Kidney biopsy is increasing in patients with diabetes and around 50–60% of patients with diabetes have non-diabetic kidney disease (NDKD). Identifying NDKD is crucial since these patients have a better renal prognosis and survival compared to patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN). The objective of this study is to provide a clinical practice tool for through a predictive model of NDKD.
Material and methodsObservational and multicenter Spanish study of the pathological results of kidney biopsies in patients with diabetes from 2002 to 2014. A logistic regression analysis and the probability of presenting NDKD was calculated using a punctuation score.
ResultsA total of 832 patients with diabetes and renal biopsy were analyzed. An accurate risk-predictive model for NDKD was developed with five top-ranked non-invasive clinical variables (age, serum creatinine, presence of diabetic retinopathy, microhematuria and peripheral vascular disease) obtaining a score for each one allowing for a proper prediction of NDKD.
ConclusionsIn our study, we developed a risk-stratification score to calculate the probability of NDKD. This could be in a next future a useful tool for the clinical indication of renal biopsy in patients with diabetes and kidney disease.
La realización de la biopsia renal está aumentando en los pacientes diabéticos, diagnosticándose entre el 50-60% de nefropatía no-diabética (NND). Este hecho es crucial dado que se ha demostrado una mejor supervivencia y pronóstico renal en la NND comparado con la nefropatía diabética (ND). El objetivo de este estudio es proporcionar una herramienta de práctica clínica a través de un modelo predictivo de NND.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional multicéntrico español del resultado anatomo-patológico en los pacientes con diabetes y biopsia renal desde 2002 hasta el 2014. Un análisis de regresión logística y la probabilidad de presentar NND fue calculada mediante una puntuación obtenida.
ResultadosUn total de 832 pacientes fueron analizados. Se desarrolló un modelo predictivo de riesgo certero para la NND con 5 variables clínicas (edad, creatinina, presencia de retinopatía diabética, microhematuria y enfermedad vascular periférica) obteniendo una puntuación para cada una que permite una predicción adecuada de NND.
ConclusionesEn nuestro estudio, desarrollamos una puntuación de estratificación de riesgo para calcular la probabilidad de NND. Esto podría ser en un futuro próximo una herramienta útil para la indicación clínica de biopsia renal en los pacientes con diabetes y enfermedad renal.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most important health problems worldwide with an increasing prevalence.1 It has been described that one third of patients with DM will develop chronic kidney disease (CKD) in their lifetime.2 CKD in patients with DM is defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60mL/min/1.73m2 and/or urinary albumin/creatinine ratio >300mg/g for six months.3 In some situations, the cause of CKD is not attributable to DM. Thus, the role of kidney biopsy is clue to identify patients affected by non-diabetic kidney disease (NDKD). Classically, the indications of kidney biopsy in patients with diabetes are in clinical situations when the presence of NDKD is suspected such as nephritic syndrome, nephrotic syndrome, nephrotic proteinuria without diabetic retinopathy (DR), microhematuria, signs or symptoms of systemic disease and acute kidney injury.4,5
Over the last few years it has been shown that a significant percentage of patients with DM are diagnosed of NDKD in renal biopsy.6–9 The most frequent NDKD evidenced in patients with diabetes is IgA nephropathy.10–15 However, in the most important studies with larger cohort of biopsied patients with DM, the most frequent NDKD evidenced were acute tubular necrosis,6 membranous nephropathy7 and hypertensive nephroangiosclerosis.8 Identifying NDKD in patients with DM has an important clinical relevance since it has been shown that these patients have a better survival and renal prognosis as compared with DN.8,16,17 Given the importance of identifying patients with NDKD, several previous studies have focused on finding predictors of NDKD.6,8,12,16,18–20 The most frequently reported predictors are: the presence of microhematuria,8,12,18 absence of DR,8,12,16,19,20 and time of evolution of DM6,16,18,20. However, with the purpose of applying these results in a daily clinical practice, only few studies have designed predictive models to determine the probability of NDKD in patients with DM with renal involvement.21–23 Nevertheless, these studies are single-centered with a small sample size. For these reasons, these studies have limited utility in daily clinical practice.21–23
In the current study, we aimed to provide a tool for daily clinical practice through a predictive model of NDKD that will be helpful when considering the indication of renal biopsy.
Materials and methodsPatientsA retrospective multicenter cohort study that has been performed in eighteen nephrology departments from the Spanish Group for the Study of Glomerular diseases (GLOSEN), the Catalonian Group for the Study of Glomerular diseases (GLOMCAT) and the Spanish Group of Diabetic Nephropathy (GEENDIAB). This study was conducted according to STROBE statement for cohort studies.24 Data from consecutive kidney biopsies performed in patients with diabetes from 2002 to 2014 was collected. The indications for kidney biopsy were: nephrotic syndrome, abrupt reduction of eGFR in patients with previous stable renal function, acute kidney injury (AKI), nephrotic proteinuria without DR, signs or symptoms of systemic disease, proteinuria >1g with DM <5 years of evolution, micro/macrohaematuria and nephrotic proteinuria with DM <5 years of evolution. Patient identification was performed by reviewing risk factors for NDKD in diabetes histopathological charts and clinical histories. Patients included in the study correspond to those published in the before mentioned work.8
The Healthcare Ethics Committee of Parc de Salut Mar, Barcelona, Spain approved the study protocol; the approval number is CEIC2013/5468/I.
Clinical and laboratory parametersA total of 112 variables were studied: 58 (51.8%) were clinical and 54 (48.2%) were laboratory data. Patient demographic characteristics were recorded (age, gender and race), along with history of hypertension, dyslipidemia, duration of DM, presence or absence of DR (diagnosed by retinography), diabetic neuropathy, ischaemic heart disease, stroke, peripheral vasculopathy (diagnosed according to the criteria of each center), malignancy and systemic disease. Furthermore, treatment with renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system blockers (RAASB), oral antidiabetics, insulin, statin and aldosterone antagonists were collected. At the time of renal biopsy, weight, height, systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were recorded. Regarding laboratory data, renal function [serum creatinine in milligram per deciliter and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) according to Modification of Diet in Renal Disease-4 in mL/min/1.73m2], urea in milligram per deciliter, basal level of blood glucose levels in milligram per deciliter, proteinuria (g/24h), urine albumin/creatinine ratio in milligram per gram, urine protein-to-creatinine ratio in milligram per gram, microhaematuria, autoimmune markers [antinuclear antibodies (ANAs), anti-double stranded DNA (Anti-DsDNA), anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs), anti-glomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) and cryoglobulins] and viral serology (anti-hepatitis C virus (HCV), surface antigen of the hepatitis B virus (HBsAg) and anti-human immunodeficiency virus (anti-HIV)) were also collected in 683 patients (82%). The indications of renal biopsy were gathered and classified in these categories: nephrotic syndrome, acute kidney injury (AKI), nephrotic proteinuria in patients with diabetes and less than five years of evolution, nephrotic proteinuria without DR, abrupt decrease in eGFR, presence of micro/macrohaematuria, signs or symptoms of systemic disease and proteinuria more than 1g/24h (excluded nephrotic) in patients with diabetes and less than five years of evolution were also recorded. Renal biopsies were reviewed for this study at every participating center. The morphological characteristics found in the biopsy (number of glomeruli, diffuse or nodular mesangial expansion, global or segmental sclerosis, percentage of glomerulosclerosis and increase of basement glomerular membrane) and the final diagnoses were collected. The diagnosis “unclassified” was for kidney biopsies with an insufficient number of glomeruli to interpret the histological findings.
Based on the diagnoses, the renal biopsies were classified into these categories: isolated DN, NDKD or DN-superimposed NDKD (DN plus NDKD). Finally, the follow-up was assessed at first, third, fifth and tenth year post-kidney biopsy. The variables collected were renal function (serum creatinine level and eGFR), urea concentration, baseline level of blood glucose, 24-h proteinuria, urine albumin/creatinine ratio, urine protein/creatinine ratio, need for renal replacement therapy (RRT) and death.
Statistical analysisStatistical analysis was performed using IBM's SPSS Statistics version 20.0 and STATA. The quantitative variables are expressed in mean and standard deviation and the qualitative variables in percentages. The distribution of variables was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Univariate comparisons between groups were performed using a Chi-squared test for categorical variables and one-way analysis of variance test for comparing means. We performed a multivariate analysis using binary logistic regression to identify potential predictors of DN vs. NDKD (dependent variable). DN is given the value 0 and the NDKD is given the value 1. The variables for the multivariate analysis have been selected with an automatic “stepwise” method, the LASSO method (“Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator”, Tibshirani, 1996). This method, unlike stepwise methods, penalized some coefficients to 0 from all to none using a lambda parameter that was maximized. As lambda increased, the variables that were 0 increased. The method automatically selected the best lambda value and the number of variables that best fit the result. The best cut point based on Youden index (Sensitivity+Specificity−1). To use the model in a predictive way, a nomogram was represented that allowed calculating the probability of NDKD using OR obtained in multivariate analysis for each variable included in model. After fitting the model, we evaluated the performance of the model. Three issues were evaluated: (a) Discrimination: The AUC, equivalent to the C-statistic for logistic regression model and their 95% confidence interval will be calculated. It can be interpreted as the probability of correct classification of each pair of subjects with and without NDKD. A value near to 1 means a good classifier. (b) Calibration: It refers to the agreement between observed and predicted endpoints. A graph will be presented and the Hosmer_Lemeshow goodness of fit test will be calculated. (c) Clinical usefulness: The decision-curve analysis provides information of the net true-positive classification rate by using a model over a range of thresholds.
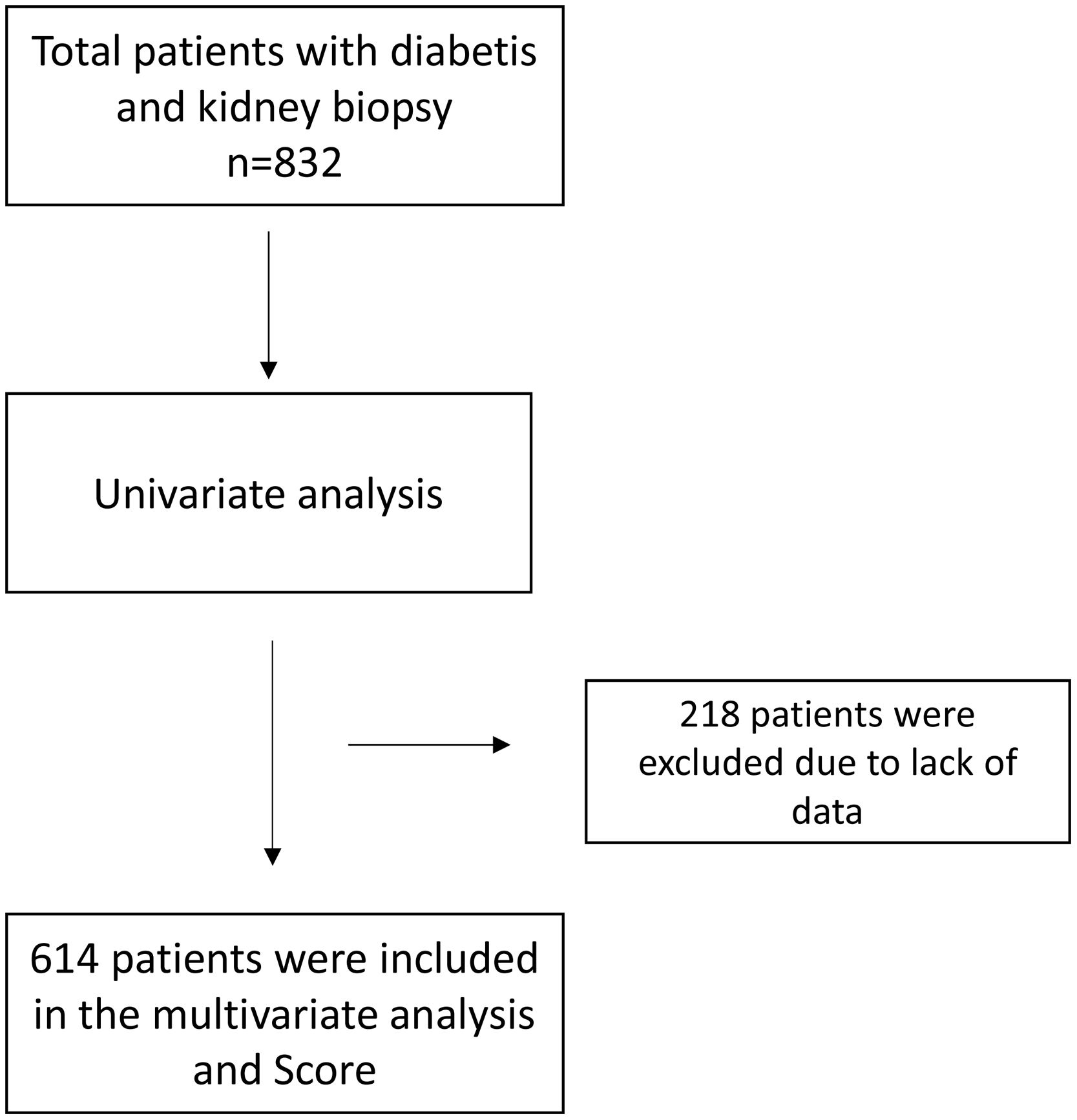
ResultsCharacteristics of populationA total of 832 patients with diabetes and consecutive kidney biopsy were included in this study (Fig. 1). The most relevant clinical and analytical data at the time of renal biopsy has been previously published8 (see supplementary Table 1). The histological diagnosis of renal biopsy has also been previously reported.8 A total of 26 cases (3.1%) were “unclassified”. The indications for renal biopsy were: nephrotic syndrome (n=261, 31.4%), abrupt reduction of eGFR in patient with stable CKD (n=173, 20.8%), AKI in patients with previous normal renal function (n=118, 14.2%), nephrotic proteinuria without DR (n=89, 10.7%), signs or symptoms of systemic disease (n=53, 6.4%), proteinuria >1g with DM <5 years of evolution (n=46, 5.5%), micro/macrohaematuria (n=42, 5%) and nephrotic proteinuria with DM <5 years of evolution (n=18, 2.2%).8
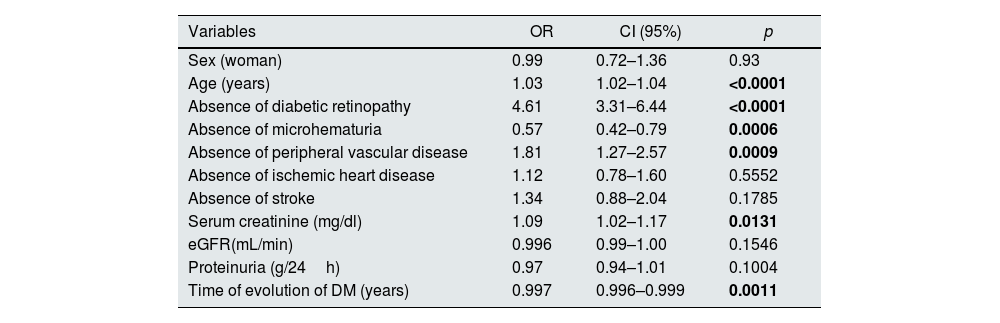
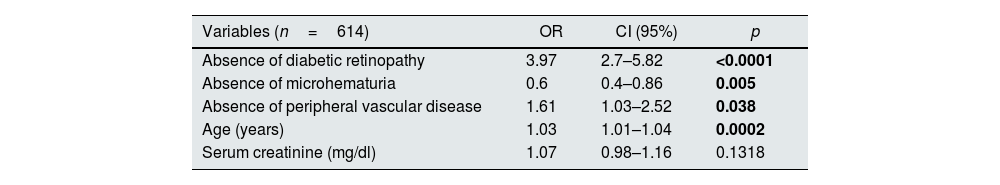
Predictive model for non-diabetic kidney diseaseAn univariate analysis was performed to study the differences between histological groups including the next variables: sex, age, presence of DR, ischemic heart disease, peripheral vascular disease, stroke, serum creatinine level, eGFR, proteinuria, presence of microhematuria and time of evolution of DM (Table 1). Patients with DN and NDKD were included in NDKD group to perform this analysis, because this group differs from DN isolated with NDKD lesions in kidney biopsy. With these results and with the purpose of identifying the predictive factors for NDKD, a multivariate binary logistic regression analysis was performed. The variable “time of evolution of DM” was excluded from analysis for missing data. The adjustment of the coefficients for the variables selected according to the Lasso model and readjusted alone were performed (Table 2).
Univariate analysis for predictive factor for NDKD on kidney biopsy in patients with diabetes.
| Variables | OR | CI (95%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (woman) | 0.99 | 0.72–1.36 | 0.93 |
| Age (years) | 1.03 | 1.02–1.04 | <0.0001 |
| Absence of diabetic retinopathy | 4.61 | 3.31–6.44 | <0.0001 |
| Absence of microhematuria | 0.57 | 0.42–0.79 | 0.0006 |
| Absence of peripheral vascular disease | 1.81 | 1.27–2.57 | 0.0009 |
| Absence of ischemic heart disease | 1.12 | 0.78–1.60 | 0.5552 |
| Absence of stroke | 1.34 | 0.88–2.04 | 0.1785 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.09 | 1.02–1.17 | 0.0131 |
| eGFR(mL/min) | 0.996 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.1546 |
| Proteinuria (g/24h) | 0.97 | 0.94–1.01 | 0.1004 |
| Time of evolution of DM (years) | 0.997 | 0.996–0.999 | 0.0011 |
Univariate analysis biopsy. Dependent variable: non-diabetic nephropathy in renal biopsy.
OR: odds ratio; 95% CI: confidence interval of 95%; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Values in bold correspond to p<0.05.
Predictive factors for NDKD on kidney biopsy in patients with diabetes.
| Variables (n=614) | OR | CI (95%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absence of diabetic retinopathy | 3.97 | 2.7–5.82 | <0.0001 |
| Absence of microhematuria | 0.6 | 0.4–0.86 | 0.005 |
| Absence of peripheral vascular disease | 1.61 | 1.03–2.52 | 0.038 |
| Age (years) | 1.03 | 1.01–1.04 | 0.0002 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.07 | 0.98–1.16 | 0.1318 |
Multivariate analysis of binary logistic regression. Dependent variable: non-diabetic nephropathy in renal biopsy.
OR: odds ratio; 95% CI: confidence interval of 95%.
Values in bold correspond to p<0.05.
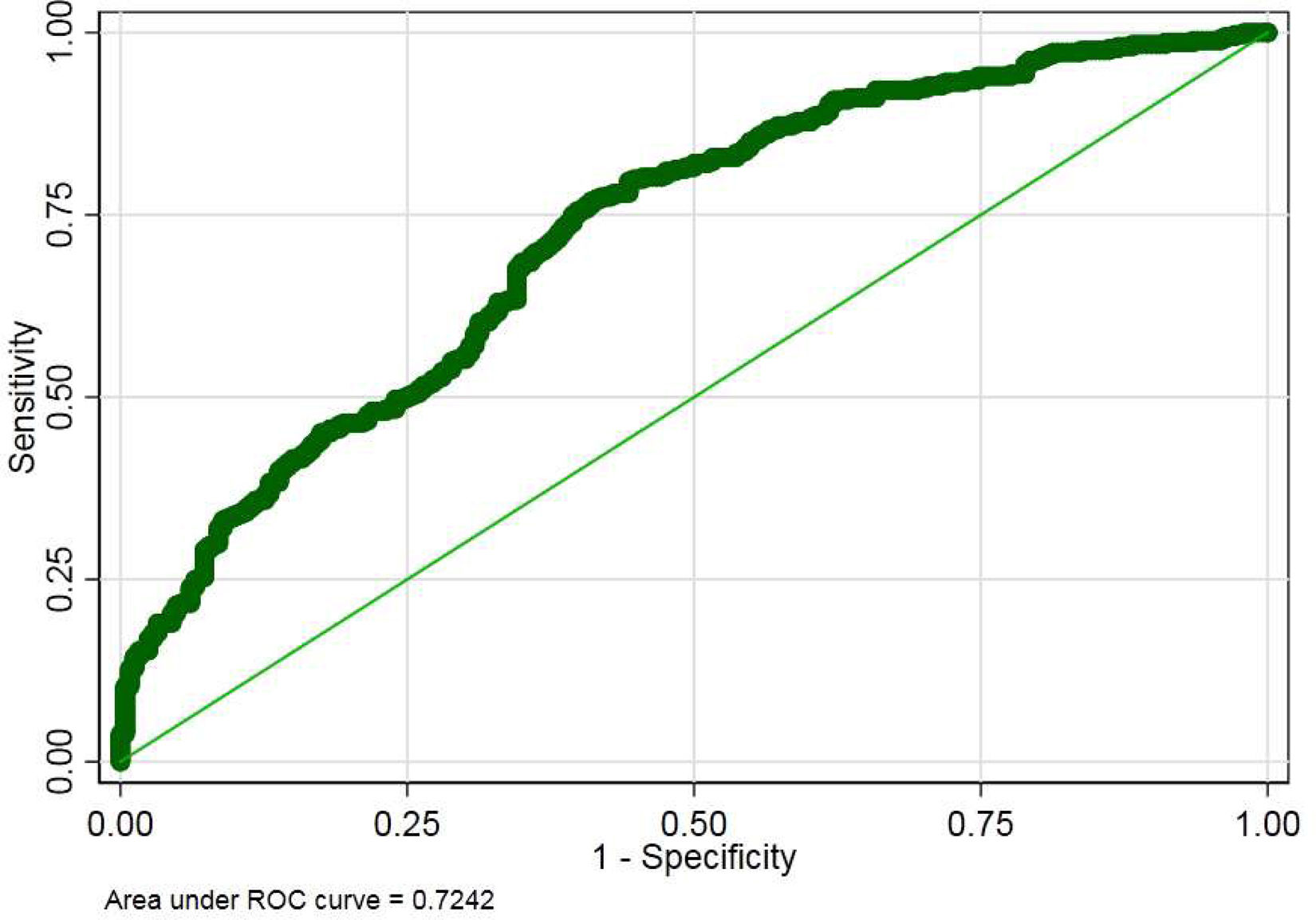
The independent risk factors for NDKD were the presence of microhaematuria, older age, the absence of DR and the absence of peripheral vascular disease. The model's discriminatory capacity obtained a ROC curve with an area under the curve of 0.7242 (Fig. 2) and the C-statistics is 0.742.
The best cut point based on Youden index (Sensitivity+Specificity−1) is 58%. The sensitivity of the model to detect non-diabetic nephropathy is 76.9 and the specificity 58.9 (supplementary Table 3).
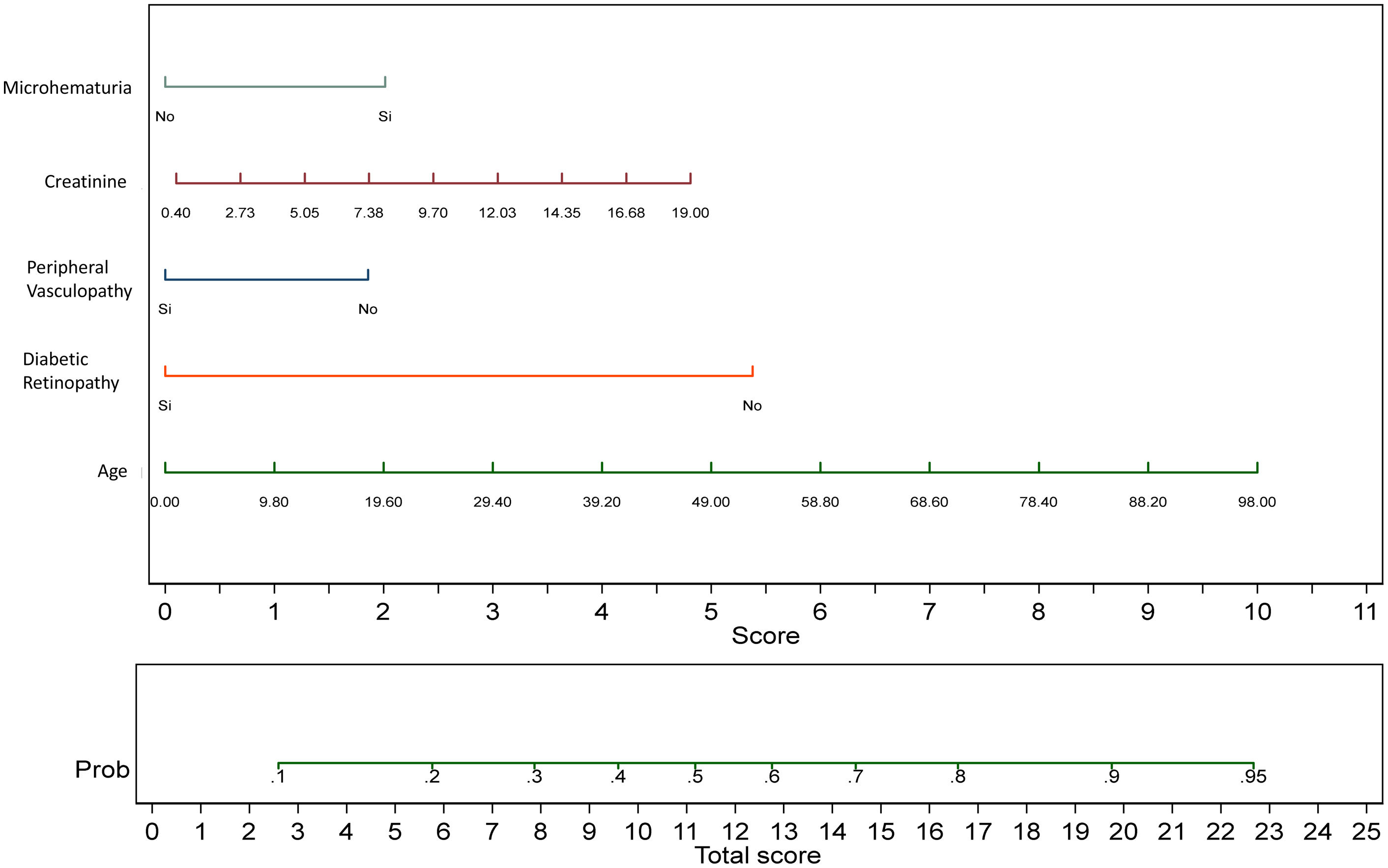
A nomogram was created that allows for calculating the probability of presenting NDKD with five variables (Fig. 3).
Depending on the value of the variables used for the model, a score number was obtained, which corresponded to a percentage of probability that patients with diabetes present NDKD in the renal biopsy. In our new score, the number obtained increases as does the probability of NDKD. The observed results suggest that the hypothesis of good calibration of the model cannot be rejected as the p value of the test is over 5%. As a clinical example of the use of our nomogram in a daily practice: a 50-year-old patient (5 points), without DR (5.5 points) or microhematuria (0 point) or vasculopathy (2 points) and serum creatinine of 2.5mg/dl (1 point), the total SCORE is 13.5 (60–65% probability of NDKD).
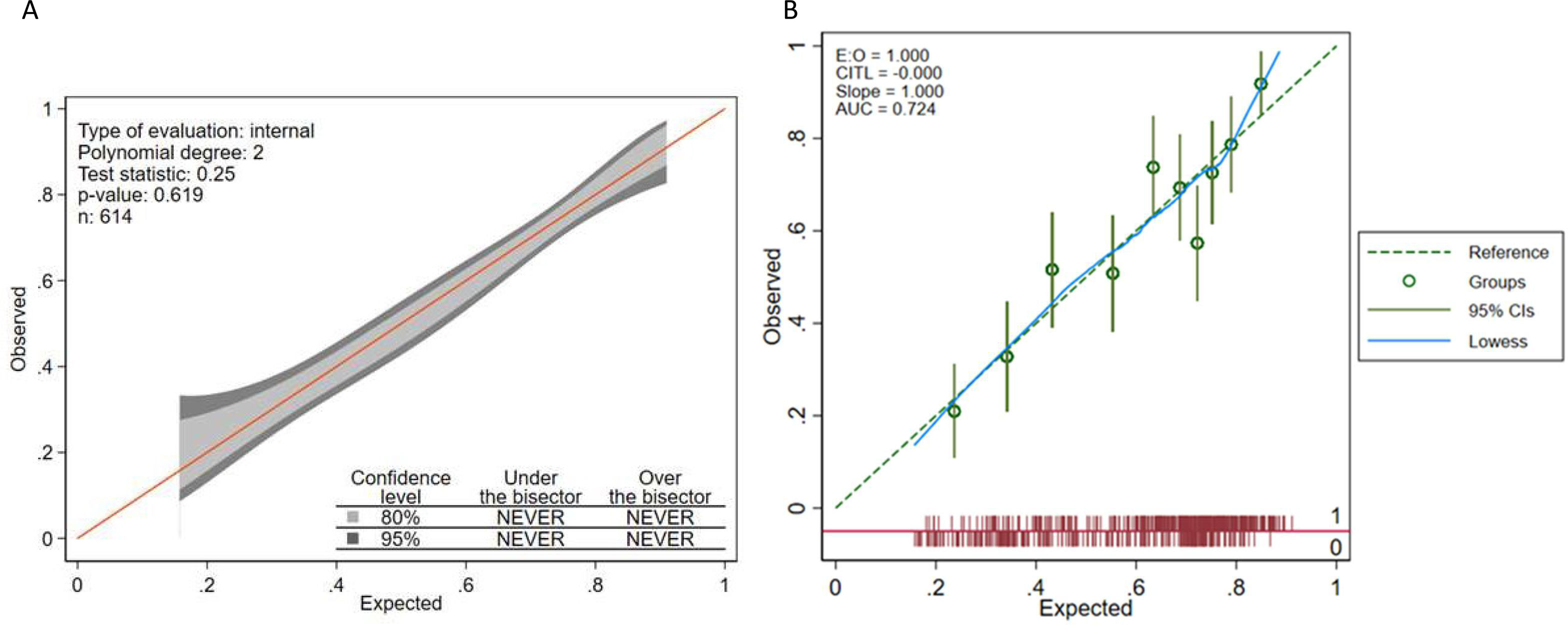
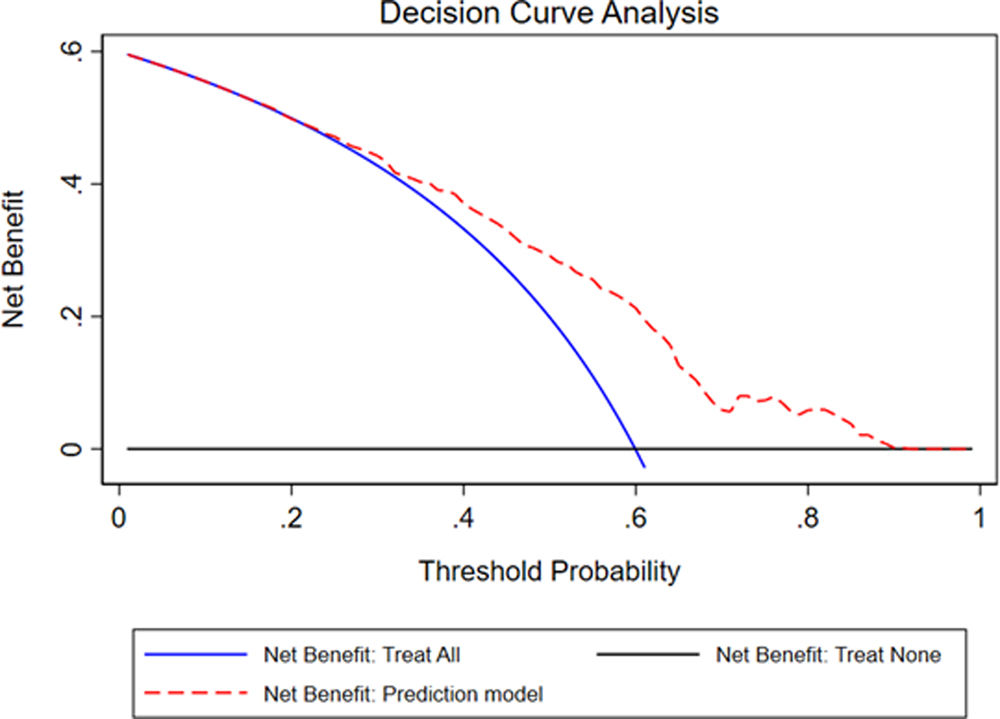
The internal calibration of nomogram is shown in Fig. 4A. Another graph for test calibration is plot the predicted probability vs. the observed frequency. Again, no deviations from the diagonal were observed (Fig. 4B). Finally, with the purpose to evaluate the clinical usefulness, the probability threshold vs. the net benefit (true positive) can be evaluated in the decision curve. NDKD means all positive, and DKD means all negative. The red line that separates from the NDKD and DKD all indicates the probability threshold on model has a net benefit (supplementary Fig. 1).
To obtain an internal validation of score, Bootstrap was used and calculated a shrinkage coefficient. If this coefficient is near 1 one can say that the internal validation is good. In our case, after 1000 bootstrap sample simulations, no differences have been evidenced between the model and bootstrap coefficients. The shrinkage coefficient is almost 1 (0.959), near 1 (supplementary Table 3).
DiscussionIn our Spanish multicenter cohort of 832 biopsied patients with diabetes, approximately two-thirds of the patients had NDKD as a unique or contributing cause of renal disease. Microhematuria, older age, absence of DR and absence of peripheral vasculopathy were identified as independent predictors of NDKD in renal biopsy in patients with diabetes. With five clinical variables a nomogram for calculating the probability of presenting NDKD was created.
Some previous studies published were focused on renal biopsies in patients with diabetes but our work has one of the biggest cohorts that have been published. Along with Sharma et al.6 and Liu et al.,7 which published with the population of the United States and China respectively, these are the studies with the largest population and are the most representative in the different world regions: Europe, Asia and United States. Regarding our cohort, we previously published the results focused in the prevalence of NDKD, indications of renal biopsy, predictors of NDKD and an analysis of renal survival and mortality depending on the histological diagnosis (DN vs. NDKD vs. mixed forms).8
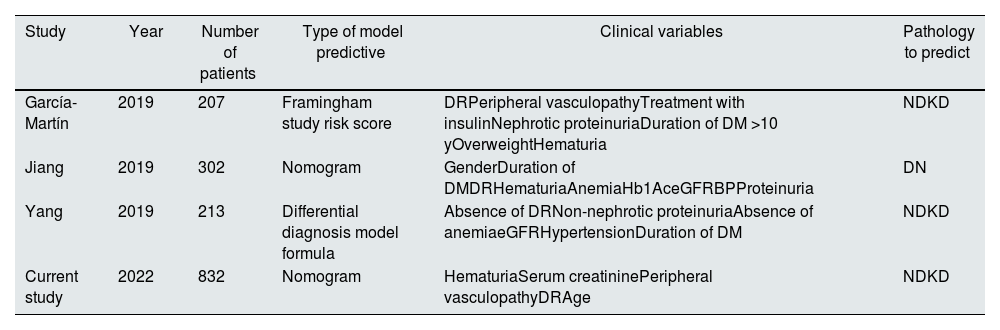
Few studies have been focused on finding a predictive model to determine whether patients with diabetes have NDKD in renal biopsy21–23 (Table 2). In our study, the differences from the previous published cohorts are the following ones: (a) multicenter study and/or (b) larger sample size and/or (c) Spanish population. Two of them are based on Asian population22,23 and one in a Spanish cohort.21 Of note that each of them uses a different statistical method to find the predictive model as illustrated in Table 3. Jiang et al.23 used a nomogram just like in our study, however, in our case the dependent variable was NDKD. Regarding the predictive clinical variables of the model, the presence or absence of DR is a common clinical factor in the three studies, in concordance with our results. Interestingly, to our knowledge the present study is the only multicenter one with larger sample size performed in a European cohort. In agreement with our work, the presence of hematuria was evidenced in three of the other published models.21,23,25 The rest of the clinical variables presented more variability, however in three of them renal function22,23 and peripheral vascular disease21 were evaluated in concordance with the results of our study. Regarding the interpretation of the results of the predictive models, in the case of García-Martín et al.,21 obtaining a value less than 1 in score would indicate a high probability of NDKD and greater than 3 would indicate a lower probability of NDKD. However, there is a gray area between 1 and 3 that should be individualized in each case. Yang et al.,22 through the formula they provided, a score for NDKD was obtained, a value less than 0.5 indicates higher probability of DN and if the value was greater than 0.5 it indicates higher probability NDKD. These models can be useful, however, there is a lack of precision when defining if it is NDKD or not and to help in the final decision of indication for renal biopsy. In the case of Jiang et al.23 in which they used the nomogram as in our study, a more precise percentage was obtained through the clinical variables provided. Recently, Zhang et al.25 performed Random Forest machine, support vector machine algorithm and logistic regression with the purpose to find the most predictive clinical variables of NDKD in patients with diabetes mellitus in Asian population. They evidenced the following variables with higher specificity and sensitivity: DR, duration of DM, Hb levels, blood pressure and the presence of hematuria. Furthermore, the researchers performed an external validation in a population of 329 patients that confirms the prediction value of previous variables mentioned. However, in this study the variables were not integrated into a model to obtain a percentage probability of presenting NDKD.
Predictive models in type 2 diabetes mellitus: non-diabetic kidney disease vs. diabetic nephropathy.
| Study | Year | Number of patients | Type of model predictive | Clinical variables | Pathology to predict |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| García-Martín | 2019 | 207 | Framingham study risk score | DRPeripheral vasculopathyTreatment with insulinNephrotic proteinuriaDuration of DM >10 yOverweightHematuria | NDKD |
| Jiang | 2019 | 302 | Nomogram | GenderDuration of DMDRHematuriaAnemiaHb1AceGFRBPProteinuria | DN |
| Yang | 2019 | 213 | Differential diagnosis model formula | Absence of DRNon-nephrotic proteinuriaAbsence of anemiaeGFRHypertensionDuration of DM | NDKD |
| Current study | 2022 | 832 | Nomogram | HematuriaSerum creatininePeripheral vasculopathyDRAge | NDKD |
DR: diabetic retinopathy; NDKD: non-diabetic kidney disease; DN: diabetic nephropathy; DM: diabetes mellitus; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; BP: blood pressure.
Our study has certain limitations. The first one derives from the retrospective nature of the study. It should be noted that renal biopsies were interpreted by different pathologists from the different hospitals (including different sample processing methods). Furthermore, a sample selection bias exists since patients with diabetes that underwent kidney biopsy have an increased probability of presenting lesions not related to DM, due to the atypical presentation or progression of renal disease in relation to DM. It is important to take into account that the nomogram are extrapolated from a population with highly heterogenous indications for kidney biopsy. Another limitation is that the DNs was not classified according to Tervaert classification due to the lack of information. Glycosylated hemoglobin was excluded from the analysis due to missing data in many cases. Finally, an external validation is necessary in a near future to validate our score.
ConclusionsIn summary, our study provides a new predictive model with clinical utility for helping the clinician to decide when to perform renal biopsy in patients with diabetes. This nomogram is a useful tool since it helps to identify patients with diabetes at risk for NDKD. If NDKD is confirmed by kidney biopsy, as a consequence, may lead to a change on treatment, renal prognosis and patient survival. Future prospective studies are necessary to evaluate the clinical utility of NDKD predictive models in patients with diabetes.
FundingThis work was supported by grants from Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria-FEDER, ISCIII, PI17/00257, PI21/01292, PI20/00744, Marató TV3 2020421/C/2020, Marató TV3 2021215/C/2021, RD16/0009/0030 (REDINREN), EIN2020-1123381, BECA SENFRO 2021 and RD21/0005/0016 (RICORS 2040).
Conflict of interestS.B. reports honorarium for conferences, consulting fees and advisory boards from AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Bayer and Mundipharma. M.J.S. reports personal fees from Novo-Nordisk, Jansen, Mundipharma, AstraZeneca, Esteve, Fresenius, Ingelheim Lilly, Vifor, ICU, Pfizer, Bayer, Travere Therapeutics and GE Healthcare and grants and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, outside the current study. N.M. reports honoraria from Alexion and GSK. N.G.-F. participates on scientific advisory virtual of Mundipharma, honoraria for lectures of Astellas and medical Statistics Consulting and payment for expert testimony of Baxter, Viforpharma and Fresenius. B.F.-F. has received grants from Esteve and AstraZeneca and have worked for Cátedra UAM-mundipharma. B.F.-F. has received consultancy or speaker fees or travel support from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Menarini, Novo-Nordisk BoeringerInheilm and Mundipharma. B.F.-F is Editor for Nefroplus. B.F.-F. has received travel support from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Menarini, Novo-Nordisk BoeringerInheilm and Mundipharma. B.F.-F. has been advisor for AstraZeneca, Bayer, Menarini, Novo-Nordisk Boeringer Inheilm and Mundipharma. M.P. reports consulting fees and payment for honoraria from Alexion, Novartis, Otsuka, Vifor, GSK, Travere. The rest of authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
We are grateful to the members of GLOSEN, GEENDIAB and GLOMCAT for their participation with helping this study become a reality.