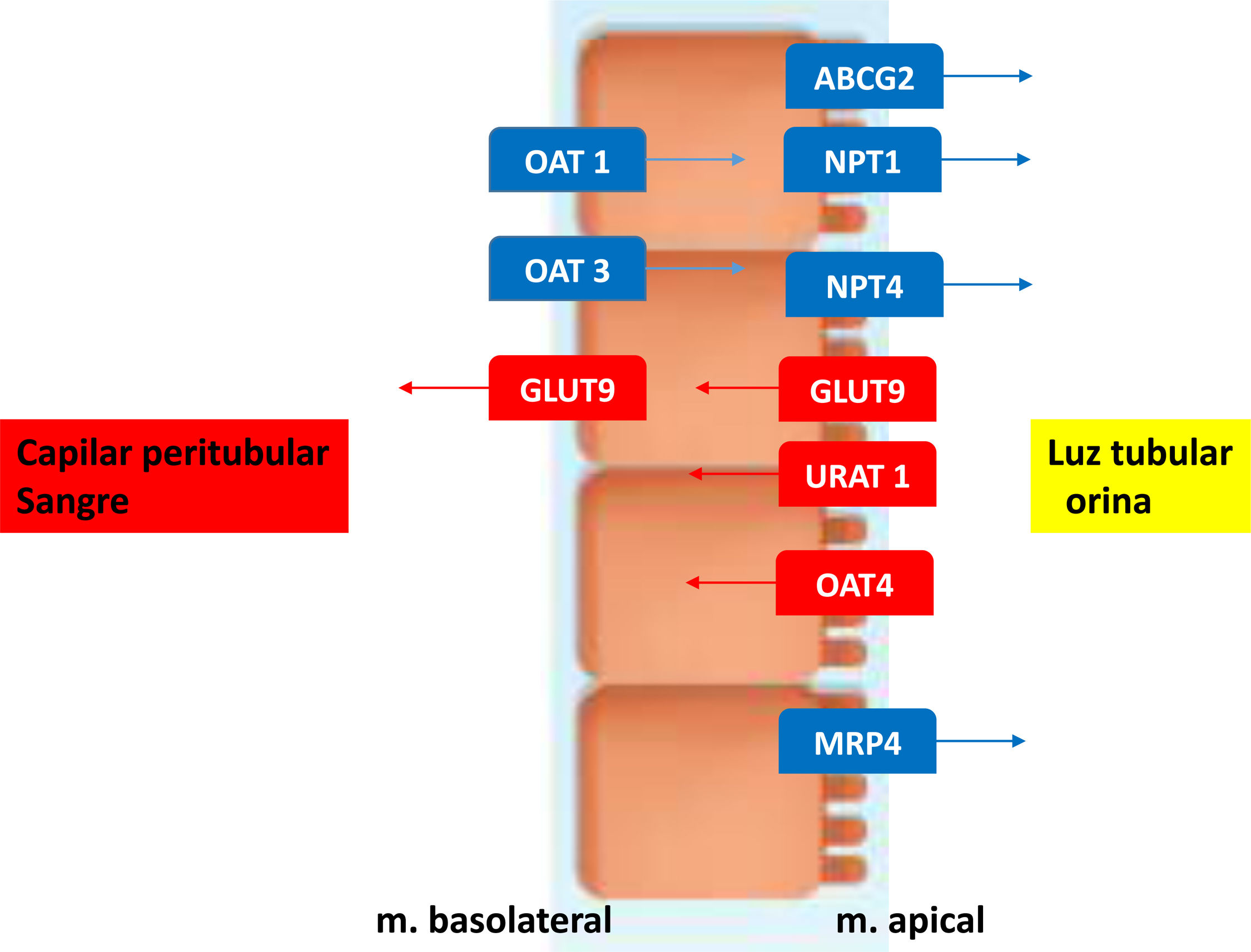
El ácido úrico (AU) es el producto final del metabolismo de las purinas, que es sintetizado principalmente en hígado e intestino, aunque también en tejidos periféricos, como el músculo, endotelio y riñones. El AU se elimina en sus 2/3 partes por el riñón y en 1/3 parte por las heces. Casi todo el AU es filtrado por los glomérulos, por lo que la cantidad de la excreción está regulada por la reabsorción y secreción de este. En el túbulo proximal renal, el transportador de aniones de urato (URAT1) y el transportador de aniones orgánicos 4 (OAT4) localizados en la membrana apical facilitan la reabsorción. El transportador de glucosa 9 (GLUT9) reabsorbe tanto el AU como la glucosa en las células tubulares, se encuentra tanto en el túbulo apical como en la membrana basolateral y media el flujo basolateral de regreso a la circulación. La secreción de AU se produce en el segmento S2 del túbulo proximal a través de transportadores como OAT1 y OAT3, localizados en la membrana basolateral, que facilitan la entrada de urato en los túbulos renales. La proteína de resistencia a múltiples fármacos 4 (MRP4/ABCC4), la proteína de resistencia al cáncer de mama (BCRP/ABCG2) y el transportador de fosfato dependiente de sodio tipo 1 y tipo 4 (NPT1 y NPT4) se localizan en el lado apical y contribuyen al transporte secretor de urato hacia la luz del túbulo para la excreción urinaria (fig. 1). La reabsorción postsecretora se produce en un sitio más distal del túbulo proximal, con aproximadamente un 10% de AU que se excreta en la orina1.
La hiperuricemia se define como el aumento del AU por encima de su punto de solubilidad en agua (6,8mg/dl) y puede aparecer por sobreproducción, disminución en la excreción o ambos procesos.
La hiperuricemia puede dar lugar a un espectro clínico variable: la artritis gotosa aguda debida a la precipitación de cristales de urato monosódico en las articulaciones; la gota tofácea debida a la precipitación de los cristales en piel y tejido celular subcutáneo; la nefrolitiasis úrica; la nefropatía aguda por AU debida a precipitación de cristales intratubulares (síndrome de lisis tumoral) y la nefropatía crónica por AU debida al depósito de cristales de urato en el intersticio medular, con inflamación y fibrosis intersticial consecuentes. Además, existen alteraciones congénitas que afectan al gen de la uromodulina y dan lugar a la nefropatía familiar juvenil hiperuricémica2.
Tratamiento de la hiperuricemia sintomáticaEl tratamiento de la gota se basa en 4principios básicos, independientemente de que el paciente tenga o no enfermedad renal crónica (ERC): a) disminuir el AU, b) administrar profilaxis cuando disminuya el AU de forma aguda, c) tratar el ataque agudo de gota y d) medidas no farmacológicas higiénico-dietéticas. El objetivo del tratamiento es mantener los niveles de AU por debajo de 6mg/dl (5mg/dl en caso de gota tofácea) para disminuir la frecuencia y duración de los ataques de gota. El 90% de las causas de hiperuricemia se deben a una excreción disminuida de AU y solo un 10% a una hiperproducción. En las últimas guías publicadas, se recomienda iniciar el tratamiento con fármacos hipouricemiantes en pacientes que presentan ≥ 2 ataques al año, tofos o nefrolitiasis. Sin embargo, se debe iniciar tratamiento tras el primer ataque de gota en pacientes con ERC con estadio mayor o igual a 23.
En relación con las medidas higiénico-dietéticas, se recomienda a todos los pacientes con gota una dieta pobre en alimentos con alto contenido en purinas, la pérdida de peso, no ingerir alcohol (sobre todo cerveza) y eliminar las bebidas con alto contenido en fructosa (refrescos). La prohibición total de alimentos con alto contenido en purinas no está recomendada, puesto que su impacto implica solo la reducción de 1mg/dl de AU y, por lo tanto, estas medidas nunca pueden sustituir al tratamiento farmacológico4.
Para el tratamiento agudo del ataque de gota en pacientes con ERC los antiinflamatorios no esteroideos están contraindicados y la colchicina debe ser utilizada con precaución, ya que se elimina por el riñón y su vida media puede aumentar 2o 3veces respecto a los pacientes con función renal normal. Además, la colchicina se metaboliza por el citocromo P453A, por lo que hay que tener precaución cuando se usan otros fármacos, como macrólidos (claritromicina), ciclosporina o estatinas. La dosis de colchicina en pacientes con ERC estadio 1 o 2 es inicialmente 1mg, seguidos de 0,5mg una hora más tarde y 0,5mg/12 h durante 3-5 días. Si el filtrado glomerular estimado (FGe) es menor de 60ml/min, la dosis recomendada es como máximo 0,5mg al día. En pacientes con ERC avanzada lo más efectivo es el curso corto de corticoides: 20-30mg de prednisona durante 3-5 días.
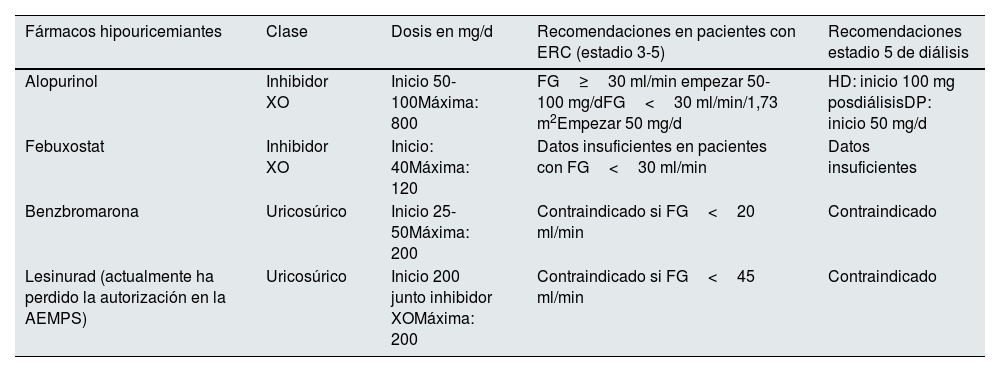
Los fármacos hipouricemiantes disponibles en la actualidad incluyen: a) inhibidores de la xantina-oxidasa (IXO), que bloquean el metabolismo de las purinas; b) uricosúricos, que actúan sobre la principal causa de hiperuricemia, que es la hipoexcreción y 3) tratamiento con uricasa, que oxida el urato a través de una reacción enzimática a alantoina. En la tabla 1 se enumeran los diferentes fármacos hipouricemiantes comercializados en España, su mecanismo de acción y sus dosis en los diferentes estadios de ERC. Aunque la diálisis en principio es uricosúrica y reduce el número de ataques de gota, algunas veces es necesario añadir fármacos hipouricemiantes en pacientes con artropatía gotosa tofácea. Independientemente del hipouricemiante utilizado, existen unas normas comunes en la utilización de todos ellos: a) iniciar siempre el tratamiento asociado con profilaxis; b) empezar con la dosis más baja, con monitorización de los niveles de AU hasta que el objetivo se alcance; c) no retirar el hipouricemiante ni modificar su dosis durante un ataque de gota y 4) en tratamientos nuevos, el fármaco debe ser introducido tras la resolución del ataque agudo de gota.
Fármacos hipouricemiantes y dosis recomendada en pacientes renales
| Fármacos hipouricemiantes | Clase | Dosis en mg/d | Recomendaciones en pacientes con ERC (estadio 3-5) | Recomendaciones estadio 5 de diálisis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alopurinol | Inhibidor XO | Inicio 50-100Máxima: 800 | FG≥30 ml/min empezar 50-100 mg/dFG<30 ml/min/1,73 m2Empezar 50 mg/d | HD: inicio 100 mg posdiálisisDP: inicio 50 mg/d |
| Febuxostat | Inhibidor XO | Inicio: 40Máxima: 120 | Datos insuficientes en pacientes con FG<30 ml/min | Datos insuficientes |
| Benzbromarona | Uricosúrico | Inicio 25-50Máxima: 200 | Contraindicado si FG<20 ml/min | Contraindicado |
| Lesinurad (actualmente ha perdido la autorización en la AEMPS) | Uricosúrico | Inicio 200 junto inhibidor XOMáxima: 200 | Contraindicado si FG<45 ml/min | Contraindicado |
HD: hemodiálisis; DP: diálisis peritoneal; ERC: enfermedad renal crónica; FG: filtrado glomerular; XO: xantino-oxidasa.
La xantino-oxidasa (XO) es una enzima que cataliza la transformación de la hipoxantina en xantina y de xantina en AU. Los IXO son considerados el primer tratamiento de elección en pacientes con gota.
AlopurinolEl alopurinol es un análogo estructural de la hipoxantina, lo que condiciona una inhibición competitiva de la XO. Además, el alopurinol es un sustrato de la XO que cataboliza su trasformación a oxipurinol. Desde hace años, se ha establecido que la dosis de alopurinol se debe ajustar a la función renal para lograr el mismo nivel de oxipurinol que conseguiría una dosis de 300mg en un paciente con función renal normal5. Este ajuste de dosis fue desarrollado para disminuir la aparición del síndrome de hipersensibilidad por alopurinol, que se caracteriza por exantema, eosinofilia, leucocitosis, fiebre, hepatitis, fracaso renal agudo y altas cifras de mortalidad. Sin embargo, con esta estrategia, menos del 50% de los sujetos con ERC alcanzan el objetivo de AU. En estudios6 recientes se ha mostrado que el pico máximo de dosis de alopurinol no se asocia con mayor hipersensibilidad, mientras que sí se asocia con la dosis inicial de alopurinol y con variantes genéticas (HLA B5801). Además, el riesgo es más elevado durante los 6 primeros meses de tratamiento7,8. Así, las últimas recomendaciones, indican que la dosis de alopurinol se puede aumentar en pacientes con ERC. Se debe empezar con una dosis baja de 50mg/día en estadio 4 y 5 (FG<30ml/min) y con una dosis de 100mg/día en el resto de los estadios. El alopurinol se puede utilizar en pacientes en hemodiálisis y en diálisis peritoneal. Empezar con la dosis más baja reduce los números de ataques gota, la hipersensibilidad al alopurinol y otras reacciones alérgicas. La dosis, posteriormente, debe ser titulada e ir aumentando de forma progresiva en 50-100mg/día cada 2-5 semanas hasta conseguir el AU deseado.
FebuxostatFebuxostat es un potente inhibidor no purínico de la XO que ejerce su inhibición sobre las formas oxidada y reducida de la enzima. Los estudios clínicos demuestran mayor eficacia en la reducción de AU con febuxostat, frente a 200-300mg con alopurinol9. Febuxostat puede administrarse en pacientes con ERC con FG menor de 30ml/min/1,73 m2. Sin embargo, los datos sobre su eficacia en estas situaciones son escasos10. En relación con los efectos adversos, se han descritos reacciones cutáneas graves e incluso síndrome de Stevens-Johnson en pacientes que previamente habían tenido reacción a alopurinol, por lo que las agencias europea y canadiense del medicamento han publicado un aviso y no se debería utilizar en pacientes con reacciones graves previas11,12. A diferencia del alopurinol, no se ha encontrado asociación con HLAB 580113.
El estudio CARES (Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in patients with gout and cardiovascular comorbidities)14 incluyó a 6.190 pacientes con gota que fueron aleatorizados a recibir alopurinol o febuxostat. Los pacientes que recibieron febuxostat no tuvieron más episodios cardiovasculares, como infarto agudo de miocardio, arritmias, angina inestable u hospitalización por insuficiencia cardiaca. Sin embargo, la mortalidad cardiovascular fue significativamente mayor en el grupo tratado con febuxostat respecto al grupo tratado con alopurinol (HR 1,34; 1,03-1,73), así como la mortalidad de cualquier causa (HR 1,22; 1,01-1,47). En este ensayo clínico fueron incluidos pacientes con ERC leve (estadio 1-3) y una de sus principales limitaciones fue el porcentaje elevado de abandono por diferentes motivos. Estos resultados originaron un aviso de la FDA (https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-adds-boxed-warning-increased-risk-death-gout-medicine-uloric-febuxostat) y otro de la AEMPS (https://www.aemps.gob.es/informa/notasInformativas/medicamentosUsoHumano/seguridad/2019/NI_MUH_FV-10-2019-febuxostat.htm) en los que se advierte de que el febuxostat aumenta la mortalidad global y cardiovascular, por lo que no debe ser recomendado en pacientes con riesgo cardiovascular. Sin embargo, el estudio CARES, a pesar de haber sido publicado en el NEJM, tiene sus limitaciones. En primer lugar y como se ha reflejado previamente, una tasa de abandono del tratamiento de casi el 50% en el grupo tratado; en segundo lugar, hay hallazgos muy diferentes con relación a los episodios cardiovasculares mortales y no mortales, sin diferencias significativas en los episodios no mortales en el grupo tratado con febuxostat y, por último, sin un grupo placebo, estos resultados no responden a la cuestión de si el tratamiento con febuxostat aumenta el riesgo de episodios fatales o si es el tratamiento con alopurinol el que los disminuye. Además, estudios posteriores no avalan estos resultados. Un estudio observacional del registro de MEDICARE15 en el que se comparan 24.936 pacientes mayores de 65 años con gota tratados con febuxostat vs. alopurinol no encontró mayor riesgo cardiovascular ni mortalidad en pacientes tratados con febuxostat respecto a los tratados con alopurinol. En junio de 2019 se publicó el ensayo clínico FREED (FebuxostatforCerebralanCaRdiorenovasculareventsPrEvEntionStudy), en el que se incluyeron 1.070 pacientes ancianos con hipertensión e hiperuricemia aleatorizados a recibir febuxostat o tratamiento estándar. El tratamiento con febuxostat disminuyó el endpoint compuesto primario (HR 0,750; 0,592-0,950; p=0,017) y no aumentó la mortalidad cardiovascular16. En 2020, se publicaron los resultados del estudio FAST (Febuxostatvs. AllopurinolStreamlinedTrial) en el que se compara el efecto de febuxostat y el de alopurinol en la prevención de episodios cardiovasculares, sin que ninguno de ellos mostrara superioridad sobre el otro y confirmando, una vez más, la seguridad cardiovascular a largo plazo17. Por lo tanto, no hay datos suficientes para apoyar la contraindicación de este fármaco, aunque sí se recomienda su uso con precaución en pacientes con antecedentes de cardiopatía isquémica y de insuficiencia cardiaca18. En España, ambos IXO corresponden a la primera línea de tratamiento de pacientes con gota.
UricosúricosLos uricosúricos aumentan la excreción renal de AU y disminuyen la uricemia. Los uricosúricos actúan a través de proteínas transportadoras que están implicadas en la reabsorción o secreción del AU. Entre estos transportadores se encuentran el URAT1, GLUT9 y transportadores de aniones orgánicos: OAT1, OAT3, OAT4 y OAT10. Actualmente solo la benzbromarona tiene la aprobación de la AEMPS. El probenecid, la sulfinpirazona y el lesinurad no están aprobados en España. Benzbromarona es un uricosúrico potente que puede ser administrado en todos los pacientes con diferentes grados de enfermedad renal. Este fármaco no está aprobado por la FDA ni por algunos países europeos por su hepatotoxicidad19. Lesinurad es un inhibidor de URAT1 y OAT4 que debe ser administrado junto con un IXO. El uso de lesinurad se ha asociado a fracaso renal agudo, está contraindicado en sujetos con FG menor de 30 y no está recomendado con FG20 menor de 45ml/min/1,73 m2. Fue comercializado y aprobado por la AEMPS, pero se retiró del mercado posteriormente por riesgo elevado de fracaso renal agudo. Los uricosúricos deben ser evitados en pacientes con nefrolitiasis y con uricosuria mayor de 800mg/24h.
UricasaLos homínidos no expresamos el gen que codifica la uricasa, enzima que degrada el AU a alantoína, una molécula con mayor solubilidad que el urato y más fácilmente eliminable. La pegloticasa es una uricasa porcina pegilada indicada en pacientes con gota refractaria a IXO. Se administra intravenosamente cada 2semanas durante 6meses. No está aprobada por la EMA, que retiró su autorización en 2016, aunque sí por la FDA. Como es porcina, tiene un alto riesgo de inmunogenicidad y produce reacciones alérgicas infusionales; también se han descrito casos de insuficiencia cardiaca. Recientemente, se ha publicado un estudio en el que se usa metotrexato asociado a pegloticasa para disminuir la inmunogenicidad y favorecer su eficacia21. Puede administrarse en pacientes con cualquier grado de ERC y también en diálisis22.
La rasburicasa está aprobada en España para la prevención del síndrome de lisis tumoral asociada al tratamiento quimioterápico. Tiene una vida media muy corta (unas 20h), a diferencia de la pegloticasa (vida media de unos 7 días).
Antagonistas de interleucina 1βLos cristales de urato monosódico activan el inflamasoma 3 y liberan interleucina 1β. Anakinra es un antagonista del receptor de IL-1 de acción corta que mejora los brotes agudos de gota en el 94% de 551 pacientes, de los cuales el 53% tenía ERC y el 3% estaba en diálisis. La mayoría de estos pacientes habían sido resistentes al tratamiento con corticoides y colchicina. La anakinra no está aprobada por la FDA ni la EMA para el tratamiento de los brotes agudos de gota, pero puede ser usada en modo compasivo en pacientes resistentes a los tratamientos clásicos. Su dosis habitual es de 100mg al día durante 3 a 5 días hasta la reducción del brote, sin tener que modificar la dosis en pacientes con ERC. Su efecto secundario más frecuentes es la neutropenia23.
El canakinumab es un anti-IL-1β monoclonal de acción prolongada que reduce el dolor en el ataque agudo de gota y disminuye los brotes. Está aprobado por la FDA y la EMA en el tratamiento de pacientes con gota y brotes frecuentes refractarios al tratamiento. La dosis es de 150mg s.c., y no se ajusta en pacientes con ERC. Su precio prohibitivo hace que su uso sea muy limitado24.
Fármacos que modifican los niveles de ácido úricoEl uso de diuréticos es la causa más frecuente de hiperuricemia secundaria. Los diuréticos de asa y las tiazidas inhiben los transportadores de aniones orgánicos (OAT1 y OAT3) implicados en la captación activa de AU en los túbulos proximales renales. La hidroclorotiazida también aumenta significativamente la absorción del AU a través del transportador de aniones orgánicos OAT4. Además, los diuréticos inducen la pérdida de sal y agua, lo que provoca una contracción de volumen y estimula la reabsorción de AU. Por el contrario, muchos medicamentos que se utilizan actualmente para tratar diversas enfermedades cardiovasculares tienen un efecto secundario positivo sobre el metabolismo y los niveles de AU. Entre ellos destacamos el fenofibrato25 y la atorvastatina, que aumentan la excreción fraccional de AU26.
Los inhibidores del cotransportador sodio-glucosa tipo 2 (iSGLT2) en los análisis post hoc de los ensayos clínicos DAPA-HF y EMPEROR-reduce se asocian con una disminución de los niveles de AU27,28
Hiperuricemia asintomáticaDesde la perspectiva experimental, se ha mostrado que la hiperuricemia a largo plazo produce cambios hemodinámicos e histológicos en el riñón que pueden conducir al desarrollo de ERC denovo no relacionada con el depósito de cristales de urato en el intersticio medular o a acelerar la progresión de una nefropatía existente. Las principales lesiones renales que produce la hiperuricemia crónica son glomeruloesclerosis, arteriolopatía y fibrosis intersticial29. El mecanismo lesional se debe al desarrollo de una arteriolopatía glomerular que deteriora la respuesta de autorregulación renal y causa hipertensión glomerular30.
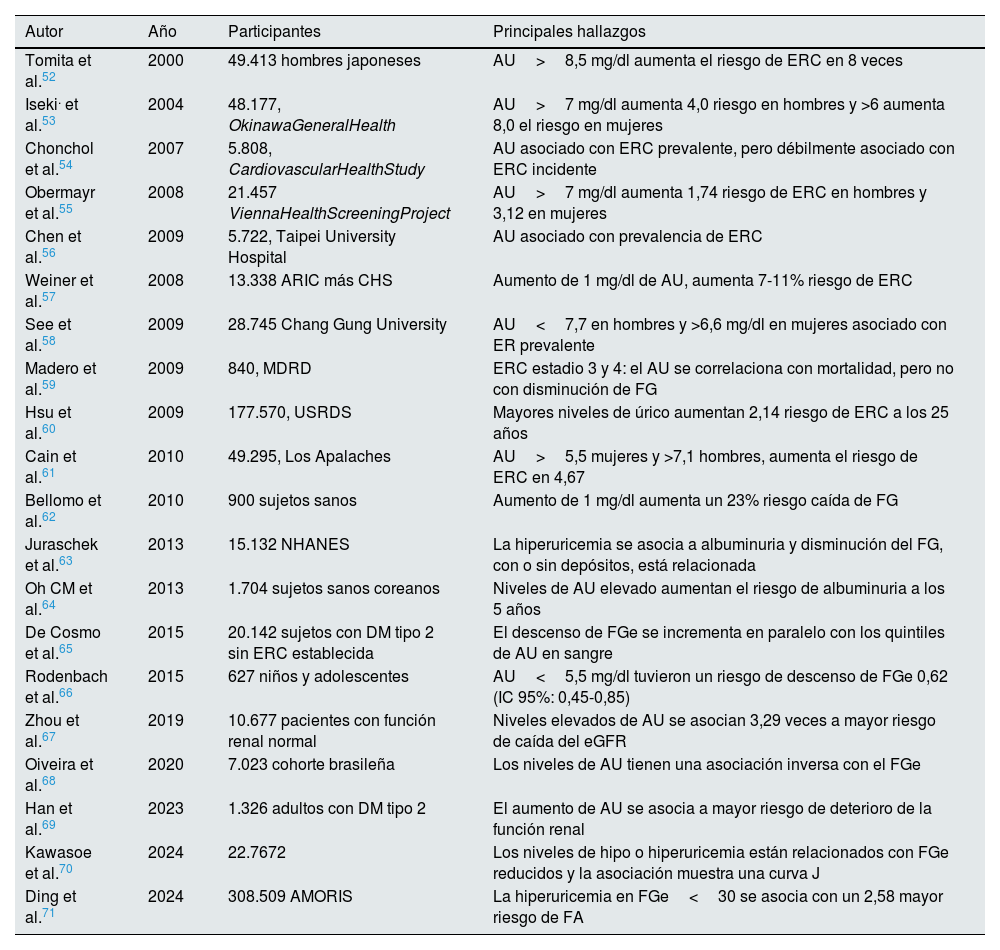
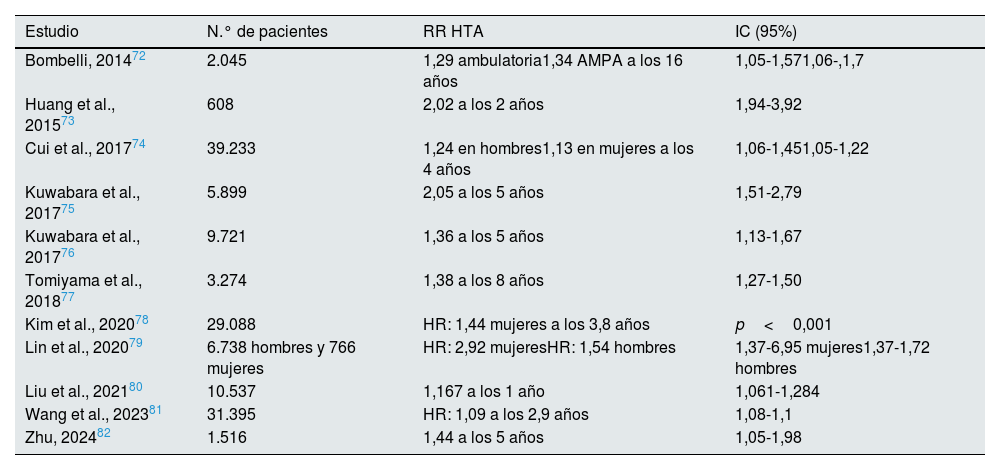
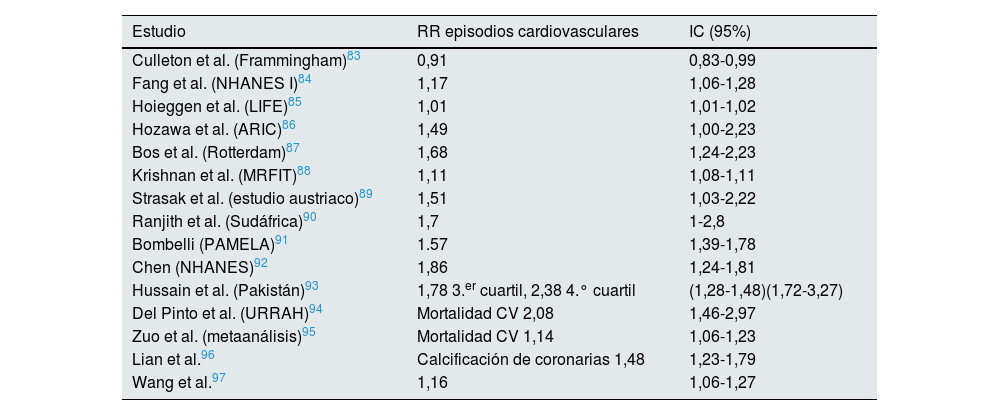
Numerosos estudios observacionales han mostrado asociación entre la hiperuricemia y el aumento de la incidencia de ERC en la población general (tabla 2). Estos resultados se han confirmado en población diabética31-34 y en trasplantados renales35. En los últimos años se ha publicado evidencia suficiente para establecer una asociación de hiperuricemia asintomática con hipertensión arterial y riesgo cardiovascular (tablas 3 y 4). Sin embargo, los estudios de intervención en los que se muestra un beneficio del tratamiento de la hiperuricemia asintomática sobre el riesgo renal y cardiovascular son escasos y controvertidos y sigue existiendo la duda de si la hiperuricemia desempeña un papel causal en la progresión de la ERC o es simplemente un marcador indirecto de enfermedad renal.
Hiperuricemia y riesgo de enfermedad renal
| Autor | Año | Participantes | Principales hallazgos |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tomita et al.52 | 2000 | 49.413 hombres japoneses | AU>8,5 mg/dl aumenta el riesgo de ERC en 8 veces |
| Iseki. et al.53 | 2004 | 48.177, OkinawaGeneralHealth | AU>7 mg/dl aumenta 4,0 riesgo en hombres y >6 aumenta 8,0 el riesgo en mujeres |
| Chonchol et al.54 | 2007 | 5.808, CardiovascularHealthStudy | AU asociado con ERC prevalente, pero débilmente asociado con ERC incidente |
| Obermayr et al.55 | 2008 | 21.457 ViennaHealthScreeningProject | AU>7 mg/dl aumenta 1,74 riesgo de ERC en hombres y 3,12 en mujeres |
| Chen et al.56 | 2009 | 5.722, Taipei University Hospital | AU asociado con prevalencia de ERC |
| Weiner et al.57 | 2008 | 13.338 ARIC más CHS | Aumento de 1 mg/dl de AU, aumenta 7-11% riesgo de ERC |
| See et al.58 | 2009 | 28.745 Chang Gung University | AU<7,7 en hombres y >6,6 mg/dl en mujeres asociado con ER prevalente |
| Madero et al.59 | 2009 | 840, MDRD | ERC estadio 3 y 4: el AU se correlaciona con mortalidad, pero no con disminución de FG |
| Hsu et al.60 | 2009 | 177.570, USRDS | Mayores niveles de úrico aumentan 2,14 riesgo de ERC a los 25 años |
| Cain et al.61 | 2010 | 49.295, Los Apalaches | AU>5,5 mujeres y >7,1 hombres, aumenta el riesgo de ERC en 4,67 |
| Bellomo et al.62 | 2010 | 900 sujetos sanos | Aumento de 1 mg/dl aumenta un 23% riesgo caída de FG |
| Juraschek et al.63 | 2013 | 15.132 NHANES | La hiperuricemia se asocia a albuminuria y disminución del FG, con o sin depósitos, está relacionada |
| Oh CM et al.64 | 2013 | 1.704 sujetos sanos coreanos | Niveles de AU elevado aumentan el riesgo de albuminuria a los 5 años |
| De Cosmo et al.65 | 2015 | 20.142 sujetos con DM tipo 2 sin ERC establecida | El descenso de FGe se incrementa en paralelo con los quintiles de AU en sangre |
| Rodenbach et al.66 | 2015 | 627 niños y adolescentes | AU<5,5 mg/dl tuvieron un riesgo de descenso de FGe 0,62 (IC 95%: 0,45-0,85) |
| Zhou et al.67 | 2019 | 10.677 pacientes con función renal normal | Niveles elevados de AU se asocian 3,29 veces a mayor riesgo de caída del eGFR |
| Oiveira et al.68 | 2020 | 7.023 cohorte brasileña | Los niveles de AU tienen una asociación inversa con el FGe |
| Han et al.69 | 2023 | 1.326 adultos con DM tipo 2 | El aumento de AU se asocia a mayor riesgo de deterioro de la función renal |
| Kawasoe et al.70 | 2024 | 22.7672 | Los niveles de hipo o hiperuricemia están relacionados con FGe reducidos y la asociación muestra una curva J |
| Ding et al.71 | 2024 | 308.509 AMORIS | La hiperuricemia en FGe<30 se asocia con un 2,58 mayor riesgo de FA |
AMORIS: Swedish Apolipoprotein-Related Mortality Risk; ARIC: Atherosclerosis Risk Communities; AU: ácido úrico; CHS: Cardiovascular Health Study; DM: diabetes mellitus; ERC: enfermedad renal crónica; FA: fibrilación auricular; FG: filtrado glomerular; FGe: filtrado glomerular estimado; MDRD: modification of diet of renal disease; NHANES: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; USRDS: United States Renal Data System.
Asociación entre hiperuricemia y riesgo de hipertensión arterial (últimos 10 años)
| Estudio | N.° de pacientes | RR HTA | IC (95%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bombelli, 201472 | 2.045 | 1,29 ambulatoria1,34 AMPA a los 16 años | 1,05-1,571,06-,1,7 |
| Huang et al., 201573 | 608 | 2,02 a los 2 años | 1,94-3,92 |
| Cui et al., 201774 | 39.233 | 1,24 en hombres1,13 en mujeres a los 4 años | 1,06-1,451,05-1,22 |
| Kuwabara et al., 201775 | 5.899 | 2,05 a los 5 años | 1,51-2,79 |
| Kuwabara et al., 201776 | 9.721 | 1,36 a los 5 años | 1,13-1,67 |
| Tomiyama et al., 201877 | 3.274 | 1,38 a los 8 años | 1,27-1,50 |
| Kim et al., 202078 | 29.088 | HR: 1,44 mujeres a los 3,8 años | p<0,001 |
| Lin et al., 202079 | 6.738 hombres y 766 mujeres | HR: 2,92 mujeresHR: 1,54 hombres | 1,37-6,95 mujeres1,37-1,72 hombres |
| Liu et al., 202180 | 10.537 | 1,167 a los 1 año | 1,061-1,284 |
| Wang et al., 202381 | 31.395 | HR: 1,09 a los 2,9 años | 1,08-1,1 |
| Zhu, 202482 | 1.516 | 1,44 a los 5 años | 1,05-1,98 |
AMPA: automedida de presión arterial; HR: hazard ratio; HTA: hipertensión arterial; IC: intervalo de confianza; RR: riesgo relativo.
Asociación entre hiperuricemia y riesgo cardiovascular en población general
| Estudio | RR episodios cardiovasculares | IC (95%) |
|---|---|---|
| Culleton et al. (Frammingham)83 | 0,91 | 0,83-0,99 |
| Fang et al. (NHANES I)84 | 1,17 | 1,06-1,28 |
| Hoieggen et al. (LIFE)85 | 1,01 | 1,01-1,02 |
| Hozawa et al. (ARIC)86 | 1,49 | 1,00-2,23 |
| Bos et al. (Rotterdam)87 | 1,68 | 1,24-2,23 |
| Krishnan et al. (MRFIT)88 | 1,11 | 1,08-1,11 |
| Strasak et al. (estudio austriaco)89 | 1,51 | 1,03-2,22 |
| Ranjith et al. (Sudáfrica)90 | 1,7 | 1-2,8 |
| Bombelli (PAMELA)91 | 1.57 | 1,39-1,78 |
| Chen (NHANES)92 | 1,86 | 1,24-1,81 |
| Hussain et al. (Pakistán)93 | 1,78 3.er cuartil, 2,38 4.° cuartil | (1,28-1,48)(1,72-3,27) |
| Del Pinto et al. (URRAH)94 | Mortalidad CV 2,08 | 1,46-2,97 |
| Zuo et al. (metaanálisis)95 | Mortalidad CV 1,14 | 1,06-1,23 |
| Lian et al.96 | Calcificación de coronarias 1,48 | 1,23-1,79 |
| Wang et al.97 | 1,16 | 1,06-1,27 |
ARIC: Atherosclerosis Risk communities; CV: cardiovascular; IC: intervalo de confianza; LIFE: The Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study; MRFIT: Multiple risk intervention factor trial; NHANES: Encuesta Nacional de Examen de Salud y Nutrición; PAMELA: Pressioni Arteriose Monitorate E Loro Associazioni; URRAH: Uric Acid Right for Heart Health.
En los siguientes apartados resumiremos la evidencia científica publicada respecto al tratamiento con alopurinol y febuxostat en pacientes con hiperuricemia asintomática y su efecto sobre el riesgo renal y cardiovascular.
Tratamiento con alopurinol en pacientes con hiperuricemia asintomáticaHasta junio de 2020 se habían publicado muchos estudios de asociación entre hiperuricemia, riesgo cardiovascular y riesgo renal, pero los trabajos de intervención eran escasos y de tamaño muestral pequeño. Kanbay et al.36 demuestran en 59 sujetos sanos que el tratamiento con alopurinol en pacientes con hiperuricemia asintomática aumenta el FG. Talaat et al.37, en 52 pacientes con ERC estadio 3 y 4, muestran que la retirada de alopurinol empeora la hipertensión arterial y la función renal. Siu et al.38 aleatorizan a 54 pacientes con ERC estadio 3 y 4 a recibir alopurinol a dosis de 100 a 300mg/día durante 12 meses o seguir con su terapia habitual. El tratamiento con alopurinol retrasó la progresión de la enfermedad renal. Kao et al. tratan a 53 pacientes con ERC estadio 3 e hipertrofia ventricular izquierda con 300mg/día de alopurinol, con lo que mejoró la función endotelial y la HVI39. Goicoechea et al. realizaron un estudio en 113 pacientes con ERC40 aleatorizados a continuar con su medicación habitual o a recibir tratamiento con 100mg/día de alopurinol durante una media de 2 años. El alopurinol disminuyó el riesgo de hospitalización, el de episodios cardiovasculares en un 71% y redujo la progresión de la enfermedad renal a los 2años. En un análisis posthoc con un tiempo de seguimiento medio de 84 meses, el tratamiento con alopurinol redujo los episodios renales en un 68% y los cardiovasculares en un 57%41. Posteriormente, Kanbay et al.42 realizaron un estudio en 105 sujetos: 72 hiperuricémicos y 33 sujetos del grupo control normouricémicos con función renal normal. Los 72 pacientes hiperuricémicos fueron aleatorizados a recibir 300mg de alopurinol durante 4 meses o nada. El tratamiento con alopurinol produjo un descenso de AU que se asoció con una mejoría de la función endotelial (p=0,003), del FGe (p=0,001) y la presión arterial sistólica (p=0,001). Shi et al.43, en un estudio abierto aleatorizado y controlado, evaluaron el tratamiento con alopurinol en 40 pacientes con nefropatía IgA y no encontraron un efecto sobre la proteinuria ni sobre la función renal, aunque sí mejoró significativamente la presión arterial.
En junio de 2020, en el NEJM, se publicaron 2ensayos clínicos aleatorizados sobre el tratamiento de la hiperuricemia en pacientes con ERC en estadio 3 y 4 (ensayo CKD-FIX)44 y en pacientes diabéticos de tipo 1 con albuminuria (ensayo PERL)45. En ambas poblaciones, el tratamiento con alopurinol no ofreció beneficios sobre la función renal. Hay que hacer 3 consideraciones sobre estos 2ensayos: 1) en el CKD-FIX se incluyó a pacientes con progresión rápida de la enfermedad renal y proteinuria mientras que, en los pequeños ensayos publicados previamente, el grado de disfunción renal y la albuminuria eran menores; 2) el nivel medio de AU en el ensayo clínico PERL fue de 6,1mg/dl, por lo que un gran porcentaje de pacientes no tenían hiperuricemia y 3) la tasa de abandonos en ambos estudios fue elevada, mayor del 20%. Por lo tanto, todavía quedan muchos interrogantes por resolver, como cuáles son los niveles plasmáticos idóneos de AU, si la mayor reducción del AU aumenta el beneficio o si el efecto beneficioso demostrado por los IXO se debe a su efecto antioxidante o a un efecto endotelial y qué población se beneficiaría más de una reducción de AU: aquella en estadios iniciales de ERC, con nefropatías intersticiales o vasculares y no glomerulares, etc. Respecto al beneficio cardiovascular, un ensayo aleatorizado (el estudio ALL-HEART) no encontró ningún beneficio del uso de alopurinol en pacientes con antecedentes de enfermedad de las arterias coronarias, pero el estudio excluyó a los sujetos con gota y tuvo una alta tasa de abandono (>55%).
Por lo tanto, algunos de estos hallazgos corroborarían que el AU puede ser un factor modificable en la progresión de la ERC, sin datos suficientes para afirmar si el efecto beneficioso del alopurinol se debe a la reducción del AU o al efecto antioxidante que se produce al inhibir el enzima XO. Sin embargo, los 2grandes ensayos clínicos aleatorizados no ofrecen resultados positivos, por lo que no existe evidencia suficiente para indicar el tratamiento con alopurinol en pacientes con hiperuricemia asintomática.
Tratamiento con febuxostat en pacientes con hiperuricemia asintomáticaIgual que con alopurinol, el febuxostat ha mostrado en pequeños ensayos clínicos que también ofrece protección renal. Así, en un estudio experimental realizado en ratas 5/6 nefrectomizadas normo- e hiperuricémicas, el febuxostat protegió del daño renal y previno la proteinuria, conservando la morfología de los vasos y la presión glomerular. Por lo tanto, previene la progresión de la ERC independientemente del efecto sobre el AU46. En el estudio de extensión FOCUS47, 116 pacientes tratados con febuxostat fueron seguidos durante 5 años. Los pacientes con una reducción de AU mayor de 6mg/dl fueron los que experimentaron una caída menor del FG a lo largo del seguimiento. El ensayo clínico FEATHER48 incluyó a 467 pacientes japoneses con ERC en estadio 3 e hiperuricemia asintomática, que fueron aleatorizados a recibir febuxostat o placebo. Los pacientes fueron seguidos durante 108 semanas. El tratamiento con febuxostat no enlenteció la progresión de la enfermedad renal, con una caída de FGe en el grupo placebo mayor que en el grupo febuxostat (−0,47±4,48 vs. 0,23±5,26ml/min/1,73 m2). Sin embargo, el febuxostat sí fue beneficioso en el grupo de pacientes sin proteinuria y con niveles menores de creatinina, lo que parece indicar que es más eficaz en pacientes con menor grado de daño renal. Este estudio tiene como importantes limitaciones que se ha realizado en población japonesa, con poco tiempo de seguimiento (2 años) y en un grupo de pacientes con muy poca progresión de enfermedad renal, ya que la caída de FGe en el grupo placebo fue menor de 1ml/min/año.
Se acaba de publicar un metaanálisis sobre el efecto de reducción de AU con febuxostat en los episodios renales y progresión de la ERC. El metaanálisis incluyó 16 estudios en los que se había tratado a pacientes con hiperuricemia asintomática o gota con febuxostat y los compararon con placebo/alopurinol: demostraron una reducción significativa en episodios renales (duplicación de creatinina o entrada en terapia renal sustitutiva): HR 0,56; IC95%; 0,37-0,84; p=0,006 y una leve disminución en la caída de filtrado glomerular (0,90ml/min/1,73 m2) y en la albuminuria49. Al igual que con alopurinol, en la actualidad no hay evidencias suficientes para recomendar el tratamiento con febuxostat para la protección renal o cardiovascular en pacientes con hiperuricemia asintomática.
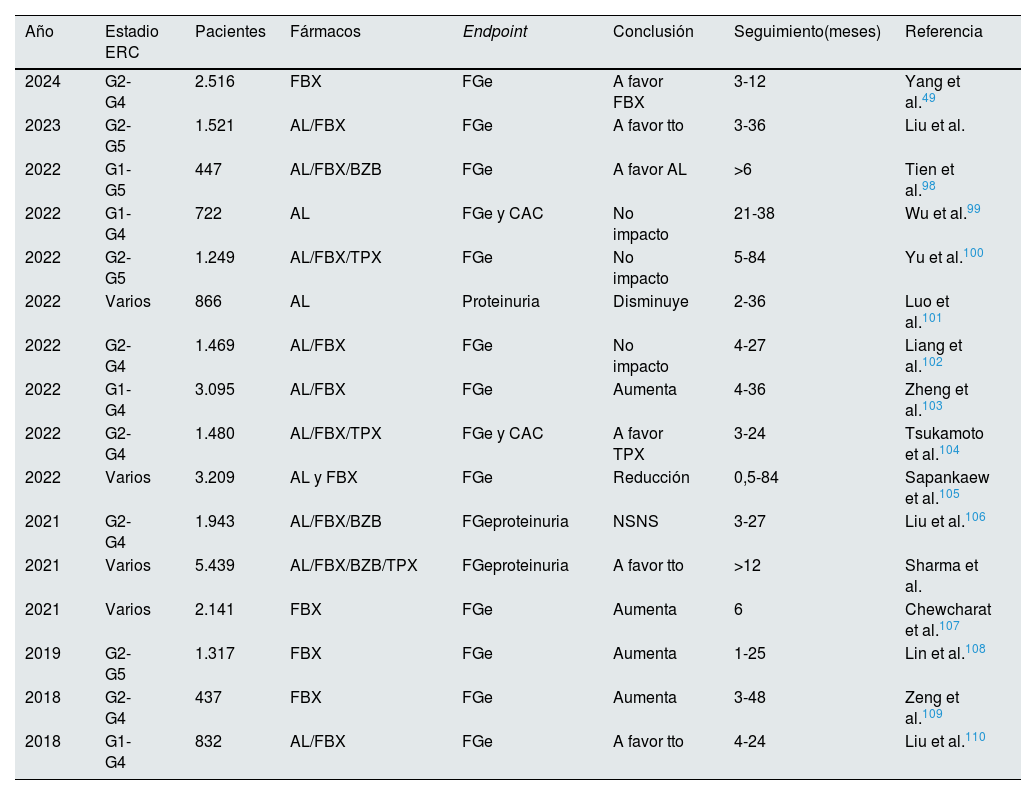
En la tabla 5 resumimos los principales metaanálisis publicados sobre el efecto del tratamiento de la hiperuricemia sobre la progresión renal. Los resultados son controvertidos, con mucha heterogeneidad en la población incluida, tiempos de seguimiento cortos y tomando como endpoint finales el FGe y la proteinuria y no episodios renales graves. Estos datos junto con los 3ensayos clínicos publicados con resultados negativos no avalan el tratamiento con fármacos hipouricemiantes en pacientes con ERC para enlentecer la progresión renal. En estos metaanálisis no se incluyeron ensayos clínicos de pacientes con gota. Recientemente se ha publicado un análisis post hoc del ensayo clínico CARES en el que se muestra un enlentecimiento en la progresión de la ERC (caída de FG de 0,5ml/min/año) en pacientes con gota tratados con alopurinol o febuxostat que mantienen un nivel de AU menor de 6mg/dl durante un tiempo medio de 2,5 años50. Estos datos parecen indicar que, al igual que en las articulaciones, los depósitos de cristales de urato monosódico en el riñón son los causantes de la progresión de la enfermedad renal. Es probable que el foco de la asociación causal entre hiperuricemia y progresión renal no se deba centrar en pacientes con hiperuricemia asintomática, y sí en la población con gota51.
Metaanálisis publicados en los últimos años sobre el efecto de diferentes fármacos hipouricemiantes en la función renal
| Año | Estadio ERC | Pacientes | Fármacos | Endpoint | Conclusión | Seguimiento(meses) | Referencia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | G2-G4 | 2.516 | FBX | FGe | A favor FBX | 3-12 | Yang et al.49 |
| 2023 | G2-G5 | 1.521 | AL/FBX | FGe | A favor tto | 3-36 | Liu et al. |
| 2022 | G1-G5 | 447 | AL/FBX/BZB | FGe | A favor AL | >6 | Tien et al.98 |
| 2022 | G1-G4 | 722 | AL | FGe y CAC | No impacto | 21-38 | Wu et al.99 |
| 2022 | G2-G5 | 1.249 | AL/FBX/TPX | FGe | No impacto | 5-84 | Yu et al.100 |
| 2022 | Varios | 866 | AL | Proteinuria | Disminuye | 2-36 | Luo et al.101 |
| 2022 | G2-G4 | 1.469 | AL/FBX | FGe | No impacto | 4-27 | Liang et al.102 |
| 2022 | G1-G4 | 3.095 | AL/FBX | FGe | Aumenta | 4-36 | Zheng et al.103 |
| 2022 | G2-G4 | 1.480 | AL/FBX/TPX | FGe y CAC | A favor TPX | 3-24 | Tsukamoto et al.104 |
| 2022 | Varios | 3.209 | AL y FBX | FGe | Reducción | 0,5-84 | Sapankaew et al.105 |
| 2021 | G2-G4 | 1.943 | AL/FBX/BZB | FGeproteinuria | NSNS | 3-27 | Liu et al.106 |
| 2021 | Varios | 5.439 | AL/FBX/BZB/TPX | FGeproteinuria | A favor tto | >12 | Sharma et al. |
| 2021 | Varios | 2.141 | FBX | FGe | Aumenta | 6 | Chewcharat et al.107 |
| 2019 | G2-G5 | 1.317 | FBX | FGe | Aumenta | 1-25 | Lin et al.108 |
| 2018 | G2-G4 | 437 | FBX | FGe | Aumenta | 3-48 | Zeng et al.109 |
| 2018 | G1-G4 | 832 | AL/FBX | FGe | A favor tto | 4-24 | Liu et al.110 |
AL: alopurinol; BZB: benzbromarona; CAC: cociente albumina/creatinina en orina; ERC: enfermedad renal crónica; FBX: febuxostat; FGe: filtrado glomerular estimado; TPX: topiroxostat (fármaco hipouricemiante solo comercializado en Japón); tto: cualquier tratamiento hipouricemiante.
- -
La hiperuricemia aumenta el riesgo de desarrollo de hipertensión arterial, enfermedad cardiovascular y enfermedad renal crónica en la población general.
- -
En el tratamiento agudo de la gota los antiinflamatorios no esteroideos están contraindicados y la colchicina hay que usarla con precaución; el tratamiento más efectivo son dosis bajas de corticoides (20-30mg) durante 3-5 días.
- -
Se debe tratar de forma crónica a todos los pacientes con gota y enfermedad renal crónica con el objetivo de conseguir niveles de ácido úrico por debajo de 6mg/dl (5mg/dl en caso de gota tofácea). Es probable que esta estrategia se asocie con un enlentecimiento en la progresión de la enfermedad renal a largo plazo.
- -
En el tratamiento crónico de la hiperuricemia los fármacos de elección son los inhibidores de xantino-oxidasa, empezando siempre con dosis bajas y monitorizando los niveles de ácido úrico hasta que se consiga el objetivo.
- -
Actualmente, con los ensayos clínicos publicados, no existen evidencias para tratar la hiperuricemia asintomática en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica y mejorar su pronóstico renal y cardiovascular.
MG ha recibido honorarios por conferencias por parte de Menarini, RGM no tiene conflicto de intereses.